MATH Unit 3 overview gr 5 - Geometry
advertisement

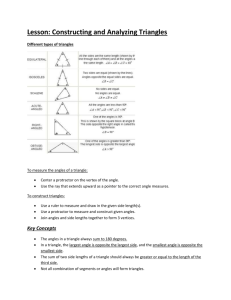
Unit 3 - Geometry – grade 5 (5TB78) Learning Goals 1. 2. 3. 4. Sort and name polygons by side and angles Measure, name, and construct angles Construct triangles, given side and angle measures Identify and construct nets of solids Geometry Key Words (5TB79) Polygon = a closed figure with three or more straight sides. We name a polygon by the number of its sides. For example, a five-sided polygon is a pentagon. (penta=five). Check p. 413 a picture. Equilateral Triangle = a triangle with all sides equal. Isosceles triangle = a triangle with two sides equal. Scalene triangle = a triangle with no sides equal. Acute angle = an angle that measures less than 90°. Right angle = two lines that meet in a square corner make a right angle. A right angle measures 90°. See p. 415 for a drawing of a right angle. Obtuse angle = an angle measuring between 90° and 180°. perpendicular = two lines that intersect at a right angle are perpendicular. Remember that a Right angle is when two lines meet in a square corner and make an angle that measures 90°. (drawing on p. 413) Acute triangle = a triangle that measures less than 90°. Right triangle = a triangle with one 90° angle. Obtuse triangle = a triangle with one angle greater than 90° and less than 180°. Regular polygon = a regular polygon has all sides equal and all angles equal. Check your text book on page 414 for a picture of this! Irregular polygon = a polygon that does not have all sides equal or all angles equal. Check your text book on page 411 for two examples! Net = An arrangement that shows all the faces of a solid, joined in one piece. It can be folded to form the solid. Check p. 412 for a visual representation of a net. Lesson 1 – Naming and Sorting Polygons by side 5TB80 A polygon is a closed figure with 3 or more sides. (poly means more!!) A quadrilateral is a polygon with 4 sides. (quadri = quatre = four!!!!) Some examples of quadrilaterals: a rectangle, a parallelogram, a trapezoid, a kite. A triangle has 3 sides (tri=trois=three). A pentagon has 5 sides (penta=5). A hexagon has 6 sides (hexa= six = 6). An octagon has 8 sides (octa/octo = 8). A vertex (plural – vertices) = 1. A point where two sides of a figure meet. 2. A point where two or more edges of a solid meet. An edge= two faces of a solid meet at an edge. A face= one side of a solid. A solid has length, width, and height. Solids have faces, edges, vertices, and bases. We name solids by the number and shape of their bases. The base is the face that names a solid. There is an example of a base on p. 408. An equilateral triangle has all sides equal (p. 81) An isosceles triangle has 2 sides equal (p. 81) A scalene triangle has no sides equal (p. 81) Lesson 2 – Measuring and Constructing Angles (5TB84) The measure of an acute angle is less than 90°. The measure of a right angle is 90°. The measure of an obtuse angle is between 90° and 180°. 3 steps to draw an angle 1. Use a ruler. Draw one arm of the angle. 2. Place the protractor on the arm. One end of the arm is at the centre of the protractor. The arm lines up with the base line of the protractor. Start at 0°on the arm along the base line. Count around the protractor until you reach the number you need. Make a mark at that number. 3. Remove the protractor. Draw a line to join the end of the arm at the centre of the protractor with the mark at your number. Label the angle with its measure. Lesson 3 - Strategies Toolkit Strategies Make a table Use a model Draw a diagram Solve a simpler problem Work backward Guess and check Make an organized list Use a pattern Draw a graph Use logical reasoning (5TB88) Lesson 4 – Naming and Sorting Polygons by Angles We can sort and name triangles by angle measure. - An acute triangle has all angles less than 90° - A right triangle has one 90° angle - An obtuse triangle has one angle greater than 90° We can sort and name quadrilaterals by angles. - A rectangle has 4 right angles - A parallelogram has 2 pairs of equal angles - A kite has 1 pair of equal angles. We can sort polygons by the numbers of equal sides and equal angles. - A regular polygon has all sides equal and all angles equal. (e.g. an equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides, each angle measures 90°. – A square is a regular rectangle. It has 4 equal sides. Each angle measures 90°. - An irregular polygon does not have all sides equal and all angles equal. Lesson 5 – Constructing Triangles (5TB94) How do you construct a triangle? (example on p. 95) Step 1: Sketch the triangle first. Label each side and angle. This sketch is not accurate! It shows each given measure. Step 2: Use a ruler to draw the given side. Step 3: Use a protractor to draw an angle. Make sure you line up your protractor at the correct space and on the correct point of your angle. Measure the given angle. Step 4: Remove the protractor. Join your first point of your side with the angle drawn, according to the length given. Mark that point. Step 5. Use a ruler to join the two points and form the other side. Label the triangle with its measures. Lesson 6 – (5TB98) Making Nets A net shows all the faces of a solid, joined in one piece. It can be folded to form the solid. 2 ways to construct a net for a solid are: 1. Cut the solid apart along the edges so it is in one flat piece. 2. If your solid is a difficult solid, label the faces first so you can put it back easily. Draw face A and B so they share one side. Unit 3 – Show what you know! 5TB106 Unit Problem – Bridges (5TB109) Check List: Your work should show: A clear explanation of what you did and why As many attributes as possible How you used what you know about geometry How you found the greatest mass your bridge could support