Ocean Habitats

Ocean Habitats
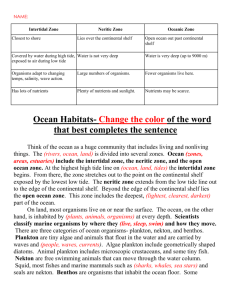
Think of the ocean as a huge community that includes living and nonliving things. The ocean is divided into several zones. Ocean zones include the intertidal zone, the neritic zone, and the open-ocean zone.
At the highest high tide line on land, the intertidal zone begins.
From there, the zone stretches out to the point on the continental shelf exposed by the lowest low tide. The neritic zone extends from the low-tide line out to the edge of the continental shelf.
Beyond the edge of the continental shelf lies the open ocean zone. This zone includes the surface zone, the transition zone or thermocline and the deep ocean zone which is the deepest, darkest part of the ocean. Here the temperature is very cold and the water pressure is very high.
On land, most organisms live on or near the surface. The ocean, on the other hand, is inhabited by organisms at every depth. Scientists classify marine organisms according to where they live and how they move. There are three categories of ocean organismsplankton, nekton, and benthos. Plankton are tiny algae and animals that float in the water and are carried by waves and currents. Plankton include geometrically shaped diatoms, krill, jellyfish, and fish eggs. . Nekton are free-swimming animals that can move throughout the water column. Squid, most fishes, and marine mammals, such as whales and seals, are nekton.
Benthos are organisms that inhabit the ocean floor . Some benthos, like crab, sea stars, octopus, and lobsters, move from place to place. Others, like sponges and sea anemones, stay in one location. Plankton, nekton, and benthos are all found in most marine habitats.
Photosynthetic plankton, called phytoplankton, are called producers. Other plankton and benthos, as well as all nekton, eat either algae or other organisms. They are called consumers.
Finally, some organisms, including many benthos, break down wastes and the remains of other organisms. They are called decomposers.
All of the feeding relationships that exist in a habitat make up a food web. In most marine food webs, each organism depends directly or indirectly on the algae plankton. Throughout the ocean, plankton are a source of food for other organisms of all sizes. Just think, Earth's largest animal,-the blue whale-feeds only on tiny plankton.
Name_________________________
Ocean Habitats
1. The part of the ocean that extends from the high-tide line to the low-tide line is called the __________________________.
2. The part of the ocean that extends from the low-tide line to the edge of the continental shelf is called
the ___________________________ .
3. The part of the ocean that extends beyond the edge of the continental shelf is called the _______________________.
4. The open-ocean zone is divided into the surface zone, the transition zone, and the _______________________zone.
5. True or False? Physical conditions are the same in each zone of the ocean.
6. Where do organisms that need light for photosynthesis live? ____________________________________________
7. What must organisms that live deep in the ocean withstand?
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
8. True or False? Organisms inhabit every depth of the ocean.
9. Scientists classify marine organisms according to a. where they live and how they move. c. where they live and how long they live. b. size and where they live. d. how they move and what they eat
10. Describe plankton. _________________________________________________________________________________
11. Name three examples of plankton. _____________________________________________________________________
12. Free-swimming animals that can move throughout the water column are called _______________________.
13. Name some examples of nekton._____________________________________________________________.
14. What are benthos? __________________________________________________________________________________
15. Give some examples of benthos. _________________________________________________________
16. Algae that use sunlight to produce their own food through photosynthesis are called __________________________________.
17. What are all nekton? a. producers b. consumers c. decomposers d. benthos
18. What do decomposers eat? __________________________________________________________________
19. Explain what a food web is. _________________________________________________________________________________________
20. Which of the following may eat plankton?
a. sea ducks b. blue whales c. other plankton d. all of the above
21.
Think about it. Name at least three ways in which the ocean's zones differ from one another?
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
22. Fill in the blanks in the diagram below.
Match each term with its correct definition. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line.
________ 23. plankton a.
organisms that inhabit the ocean floor
________ 24. nekton
________ 25. benthos b . tiny algae and animals that float in the water and are carried by waves and currents c. free-swimming animals that can move throughout the water column
Write the correct answer on the space provided.
26.
What is the combination of all of the feeding relationships in a habitat called?
______________________________________________________________________________
. a.
food from chemicals in the hot water. b.
Tubeworms get their food from the bacteria inside them. c.
The process of making food with heated water and chemicals is called photosynthesis. d.
Giant clams feed on the algae.
14. Bacteria are
____________________
_____, that is, they are the producers in the food web of the deep ocean.