Useful Fact Sheet
advertisement

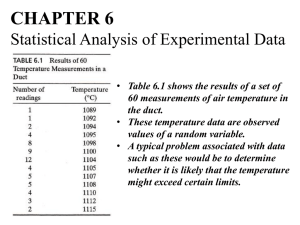
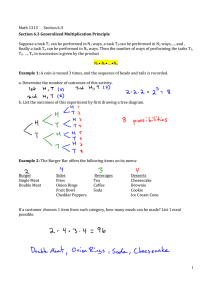
Useful Fact Sheet Exam 2- Chapter 3 and 4 Classical (or Theoretical) Probability Empirical (or Statistical) Probability The Sum Rule • The sum of the probabilities of all the simple events in the sample space must equal 1. The Complement Rule • The complement of event E is the event that E does not occur, denoted by Ecor E’ The compliment of E is the set of all outcomes in S that are not in E. P(E’) = 1 – P(E) P(E) +P(E’) = 1 Probability of Occurrence of both Events A and B Probability of Occurrence of either Events A or B Conditional Probability Independent Events . Two event s A and B are called dependent events if the occurrence of event B has changed the probability that event A will occur, that is Intersection of Sets – The intersection of sets A and B, written A⋂B, is the set of elements common in both A and B, or Union of Sets – The union of sets A and B, written A⋃B, is the set of elements belonging to wither of the sets, or Disjoint Sets (Mutually Exclusive) – Two sets have no elements in common, sets A and B are disjoint if A⋂B = ø. Permutations of n objects taken r at a time: Distinguishable Permutations: n1 alike, n2 alike … nk alike: Permutations of n objects taken r at a time: The Factorial Mean of a Discrete Random Variable: also called the Expected Value Variance of a Discrete Random Variable: Standard Deviation of a Discrete Random Variable: Binomial Probability of x successes in n trials P( x) n C x p x q n x Population Parameter of a Binomial Distribution: Mean: Standard Deviation: Variance: n! p x q n x . x !(n x)!