Reading Vocabulary: OAA Terms & Definitions
advertisement

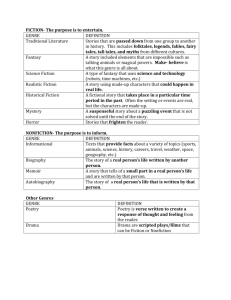
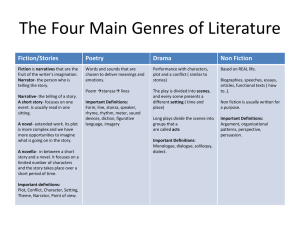
Reading OAA Vocabulary Words Abbreviation: commonly known, shortened words Analyze: to separate into parts, to identify it or study its structure Antonym: a word that has an opposite meaning to another word Atlas: a book of maps Almanac: a book of facts that is published every year Author's purpose: the reason the author wrote a selection (to explain, to inform, to entertain, to persuade) Beginning, middle, end: a sequence of how a story happened Benefit: an advantage or good thing Cause: Is something that makes something else happen Central Idea: same as the main idea; it is sometimes stated this way Character Trait: word or words decsribing a character. (kind, silly, smart, mean) Climax: the most exciting part of a story or novel Compare: to find the similarities of two or more things Complete: finish Conflict: problem in a story the characters need to solve Context Clues: wordfs found in the text that the reader can use to help him or her figure out the meaning of an unknown word. Contrast: to find the differences of two or more things Copy Right Date: the date that the book was written. Can help the reader know if the source is reliable with current information. Data: information; usually in number form Define: explain what a word means Definition: what a word means, some words have more than one definition Describe: tell about the given subject using details, (for example; what happened, what does it look like) Describe two ways: to tell two different ways something happened Detail: particular piece of information that supports the main idea Dictionary: a book with words and their meanings. arranged in alphabetical order. Draw Conclusions: using what you have read to come to a conclusion or decision Effect: Is the result of the cause Encyclopedia: a set of books of general facts and information about a variety of topics. arranged in alphabetical order. Entertain: to amuse; for fun Evaluate: form an opinion about something's value (good/bad, etc) Explain your answer: Use details to tell why you chose that answer Examine: inspect or look at closely Fact: A statement that can be proven true or false Figurative Language: a way of saying something other than the literal meaning of the words (examples, hyperbole, metaphor, simile, personification, idiom) Formulate: develop, come up with, put into words Genre: the type and style of the selection; could be fiction or nonfiction (needs to be as specific as possible, historical fiction, realistic fiction, fantasy, folk tale, biography, informational, etc.) Autobiography: genre of nonfiction that tells about a person’s life, the book was written by the actual person Biography: genre of nonfiction that tells about a person’s life, the book was written by someone else. Fantasy: a genre of books that contain parts about magical creatures, faraway lands, monsters, etc. Fable: a genre of books that usually involves animals and teaches the reader a moral or lesson. Fiction: a story or tale that is made up from the author’s mind Historical Fiction: a story that has made up characters and events, but the setting, famous characters or major story events are real and from the past (example; The Boy in the Striped Pajamas, Liberty’s Kids [TV show]) Mystery: A book with characters that are involved in a puzzle. There are clues and something that must be figured out. Nonfiction: A selection that is entirely based on real people and/or events, none of it is from someone’s imagination. Usually meant to inform the reader. Poem/Poetry: A short piece of writing that usually contains rhyme, rymthm, stanzas, lines, figurative language, and a beat (but sometimes it doesn’t have any of those), it is meant to paint a picture with words and express a feeling. Realisitic fiction: a story that could really happen, but is still made up from the writer’s imagination, no elements of fantasy or magic. Science Fiction: A story with unusual happenings that seem impossible but are based on scientific fact. It often takes place in the future. Glossary: A list of words and definitions used in the book. It is located at the back of a book. Graphic organizers: a way to organize data (examples; maps, charts, graphs, tables), students may need to use them to determine an answer or use them to organize their own answer Homograph: words that have the same spelling but different meanings and sound (example; live-to exsist & live-watching something as it is happening) Homonym: Words that have the same sound and spelling but different meanings (example; nickel-a chemical element & nickel-5 cent coin) Homophone: words that sound the same, but have different spelling (example; would & wood, bear & bare, to & too & two) Hyperbole: an over-exaggerated statement (example; I have said it a thousand times; he was running, like, a million miles an hour) Idiom: a sentence or phrase whose meaning cannot be predicted from the meanings of the actual words (example; out of the blue; spill the beans, cat have your tongue) Index: gives you the exact location of specific topics and information in a book. It is located at the back of the book. Infer: come to a conclusion or form an opinion by using clues from the text (these conclusions go beyond the obvious given facts) Inference: to infer from a pasage or text Inform: to explain something using facts Irrelevant information: a statement or sentence that has little or nothing to do with the rest of the text. Having irrelevant information might confuse a reader. Relevant information: a statement or sentence that is on topic and relates to the rest of the text. This statement might give important information. Main Idea: what the selection is about; tells more than just a topic For example; the topic might be jelly fish, but the main idea of a selection would be something like jellyfish that can stand the cold waters of Antarctica. Metaphor: a figure of speech in which a word or phrase is applied to an object or action that it does mean literally Mood: how the story or poem makes the reader feel (usually done through specific words and descriptions of the setting) Number these events in the order that they happened: Put these events in sequential order Opinion: A statement that is based on feelings or emotions; cannot be proven Personification: Giving human characteristics to non-human things (example; my stomach is telling me its hungry) Persuade: to try and influence someone to do or think a certain way Plot: the main events in a story, including the climax and reolution. Point of View: how the narrator presents the information 1st person – A character in the story is telling the story 3rd person – A narrator not in the story is telling the story Predict: Make an educated guess of what is going to take place Prefix: an addition to a word that goes at the beginning of a base word to change the meaning of the word Resolution: how the character(s) solve the problem or conflict Root or Base Word: Does not have any prefix or suffix added to it Select: Pick from different choices Selection: the story or passage that is to be read Sequence: Placing things in an order; could be the way they happened in a story; set of directions, chronological (time), numerical (number) Setting: Where and when the story took place Simile: a type of figurative language that comparies two things using like or as Speaker: the person telling a story, also called the narrator. This could also be the person saying a quote. Stanza: A set of lines in a poem. A stanza to a poem is like a paragraph to an essay. State: Clearly give an opinion or information Subheading: A title or heading that tells what the selection will be about Suffix: the part of a word at the end that changes the meaning of the root word Summarize: to make a summary; restate in a shorter way; give only main points Support (or Supporting Details): back up your answer with examples and details; Give a quote from the text; find evidence Synonym: a word that has a similar meaning to another word Table of Contents: tells the chapter titles in a book. It is located at the front of the book. Theme: what we learn from a story that we can apply to our own lives; theme could be as simple as “bravery” or a complex as “sometimes bad things can make good things happen” Thesaurus: a book that lists words in groups of synonyms and related concepts. Timeline: sequencing events by the time or date that they happened