Science
advertisement

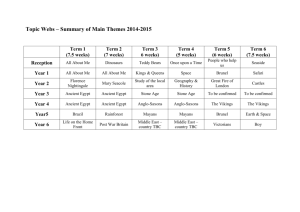
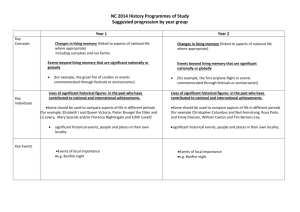
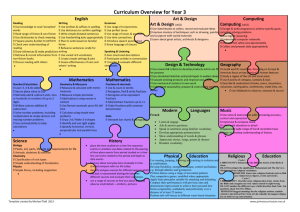
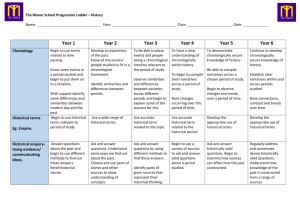
Thomas Bullock Church of England Primary Academy History Curriculum 2015/16 History Areas of Study by Key Stage and Year Group Key Stage One Year 1 Changes in living memory Year 2 Events beyond living memory Significant individuals Significant local events Lower Key Stage Two Year 3 Stone Age to Iron Age Ancient Egypt Year 4 The Tudors Roman Empire The Greeks Ancient Greeks Upper Key Stage Two Year 5 Anglo Saxons History of Food Year 6 Benin Vikings World War II Evolution of the media History Key Stage One Key Stage One Progression of skills During years 1 and 2, pupils should be taught to use the following skills: sequence events, artefacts and photographs from different periods. (These should be mainly from their own lives.) use a range of sources to find out about people and places in other times. investigate why people did certain things and develop empathy and understanding through drama. compare different versions of the same event and consider how reliable they are. recognise similarities and differences between artefacts, sources and accounts. investigate a wide range of sources considering why, what, who, how and where. Year One Program of Study Changes in living memory Events beyond living memory Significant individuals Significant local events History Key Stage One Key Stage One Progression of skills During years 1 and 2, pupils should be taught to use the following skills: sequence events, artefacts and photographs from different periods. (These should be mainly from their own lives.) use a range of sources to find out about people and places in other times. investigate why people did certain things and develop empathy and understanding through drama. compare different versions of the same event and consider how reliable they are. recognise similarities and differences between artefacts, sources and accounts. investigate a wide range of sources considering why, what, who, how and where Year Two Program of Study Changes in living memory Events beyond living memory Significant individuals Significant local events History Lower Key Stage Two History skills progression: begin to date events from the period studied and place them on a timeline. sequence several events or artefacts. find out about everyday lives of people in times studied and compare with our life today. identify reasons for and results of people’s actions and understand why someone may have wanted to do something. look at the evidence available and use it to reconstruct life in times studied. identify and give reasons for different ways in which the past is represented and compare different versions use a range of sources and consider their usefulness ask a variety of questions and use a range of resources to research the answers communicate knowledge and understanding in a variety of ways and display findings in a variety of ways Year Three Program of Study Stone Age to Iron Age Ancient Egypt The Tudors Changes in Britain from the Stone Age to the Iron Age. The achievements of the earliest civilisations – an overview of where and when the first civilisations appeared and a depth study – Ancient Egypt. A study of an aspect or theme in British history that extends pupils’ chronological knowledge beyond 1066 – The Tudors. History Lower Key Stage Two History skills progression: begin to date events from the period studied and place them on a timeline. sequence several events or artefacts. find out about everyday lives of people in times studied and compare with our life today. identify reasons for and results of people’s actions and understand why someone may have wanted to do something. look at the evidence available and use it to reconstruct life in times studied. identify and give reasons for different ways in which the past is represented and compare different versions use a range of sources and consider their usefulness ask a variety of questions and use a range of resources to research the answers communicate knowledge and understanding in a variety of ways and display findings in a variety of ways Year Four Program of Study The Romans Greeks Ancient Greeks The Roman Empire and its impact on Britain. The legacy of Greek culture (art, architecture or literature) on later periods in British History, including the present day. Ancient Greece – a study of Greek life and achievements and their influence on the western world History Lower Key Stage Two History skills progression: recall and sequence key events of time studied and use relevant dates and terms make comparisons between different times in the past sequence up to 10 events on a timeline examine causes of events and the impact on people find out about beliefs, behaviour and characteristics of people, recognising that not everyone shared the same views and feelings compare accounts of events from different sources and offer some reasons for different versions of events consider ways of checking the accuracy of interpretations and be aware that different evidence will lead to different interpretations use a range of sources and begin to recognise primary and secondary sources bring knowledge gathered from several sources together in a fluent account plan and carry out individual and group investigations and then record and communicate knowledge and understanding in a variety of ways Year Five Program of Study Anglo Saxons History of Food Benin Britain’s settlement by Anglo-Saxons and Scots. Changes in an aspect of social history, such as crime and punishment from the Anglo-Saxons to the present or leisure and entertainment in the 20th Century. A non-European society that provides contrasts with British history – one study chosen from: early Islamic civilisation, including a study of Baghdad c. AD 900; Mayan civilisation c. AD 900; Benin (West Africa) c. AD 900 – 1300. Understand the impact of the Roman withdrawal Understand why the Anglo-Saxons settled in Britain Investigate daily life for the Anglo-Saxons: o Settlements o Religion o Laws o Society Availability of food The change of diets Preservation of food Significant new foods Production of food and fair trade Compare the two version of the Benin story Understand their beliefs Investigate daily life for the Benin o Settlements o Religions o Laws o Society History Lower Key Stage Two History skills progression: recall and sequence key events of time studied and use relevant dates and terms make comparisons between different times in the past sequence up to 10 events on a timeline examine causes of events and the impact on people find out about beliefs, behaviour and characteristics of people, recognising that not everyone shared the same views and feelings compare accounts of events from different sources and offer some reasons for different versions of events consider ways of checking the accuracy of interpretations and be aware that different evidence will lead to different interpretations use a range of sources and begin to recognise primary and secondary sources bring knowledge gathered from several sources together in a fluent account plan and carry out individual and group investigations and then record and communicate knowledge and understanding in a variety of ways Year Six Program of Study Vikings World War II Evolution of the media The Viking and Anglo-Saxon struggle for the Kingdom of England to the time of Edward the Confessor. A local history study – World War 2, Shipdham Airfield. A significant turning point in British history, e.g. the first railways or the Battle of Britain. Understand the Key events and leaders of World War 2 Understand who the Vikings were and where they were from Understand the impact that World War 2 had on Shipdham Understand the values and belief of the Vikings Understand what life on the Home Front was like including: Understand the time line of evolution of the media o Early writing, the printing press, radios, television, the internet, the future Understand their early visits to Britain and the purpose of these o The impact of rationing Understand the key milestones in the evolution of the media Understand how the Vikings conquered the Anglo-Saxons o The Blitz and the consequences that this had upon this had on the United Kingdom Explore the role of public service broadcasters o Why the Home Guard was formed and their role in protecting the Home Front. Viking life in the 10th century Understand the events at the end of the War. Understand how news is produced The use of advertisement and the media