Life Science CRCT Study Guide 1
advertisement

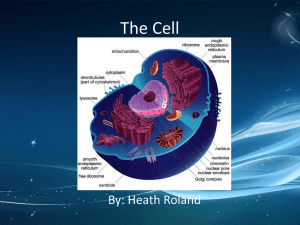
Life Science CRCT Study Guide S7L2. Cells - Cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials for repair and reproduction - Cells are organized into tissues→ tissues are organized into organs→ organs are organized into organ systems→ organ systems make organisms - Four types of tissue: 1- muscle tissue: contracts for movement and support, 2- Nerve tissue: signals to muscles, informs us of environmental conditions (hot, cold, humid, 3Epithelial Tissue: Lines our organs, 4- Connective Tissue: Connects, supports, and protects other tissues 1. Chloroplast - (solar panel) allows plants to produce food from sunlight, gives green color /only in plants 2. Large Vacuole- (warehouse) storage center of cell, provides stability and support when filled with liquid (on plant cell) 3. Cell Wall- (wall) gives the cell shape, strength, and support / only in plants 4. Mitochondria- (power plant) produces 90% of cell’s energy / both 5. Lysosome- (city dump) breaks down old parts and large molecules /only in animals 6. Nucleus- (city hall) control center of cell / both 7. Cell Membrane- (border) outer coverage of cell for exiting and entering the cell / both 8. Cytoplasm- (air) jelly-like substance found inside cell in which organelles are found / both 9. ER- (highway) transports materials around cell / both 10. Ribosome- (factory) manufactures protein / both 11. Golgi body- (post office) packages materials for export from cell / both 12. Vacuole- (warehouse) cell’s storage centers (on animal cell) Major Human Body Organ Systems Body Organization and Structure Integumentary System: your skin, hair and nails protect your inside from your outside and prevent infection while maintaining homeostasis ( stable internal temperature). Muscular System: your muscular system works with the skeletal to help you move by contracting your muscles. Skeletal System: your bones provide a frame to support and protect your body parts. Circulation and Respiration Cardiovascular System: your heart pumps blood through all your blood vessels passing nutrients and oxygen to your cells; pumps blood Circulatory System: carries blood throughout the body Lymphatic System: returns leaked fluids to blood vessels and helps get rid of bacteria and viruses; cleans you blood. Respiratory System: your lungs absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide; breathing The Digestive and Urinary System Digestive System: breaks down the food you eat into nutrients that your body can absorb. Urinary System: removes wastes from the blood and regulates your body’s fluids. Reproduction and Development Male Reproductive System: produces and delivers sperm Female Reproductive System: produces eggs and nourishes and protects the fetus. Communication and Control Nervous System: receives and sends electrical messages throughout your body Endocrine System: your glands send out chemical messages called hormones. Ovaries and testes are part of this system. Heredity and genetics S7L3. Biological traits are passed on to successive generations (offspring of first generation) -Selective Breeding: producing or breeding plants and animals with the most desired traits or features. Heredity- is the passing of traits from parents to their offspring Characteristics –is a feature that has different forms Incomplete dominance– both parents influence the offspring/one white and one red and the offspring is pink Alleles –different versions of a gene Punnett Square- a tool used to determine the probability or chance of an offspring getting a trait • Homozygous – possessing 2 of the same alleles for a particular trait (SS or ss or TT or tt) • Homozygous dominant = SS or TT • Homozygous recessive = ss or tt • Heterozygous – possessing different alleles for a particular trait (Ss or Tt) • Genotype - the genetic make-up of an organism HH: homozygous dominant Hh: heterozygous dominant hh: homozygous recessive • Phenotype: the way an organism looks or behaves based on the genotype (trait) Examples: blond hair, brown eyes, long nose Asexual and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction: only one parent is needed to produce offspring and the offspring has exact copies of the parent’s genotype. (Budding, regeneration, fragmentation, mitosis) Sexual Reproduction: cells from two parents join to form offspring. The offspring shares traits from both parents but the offspring are not exactly alike each other. (Meiosis: Every adult has 46 chromosomes and in sexual reproduction the mother gives 23 chromosomes and the father gives 23 chromosomes. In those chromosomes are genes which are instructions for an inherited trait from your parents.) Interdependence of Life S7L4.Matter and energy is transferred or passed in a food web or food chain from one organism to another, such as: -from the sun to producer -from producer to primary consumer -from primary consumer to secondary consumer -from secondary consumer to tertiary consumer -from tertiary consumer to decomposer -from decomposer back to the producer * All matter, nutrients, energy, water, nitrogen and carbon is recycled between organisms and their environments. * All energy originated from the sun and moves from organism to organism in a food web, food chain, or energy pyramid * In an energy pyramid the # of organisms decrease and the amount of energy decreases as you go up the energy pyramid * Only 10% of the energy in an organism is passed on when it is eaten because it has used the other 90% on life processes *Food webs are made up of multiple food chains Changes in environmental conditions can affect the survival of both individuals and entire species (floods, oil spills, droughts, hurricanes, etc…) Relationships between Organisms -predator (eat other organisms)/ Prey (eaten by predator) -competition: when two organisms fight for the same resources (water, food, sunlight, or space). -mutualism: relationship when both organisms benefit from each other (win/ win) -parasitism: relationship when one organism (parasite) benefits from another organism (host) while the host is harmed (win/ lose) -commensalism: relationships when one organism benefits and the other organisms are unharmed or unaffected (win/ unharmed) Levels of Environmental Organization Smallest-organism (one individual) → population (more than one organism of the same specie) → community (more than one population in the same area) →ecosystem (more than one community in the same area) →biosphere ( Area where all living things exist) Largest Biomes Biomes: a large are of land with similar biotic and abiotic factors Abiotic: nonliving part of the environment (ex. air, weather, rocks, water, soil, sun) Biotic: living or once living part of the environment (ex. plants and animals) Land or Terrestrial Biomes Forest: 1- Tropical rainforest: greatest variety of plants and animals that live the canopy (tree tops) of the trees. Subtropical or tropical weather and found near the equator. 2-Coniferous (Taiga): conifer trees which have needle-shaped leaves covered in a thick, waxy coating that help them to conserve water and stay green year round (evergreen);Cold weather. 3-Temperate Deciduous: Shed their leaves to save water during the winter; Found in Savannah, Ga. Grassland: 1- Temperate (praire): Fires and droughts prevent trees and shrubs from growing. It has seed eating animals, many kinds of tall grass with no trees, and warm summers and cold winters. 2- Savannas: It has lots of rainfall during some seasons and very little rain during dry season. It also has lions, zebra, and wildebeests. Desert: Very dry biome and most are very hot. Tundra: Very cold biome with little rainfall and it also has permafrost all year long which is a frozen layer of soil; 1-Polar: North and South poles 2-Alpine: Similar to polar but are found at the top of tall mountains Marine Ecosystems *Marine ecosystems are saltwater. They are warm near the surface and colder as you go to deeper depth. (Sea, Ocean, Coral reef, Estuary) Plankton: are tiny organisms that float near the surface of the ocean. Major Zones: Intertidal: where the ocean meets the shore, neritic: further from the shore where the ocean floor begins to slope downward, oceanic: the surface of the open ocean where the phytoplankton and many of the consumers live, benthic: ocean floor and the zone that is the coldest and receives no sunlight Freshwater *Water with no salt. *Rivers are larger than streams (Moving water)/ Lakes are larger ponds. (Stored water) *Wetland: an area of land that is sometimes under water or whose soil contains a lot of water; marsh: treeless wetland, swamp: wetland in which trees and vines grow S7L5. Evolution *Organisms adapt (gradually change to fit) to their environment over time and generations through natural selection (the stronger or better adapted traits survive while the weaker traits are not passed on) vestigial adaptation: A change in the features of an organism that has no purpose Evolution: the process in which populations change over time Sedimentary rocks forms when pieces of sand, dust, or soil are laid down in flat layers; they may contain fossils. Fossils are remains or imprints of once living organisms. Charles Darwin developed the theory that humans may have evolved from a common ancestor with monkeys. *Some animals survive nature by developing defense mechanisms like: camouflage, mimicry, venom, bright colors, running, herding, etc…… THE CELL 1. What part of the cell is responsible for breaking down and digesting things? ribosomes lysosomes endoplasmic reticulum vacuole 2. Identify the organelle pictured. chloroplast endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus mitochondria 3. What part of the cell serves as the intracellular highway? endoplasmic reticulum golgi apparatus cell membrane mitochondria 4. Which of the following would you NOT find in a bacterial cell? DNA cell membrane golgi apparatus ribosomes 5. Which of the following is found in plant cells, but not animal cells? cell wall vacuole mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum 6. The jellylike interior of the cell is called the: vacuole cytoplasm cytoskeleton nucleus 7. Identify the organelle. golgi apparatus endoplasmic reticulum mitochondria lysosome 8. What part of the cell makes proteins? ribosomes mitochondria lysosomes vacuole 9. Where are ribosomes usually located in animal and plant cells? inside the nucleus near the cell membrane on the endoplasmic reticulum inside the vacuole 10. What part of the cell serves to process, package and export proteins? mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum nucleolus golgi apparatus