Motion in 1 and 2 D
advertisement

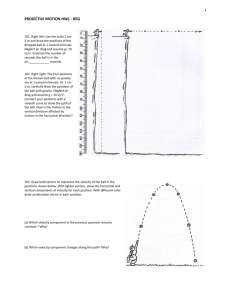
Page 1 of 2 MOTION UNDER GRAVITY (Near the surface of the Earth) Motion in I-D 1. A ball is released from rest and falls freely. It is found to fall through 44.1 m in the 5th second of its journey. Calculate the value of 'g'. 2. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 19.6 m/s. (a) How high does it rise? (b) How long does it take to reach the highest point? 3. A body falls freely from rest for 6 seconds. Find the distance travelled in the last 2 seconds (g = 9.8 m/s2). 4. A ball thrown vertically upwards returns to the thrower in 4 s. Find: (a) The initial velocity, (b) The maximum height attained. 5. A ball is projected vertically upwards with a velocity of 100 m/s from a platform (a) Which is at rest, (b) Which is moving vertically upwards with a constant velocity of 10 m/s. When and with what velocity will the ball return in each case? Why are the results in the two cases identical? 6. When a body is projected vertically upward from the top of a tower it reaches the ground in tl seconds. However, when it is projected straight downward with the same speed it reaches the ground in t2 seconds. How much time would the body take if it were simply dropped from the top of the same tower? 7. A stone is dropped from a rising balloon at a height of 91.8 m above the ground and it reaches the ground in 6 s. What was the velocity of the balloon just at the moment when the stone was dropped? 8. A boy stands on a bridge, which is 5 m above the water surface. He throws a stone vertically upward with a velocity of 20 m/s. (a) How high above the bridge will the stone rise? (b) After how many seconds from the start will the stone hit the water? (Take g=10 m/s) 9. From the top of a tower a body ‘A’ is dropped. One second later another body ‘B’ is dropped from the same tower. How long after the body ‘A’ begins to fall will the two bodies be 10 m apart? (g=10 m/s2) 10. One body is dropped while a second body, at the same instant, is thrown downward with an initial velocity of 1 m/s. When will the distance between them be 18 m? (g=10 m/s2). 11. Two bodies are thrown vertically upward with the same initial velocity of 98 m/s. The second body is thrown 4 s later. How long after the first one is thrown will they meet? 12. A stone is dropped from a high altitude and 3 s later another is projected vertically downward with a speed of 50 m/s. When and where will the second overtake the first? (g=10 m/s2). Motion in 2-D (Projectile Motion) 1. A rifle is aimed at an angle of 53° above the horizontal and a bullet is fired from it with a speed of 100 m/s. Just as the bullet leaves the barrel of the rifle, (a) How fast is it rising? (b) How fast is it moving parallel to the ground? 2. A stone is thrown at 45° to the horizontal. It attains a maximum height of 10 m. Find its range on the horizontal surface. 3. Calculate the angle of projection, with the horizontal, for a projectile for which the maximum height is equal to the horizontal range. Page 2 of 2 4. With what minimum velocity and in which direction should a projectile be thrown so as to hit a target 200 km away on a plane ground? (g=10 m/s2 ). 5. A shell is fired horizontally from a gun situated at a height of 44.1 m above a horizontal plane with a muzzle velocity of 300 m/s to hit a target on the same horizontal plane. Find: (a) The time taken to hit the target. (b) The horizontal distance of the target. (c) The horizontal and vertical components of the velocity with which the shell will strike the target. (g =10 m/s ) 6. A body is thrown horizontally with a velocity of 8 m/s from a high building. Find the magnitude and direction of its velocity after 0.6 s. (g=10 m/s2) 7. A ball rolls off the edge of a horizontal tabletop 0.8 m high and strikes the floor at a distance of 1.6 m from the foot of the table. What was the velocity of the ball just at the instant of leaving the table? (g=10 m/s2) 8. The range of a projectile, which is launched at an angle of 15o with the vertical, is 1.5 km. What is the range of the projectile if it is projected at an angle of 45o to the horizontal? 9. A particle is projected at a speed of 10 5 m/s at an angle of 60o to the horizontal. What is the velocity of the projectile when it reaches a height of 10 m? (g =10 m/s2) 10. A ball is pushed from the top of a flight of stairs with a horizontal velocity of 2 m/s. If each step has a depth 0.25 m and a height of 0.25 m, on which step will the ball hit? (g=10 m/s2 ) 11. A distance of 100 m separates two paper screens ‘A’ and ‘B’. A bullet pierces ‘A’ and then ‘B’. The hole in ‘B’ is 10 cm below the hole in ‘A’. If the bullet is travelling horizontally at the time of hitting the screen ‘A’, calculate the velocity of the bullet when it hits the screen ‘B’. Neglect the resistance of paper and air. 12. A pilot flying horizontally 300 m above the ground at 300 km/h wishes to drop a package on a platform moving at 30 km/h in the same direction. How many seconds before he is directly above the platform must he release the package and what must be the distance measured in the horizontal direction separating the plane and the platform? 13. Two seconds after projection, a projectile is travelling in a direction inclined at an angle 30o to the horizontal. After one more second it is travelling horizontally. Determine the magnitude and direction of its velocity. 14. A particle is projected with a velocity of 19.6 m/s at an angle of 30o with the horizontal. After how long will it move at 90o to its initial direction of motion? Answers Motion in 1-D 1. 9.8 m/s2 2. 19.6 m; 2 s 3. 98 m 4. 19.6 m/s; 19.6 m 5. 20 s; 100 m/s 6. t1 t 2 s 7. 14.1 m 8. 20 m; 4.23 s 9. 1.5 s 10. 18 s 11. 12 s 12. 5.25 s; 137.8 m Motion in 2-D 1. 80 m/s; 60 m/s 2. 40 m 3. tan 1 (4) 4. 1414 m/s 5. 3 s; 900 m; 300 m/s & 29.4 m/s 3 6. 10 m/s; tan 1 4 7. 4 m/s 8. 3.0 km 9. 10 3 m/s 10. 4th step 11. 707 m/s 12. 7.82 s; 586.8 m 13. 20 3 m/s; 60o 14. 4 s