More Dividing Decimals by Decimals
advertisement

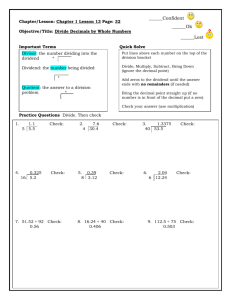
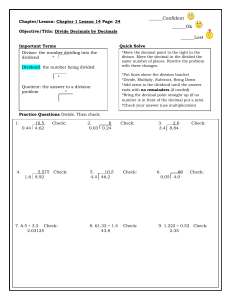
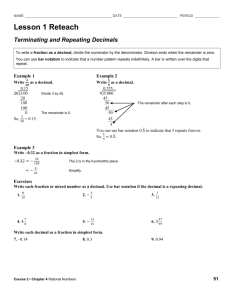
More Dividing Decimals by Decimals What is a Repeating Decimal? What is a terminating Decimal? When do I use Bar Notation? Parts of a division problem Remember: Remember: How do I know where to put a decimal in partial quotient? Example# 1 of zero in the quotient: A decimal that shows a repeating pattern and does not end – goes on infinitely. A decimal number that ends or terminate. Represent a repeating decimal using bar notation. The bar goes above the number(s) that repeat. quotient Divisor| dividend The divisor cannot have a decimal. Multiply by a power of 10 or SWOOP to make the divisor a whole number. Use zeros as place-holders in the quotient. 1. SWOOP your decimal to make the divisor a whole number. 2. Divide like you normally would. 3. Once you have found your sum you will need to place your decimal in your answer. The number of places after the decimal in your answer should match the number of places after the decimal in your dividend. 0.012 0.6 0.6 | 0.012 Need zero to hold the tenths place! Example #2 of zero in quotient What if I use long division and there is a remainder? What if I use partial quotient and there is a remainder? 0.02 6 | 0.12 - 12 0 45.05 2.5 = 18.02 * answer is a terminating decimal If there is a remainder in long division add zeros to the end of the dividend and bring them down. This can be done as many times as necessary. Remember to put a decimal after the ones place. 1. If you have a remainder find the sum of the partial quotients you have listed. 2. Move the decimal so the decimal places in your answer matches the number of decimal places in your dividend. Example #3 of zero in quotient Remember: Example #1 of zero in dividend 3. Add a zero to your last remainder. 4. Find the next partial quotient. 5. Write the partial quotient at the end of the answer. 6. Continue adding zeros and adding the next partial quotient to the end of your answer until you have enough information to solve the problem. .844 .12 = 7.03… * answer is a repeating decimal No remainders allowed! Instead – keep adding “Phantom Zeros” to the dividend until an answer is arrived. 20.7 0.6 A zero here 0.6 | 20.7 doesn’t change the value of the dividend, but helps to solve the problem. Example #2 of zero in dividend Example #3 of zero in dividend 34.5 6 | 207.0 18 27 24 30 30 0 .184 .24 = .76… * answer is a repeating decimal 32.5 2.6 = 12.5 * answer is terminating decimal Dividing Decimals by Decimals What is a Repeating Decimal? What is a terminating Decimal? When do I use Bar Notation? A ______________ that shows a ______________ pattern and does __________ end – goes on __________________________. A decimal number that ______________ or ___________________________. Represent a ___________________ decimal using _______ notation. The bar goes above the ____________________ that _________________. Parts of a division problem | Remember: The ______________ cannot have a _____________. _____________ by a power of 10 or ____________ to make the divisor a Remember: How do I know where to put a decimal in partial quotient? Example# 1 of zero in the quotient: _____________ number. Use _____________ as place-holders in the _________________. 1. ___________ your decimal to make the ______________ a ____________ number. 2. _____________ like you normally would. 3. Once you have found your ___________ you will need to___________ your _____________ in your answer. The number of _____________ after the _____________ in your ______________ should match the number of _______________ after the ________________ in your __________________. 0.012 0.6 0.6 | 0.012 Need zero to hold the tenths place! Example #2 of zero in quotient 45.05 2.5 What if I use long division and there is a remainder? If there is a __________________ in long division add ______________ to the end of the _______________ and bring them ___________. This can be done as many times as __________. Remember to put a _______________ after the __________ place. What if I use partial quotient and there is a remainder? Example #3 of zero in quotient 1. If you have a remainder find the __________of the ______________ quotients you have listed. 2. _______________ the decimal so the decimal places in your ______________ matches the number of _____________places in your ______________________. 3. Add a ___________ to your last _________________. 4. Find the ____________ partial quotient. 5. Write the partial quotient at the ___________ of the ___________________. 6. Continue adding ___________ and writing the next partial quotient at the __________of your answer until you have enough __________________ to __________ the problem. .844 .12 = Example #1 of zero in dividend 20.7 0.6