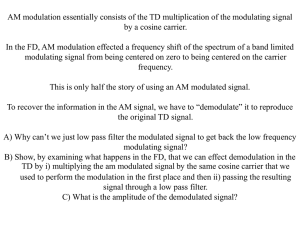
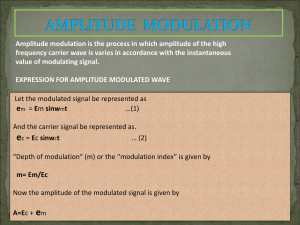
Limiters and Effect of Noise on FM Demodulation
advertisement

EXPERIMENT NO.8 FREQUENCY MODULATION COMPUTER SIMULATIONS Objective A Concepts of Frequency Modulation Practical to be used: Concept of Frequency Modulation and Frequency Modulator 1. Choose two voltages levels at the control input to the oscillator and measure the corresponding output frequencies. Then calculate the 'frequency slope' of the oscillator in kilohertz per volt. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. Can you see any amplitude variation over the frequency range? Should there be any? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 3. Is it easier to measure the frequency range on the oscilloscope or on the spectrum analyser? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 4. What relationship can you derived between voltage and frequency? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ In this practical the variable voltage used to control the VCO frequency has been replaced by a sine wave oscillator. This sine wave now frequency-modulates the carrier. Set Carrier level to about half scale. Look at the signal at 4 with the oscilloscope. Turn the modulation level up and down and observe the effect. Notice that the frequency is changing. Use the spectrum analyzer to examine the sidebands of the signal. 5. By looking at the spectrum of the modulated signal, can you estimate the frequency of the modulating signal? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 6. Would it be equally easy to estimate the bandwidth of the modulating signal from the spectrum if the modulating signal were complex, having many frequencies? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 7. As the modulation level varies, how constant is the carrier-frequency component of the modulated signal? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 8. As the modulation level varies, how constant is the amplitude of the modulated signal? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Objective B FM Spectrum Practical to be used: FM Spectrum with 5 kHz Source 1. If the modulating frequency is 5 kHz and the deviation is 50 kHz, calculate the modulation index. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. Calculate the signal bandwidth using Carson's rule. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Note: BW (Carson’s Rule) = 2 (fm + ) Where fm = modulating frequency = frequency deviation 3. What relationship can you get between bandwidth and the modulation level? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 4. If a bandpass filter were to be added at the input of an FM detector what factors determine the bandwidth required? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 5. If you would increase the frequency of the modulating signal, what would happen to the deviation? to the bandwidth? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Objective C Demodulation of Frequency Modulated Signals Practical to be used: Quadrature Detector, Phase Locked Loop Detector 1. What can you say about the output (amplitude) of the phase comparator relative to the phase difference? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. What should be the passband of the output filter? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 1. What is the output of the phase detector when there is no modulation? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. Compare the output of the filter to the output sent back by the VCO? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ Objective D Limiters and Effect of Noise on FM Demodulation Practical to be used: Quadrature Detector with Limiter, PLL with Limiter 1. In the absence of a limiter, does the demodulated output depend on the carrier amplitude? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. With the limiter in use, how does the demodulated output vary with carrier amplitude? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 3. How does the waveform of the input to the phase comparator (point 9) differ with and without the limiter? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 4. Above what amplitude is the limiter designed to clip off? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 1. In the absence of a limiter, with maximum noise, describe the demodulated output. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. With the limiter in the circuit, describe the effect of adjusting the noise level, minimum to maximum, on the demodulated output. ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 3. Tapping at monitor point 4, in the spectrum of the frequency modulated signal, describe the effect of adjusting the noise level. What signal frequencies are affected by noise? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 4. What does the term SNR stand for and what does it mean? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 5. Why do you think it is more convenient to express it in decibels? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 6. Why is it that the use of the limiter reduces the noise on the output? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 7. With the limiter in circuit, observe that reducing the carrier level causes an increase in the noise on the output. Why is this? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 1. Compare the effect of limiter in this practical and in the previous? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 1. How does limiting the signal improve the signal to noise ratio? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. How does the performance of the PLL demodulator compare with the phase comparator demodulator? ____________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________