Chp 9 Lesson #2 key
advertisement

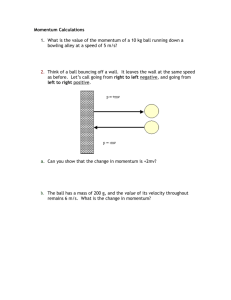
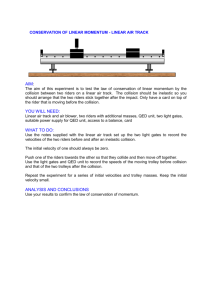
Name:____________________ Date:____________________ 9.2 – The Conservation of Momentum * To study momentum changes in collisions, we must use a ______________ , ______________ _____________. A system is closed if objects neither enter nor leave it. It is isolated if no net external force is exerted on it. Conservation of Momentum – 1- Two Body Push Apart This problem involves the explosion of two masses. A spring between two masses will push them apart. The names of the masses are mass 1, or m1, and mass 2, or m2. The masses move apart, each with its own velocity. The velocity of m1 is v1’; the velocity of m2 is v2'. In the diagram below, m1 is shown moving to the left after the explosion. However, this is not necessarily so. It could also be moving to the right after the explosion. Its movement depends upon the size of the impulse produced by the spring. 2- Two Body Stick Together Collision This problem involves the collision of two masses which stick together. The names of the masses are mass 1, or m1, and mass 2, or m2. Before the collision: Both masses are in motion, moving in positive directions. (See note below.) Mass 1 is behind mass 2. Their velocities before the collision are v1 and v2. The velocity of mass 1 is greater than the velocity of mass 2. So, mass 1 will eventually catch up to mass 2. Before After the collision: The masses stick together and move off to the right as one object. Therefore both masses are traveling at the same velocity after the collision. This mutual velocity is called v'. After __ 3- Total Momentum, Two Body System, Two Dimensions Imagine two objects in motion. This will be our system of two objects. We will calculate the total momentum of this system. This situation does not consider the collision of the two objects, just the total momentum of the two objects. Decide upon values for the masses of the two objects. Call these two masses m1 and m2. Decide upon values for the sizes and directions of the velocity vectors for these masses. Call these velocities v1 and v2 for m1 and m2 respectively.v1 should be directed South of East as shown v2 should be directed North of East as shown here: _________________________________ * Law of Conservation of Momentum – the momentum of any closed, isolated system does not change! The total momentum before an interaction equals the total momentum after the interaction ______________________________________________ (equation) Ex1: Ball A of mass 0.355 kg has a velocity of 0.095 m/s. It collides with ball B of mass 0.710 kg moving in the same direction at a velocity of 0.045 m/s. After the collision, ball A continues in the same direction with a velocity of 0.035 m/s. What is the velocity of ball B after the collision? Homework: 1. Read pgs 180 – 188 2. Do pgs 185 # 5 – 8 3. Do pgs 188 – 189 # 9-11