22-Colorado Montane Autecology Notes
advertisement

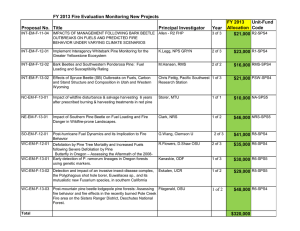
NOTES ON THE AUTECOLOGY OF TREE SPECIES IN THE MONTANE ZONE (BELOW C. 9300 FT.) IN THE COLORADO FRONT RANGE A. Ponderosa pine (Pinus ponderosa var. scopulorum) Habitat: Drier than Douglas fir; wetter than Rocky Mt. juniper, limber pine and grasslands. Reproduction: Some seeds produced each year but with large crops at 3 to 5 year intervals. Longevity: Up to 600 years, but very few trees over 400 years in Colorado. Understory tolerance: Less tolerant than Douglas fir. Seedling establishment: Best on bare mineral soil. Does not compete well with grasses on finely textured soils. Damaging agents: Thick bark gives adults much resistance to fire. Fire kills seedlings. Weakened by dwarf mistletoe (Arceuthobium spp.) Killed by bark beetles (Dendroctonus spp.) and associated fungus--especially mt. pine beetle (D. ponderosae). Relatively windfirm due to deep taproot. B. Douglas fir (Pseudotsuga menziesii) Habitat: More mesic sites than Ponderosa pine (north-facing slopes and higher elevations). Reproduction: Normally some seeds produced each year. Longevity: Can be very long-lived but few trees in Colorado are older than 400 years. Understory tolerance: Semi-shade tolerant. Can grow under lower light levels than Ponderosa pine. Seedling establishment: Favored by bare mineral soil but less dependent on bare mineral soil than Ponderosa pine. Damaging agents: Thick bark and high fire resistance of adults. Seedlings easily killed by fire. Defoliated by western spruce budworm (Choristoneura occidentalis) which also eats the cones. Amount of mortality varies with stand characteristics, tree vigor, duration of outbreak, and climatic variability. Killed by Douglas fir bark beetle (Dendroctonus pseudotsugae). Bark beetle attacks typically follow budworm outbreaks.