Name
advertisement

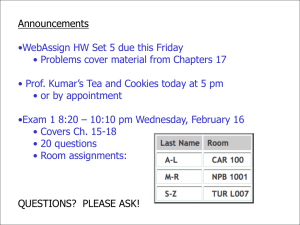
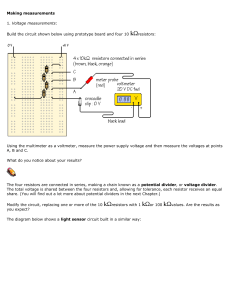
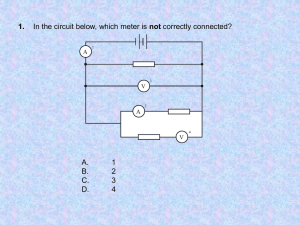
Name __________________________ Period ______ Date _______________ Lab Partners _____________________ V _____________________ DC Circuits Lab Purpose: To verify the behaviors of resistors wired in series and parallel circuits by comparing calculated to measured voltages and currents for three resistors wired first in a series circuit configuration, then wired in a parallel circuit configuration. Materials: Power supply (or batteries) that can be set to voltages between 3.0 volts and 6 volts Three different value resistors ranging from 50 ohms to 500 ohms Four wire leads Multimeter Procedure: Part I – SERIES CIRCUIT Read and record the values of the three different resistors you chose in the data table, including the tolerance (%error) factor for each reading. Set the multimeter to read ohms and measure the resistor value for each of the three resistors you chose, as shown in the diagram below. Using the Multimeter To measure Resistance Set up a simple series circuit with the power supply connected to the first of your resistors Set the voltage to somewhere between 3 and 6 volts (or use a single dry cell) and turn the power supply on Set the multimeter to read DC Volts at its lowest reading, then turn on the multimeter Measure and record the voltage across each resistor as demonstrated in class and in the picture below by: o touching the positive probe to the side of the resistor leading to the positive connection at the power source and simultaneously o touching the negative probe to the side of the resistor leading to the negative connection at the power source (see diagram on following page) Using the Multimeter as a Voltmeter Power source Measure and record the total voltage for the entire span of three resistors by touching one probe before the first resistor and the second probe after the third resistor. Measure and record the current through each resistor. To do so: o Disconnect the negative end of the resistor from the line and attach it instead to the positive probe on the multimeter. o Attach the negative probe of the multimeter to the line. o Turn the multimeter dial to measure the smallest amount of DC current (DC Amps) o Turn on the multimeter and record the current measurement, being careful to note the prefix (milli-, micro-) before the amperage reading. Using the Multimeter to measure Current Measure and record the total current for the entire span of three resistors. Remove the probes from the resistors and turn off the multimeter. Calculate and record the total resistance expected from reading the resistor band codes. Calculate and record the total current expected from the power box voltage setting and the total resistance. Calculate and record the expected voltage drops for each resistor based on the resistor band reading and the power source setting. Compare the calculated to the measured total voltage and current by calculating percent difference based on the calculated values being the more accurate. Part II – PARALLEL CIRCUIT Set up a simple parallel circuit with the same three resistors you used for the series circuit. Set the voltage to the same voltage you used for the series circuit Measure and record the voltage drop across each resistor as demonstrated in class Measure and record the currents through each resistor as demonstrated in class Measure and record the total voltage across all three resistors together. Measure and record the total current through all three resistors together. Calculate the total resistance for the circuit using the resistor band codes. Calculate the expected voltage drops and individual resistor currents. Calculate the percent difference between your measured and calculated values for current and voltage Questions: 1. Draw a circuit diagram below showing the setup for the series circuit part of this experiment by using the appropriate circuit symbols. Be sure to include the power source, the resistors, the ammeter, and the voltmeter in your diagram. Label each device with the appropriate letter. 2. Draw a circuit diagram below showing the setup for the parallel circuit part of this experiment by using the appropriate circuit symbols. Be sure to include the power source, the resistors, the ammeter, and the voltmeter in your diagram. Label each device with the appropriate letter. 3. According to your lab results, what relationship exists between the total voltage and the individual voltages through each particular resistor when the circuit was: Series: Parallel: 4. According to your lab results, what relationship exists between the total current and the current through each resistor when the circuit was: Series: Parallel: 5. According to your lab results, which resistor put out the most power (biggest or smallest resistor) when in: Series: Parallel: 6. What would happen if the total voltage in each circuit was not used up by the resistors? 7. What happens if you use the multimeter as a voltmeter when you have it set as an ammeter? 8. Should the voltmeter have a high or a low resistance? Why? 9. Should the ammeter have a high or a low resistance? Why? Data Table: Power Box Voltage Setting : ________ Resistor 1 colors____________ ____________ ____________ +/-color band __________ Resistor 2 colors____________ ____________ ____________ +/-color band __________ Resistor 3 colors____________ ____________ ____________ +/-color band __________ SERIES CIRCUIT Quantity R1 code value Calculated Measured % Error R2 code value R3 code value Total Current Total Voltage Voltage R1 Voltage R2 Voltage R3 Current I1 Current I2 Current I3 PARALLEL CIRCUIT Quantity R1 code value R2 code value R3 code value Total Current Total Voltage Voltage R1 Voltage R2 Voltage R3 Current I1 Current I2 Current I3 Calculated Measured % Error Quantity Series Rtotal % Error Rmeasured versus Rcalculated Itotal Series Series Vdrop R1 Series Vdrop R2 Series Vdrop R3 % Error Imeasured versus Icalculated series % Error series V TOTAL (meas) versus V TOTAL (calc) Parallel Rtotal Itotal Parallel Parallel I1 Parallel I2 Parallel I3 % Error parallel I TOTAL (meas) versus I TOTAL (calc) Formula SAMPLE CALCULATIONS Substitution Answer with Units