החמרה לעלון
advertisement
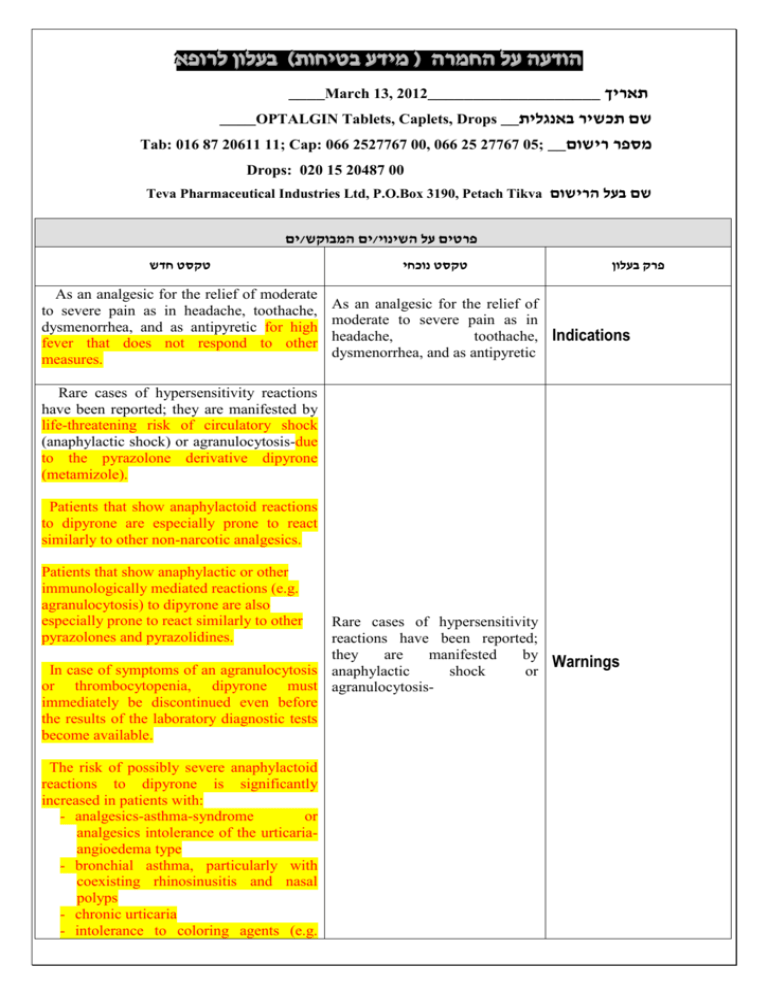
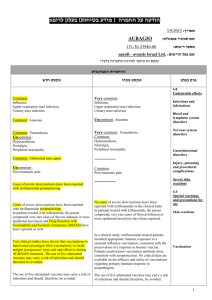
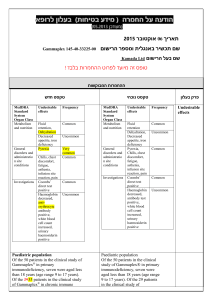
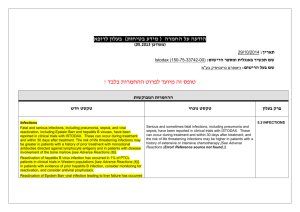
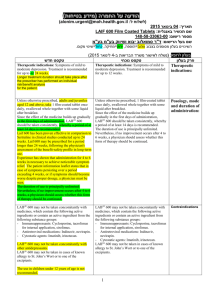
רופא בעלון ללרופא בטיחות) בעלון )מידע בטיחות החמרה (( מידע על החמרה הודעה על הודעה ____March 13, 2012___________________ תאריך ____OPTALGIN Tablets, Caplets, Drops __שם תכשיר באנגלית Tab: 016 87 20611 11; Cap: 066 2527767 00, 066 25 27767 05; __מספר רישום Drops: 020 15 20487 00 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, P.O.Box 3190, Petach Tikva שם בעל הרישום ים/ים המבוקש/פרטים על השינוי טקסט חדש As an analgesic for the relief of moderate to severe pain as in headache, toothache, dysmenorrhea, and as antipyretic for high fever that does not respond to other measures. טקסט נוכחי פרק בעלון As an analgesic for the relief of moderate to severe pain as in headache, toothache, Indications dysmenorrhea, and as antipyretic Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions have been reported; they are manifested by life-threatening risk of circulatory shock (anaphylactic shock) or agranulocytosis-due to the pyrazolone derivative dipyrone (metamizole). Patients that show anaphylactoid reactions to dipyrone are especially prone to react similarly to other non-narcotic analgesics. Patients that show anaphylactic or other immunologically mediated reactions (e.g. agranulocytosis) to dipyrone are also especially prone to react similarly to other pyrazolones and pyrazolidines. Rare cases of hypersensitivity reactions have been reported; they are manifested by Warnings In case of symptoms of an agranulocytosis anaphylactic shock or or thrombocytopenia, dipyrone must agranulocytosisimmediately be discontinued even before the results of the laboratory diagnostic tests become available. The risk of possibly severe anaphylactoid reactions to dipyrone is significantly increased in patients with: - analgesics-asthma-syndrome or analgesics intolerance of the urticariaangioedema type - bronchial asthma, particularly with coexisting rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps - chronic urticaria - intolerance to coloring agents (e.g. tartrazine) or preservatives (e.g. benzoates) - intolerance to alcohol. Such patients react to even small amounts of alcoholic beverages with symptoms such as sneezing, watery eyes and a pronounced redness of the face. Such alcohol intolerance can be a sign of a previously undiagnosed analgesicsasthma-syndrome. Dipyrone can cause hypotensive reactions. These reactions are possibly dosedependent. The risk of such reactions is also increased in: patients with preexisting hypotonia, hypovolemia or dehydration, unstable circulation or beginning circulatory failure (e.g. patients with cardiac arrest or polytrauma) patients with high fever. Therefore, careful indication analysis and close monitoring are required in these patients. Preventive measures (e.g. circulatory stabilization) may be necessary to reduce the risk of hypotensive reactions. In patients, who would be at particular risk from a reduction in blood pressure (e.g. patients with severe coronary heart disease or relevant stenoses of blood vessels supplying the brain), dipyrone must only be used under careful monitoring of the hemodynamic parameters. In patients with impaired kidney or liver function, dipyrone should only be administered after strict risk-benefit assessment and with appropriate precautions. Use in Pediatrics Use of dipyrone is contraindicated in infants with a body weight less than 5 kg. See Contraindications. There is insufficient data regarding the use of dipyrone in pregnant women. Dipyrone passes into the placenta. In animal studies, See Contraindications dipyrone showed no teratogenic effects. Although dipyrone only slightly inhibits the prostaglandine synthesis, a premature (intrauterine) closure of the Ductus Botalli Use in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding as well as complications due to platelet aggregation inhibition cannot be excluded. Metabolites of dipyrone enter the breast milk. Precautions Known hypersensitivity to dipyrone or to pyrazolone and pyrazolidine derivatives (e.g.: to medicines containing dipyrone, propyphenazone, phenazone or phenylbutazone) or to any other ingredient of the preparation. Pregnancy and breastfeeding. Acute hepatic porphyria. Genetic deficiency of the enzyme glucose6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). In case of impaired bone marrow function (e.g., following a treatment with cytostatics) or disorders of the hematopoietic system, as well as history of blood dyscrasias or acute bone marrow suppression. In patients with a body weight less than 5 kg very common common uncommon rare very rare 1/10 1/100 up to <1/10 > 1/1,000 up to <1/100 1/10,000 upto <1/1,000 <1/10, 000 or unknown (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data) 1/10 Known hypersensitivity to dipyrone or to pyrazolone derivatives or to any other ingredient of the preparation. Pregnancy and breastfeeding. Acute porphyria. Contraindications Genetic deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). History of blood dyscrasias or acute bone marrow suppression. Allergic Agranulocytosis has rarely been reported. It is an immunoallergic adverse reaction lasting at least 1 week. Agranulocytosis is unpredictable, not dose-related and may occur even after a single dose. Anaphylactic shock (see Warnings). Dermatological reactions (see Warnings). Hematological Rarely agranulocytosis, Adverse events anemia, leucopenia and thrombocytopenia, have been The main side effects of dipyrone are reported. hypersensitivity reactions. The most important reactions are circulatory and Renal Isolated cases of acute renal agranulocytosis. These reactions occur or interstitial rarely or very rarely but are life-threatening. insufficiency They can occur even if metamizole sodium nephropathy have been reported. has been formerly used without any Other complications. Drowsiness, tiredness, and headache have been reported Immune System Disorders In rare occasions, anaphylactoid or with dipyrone administration. Hypotension has been reported anaphylactic reactions can occur that only intravenous very rarely turn out severe and life- following very common threatening. Such reactions to medicines can develop during injection or immediately after administration, but also many hours later. However, they mostly occur within the first hour after administration. Minor reactions typically appear inform of skin and mucous membrane reactions (such as itching, burning, redness, urticaria, swellings), dyspnea and - less frequently gastrointestinal complalnts (such as nausea, dyspepsia, vomiting). These minor reactions can develop into severe forms with generalized urticaria, severe angioedemas (also in the larynx region), severe bronchospasm, cardiac arrhythmias, drop in blood pressure (sometimes preceded by a rise in blood pressure) and circulatory shock. In patients with analgesics-asthma-syndrome, intolerance reactions typically appear in form of asthma attacks. At the first signs of a state of shock such as cold sweat, vertigo, dizziness, skin discoloration, feeling of constriction in the heart region, the appropriate immediate actions must be taken. Vascular Disorders In rare occasions, hypotensive reactions may occur during or after the administration, that are possibly pharmacologically induced and are not accompanied by other signs of an anaphylactoid or anaphylactic reaction. These reactions only rarely lead to a severe drop in blood pressure. A rapid intravenous injection increases the risk of such hypotensive reactions. Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders In rare occasions a leukopenia and in very rare occasions an agranulocytosis or thrombocytopenia may occur. These reactions can occur even if metamizole sodium has been formerly used without any complications. The risk of an agranulocytosis rises if diopyrone is used for a longer than a week. The typical signs of an agranulocytosis administration of dipyrone. Nausea, vomiting, gastric irritation and xerostomia have been described with oral and parenteral dipyrone administration include inflammatory mucosal changes (e.g. in the mouth, nose or throat or in the genital or anal region), sore throat, swallowing difficulties, fever and chills. In patients that receive antibiotics, these signs can however be minimal. Lymph node or spleen swellings are minor or completely absent. The blood sedimentation is strongly accelerated, the granulocytes are significantly reduced or completely absent. The hemoglobin, erythrocyte and thrombocyte values are usually within the normal range. An unexpected deterioration of your general condition can be an indication of an agranulocytosis. The treatment of these reactions requires immediate discontinuation of the medicine. Therefore it is strongly recommended to discontinue dipyrone upon the first signs of an agranulocytosis and not to wait for the results of the laboratory diagnostic tests. Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders In rare occasions, a fixed drug eruption or other dermatological (rash) can occur. In isolated cases, a Stevens-Johnson syndrome (allergy-induced skin disorder) or Lyell's syndrome (life-threatening disorder with extensive skin blistering) can occur. Therefore, dipyrone must be immediately discontinued in case of skin reactions. In rare occasions, a fixed drug eruption or other exanthemas (rash) and in isolated cases, Stevens-Johnson syndrome or LyclI's syndrome may occur. Other Reactions Very rarely - particularly in case of hypovolemia, preexisting disorders of the kidneys and overdose -kidney function disorders with anuria or oliguria, proteinuria and interstitial nephritis may occur. Allergic Agranulocytosis has rarely been reported. It is an immuno-allergic adverse reaction lasting at least 1 week. Agranulocytosis is unpredictable, not dose-related and may occur even after a single dose. Anaphylactic shock (see Warnings). Dermatological reactions (see Warnings). Hematological Rarely agranulocytosis, anemia, leucopenia and thrombocytopenia, have been reported. Renal Isolated cases of acute renal insufficiency or interstitial nephropathy have been reported. Other Drowsiness, tiredness, and headache have been reported with dipyrone administration. Hypotension has been reported following intravenous administration of dipyrone. Nausea, vomiting, gastric irritation and xerostomia have been described with oral and parenteral dipyrone administration. Dipyrone/ Chlorpromazine: Concurrent use of dipyrone and chlorpromazine may cause severe hypothermia; therefore combined therapy with these two drugs should be avoided. Dipyrone/Cyclosporin: Dipyrone may cause a reduction in cyclosporin blood Dipyrone/ Chlorpromazine: levels, by an unknown mechanism. A higher Concurrent use of dipyrone and dose of cyclosporin may be required. chlorpromazine may cause hypothermia; therefore Oral Anticoagulants/ Pyrazolones/ combined therapy with these two Captopril/ Lithium/ drugs should be avoided. Drug Interactions Methotrexate/Triamterine/Anihypertensive Dipyrone/Cyclosporin: s/Diuretics: Dipyrone may cause a reduction The substance class of pyrazolones is in cyclosporin blood levels, by known to cause interactions with oral an unknown mechanism. anticoagulants, captopril, lithium, methotrexate and triamterene as well as to alter the effectiveness of antihypertensives and diuretics. To what extent dipyrone causes these interactions too, is yet unknown. Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines Dipyrone can impair the ability to drive vehicles or operate machines. In the recommended dose range no effect on the ability to concentrate and react is known. However, since dioyrone is supposed to have a central component of action and central side effects can occur in case of overdose, the possibility of an Effect on ability to drive and use machines impairment should be taken under consideration at least at higher doses and driving vehicles, operating machines or other potential dangerous activities should be avoided in this case. This applies particularly in combination with alcohol. Pharmacological Properties Pharmacodynamic properties Pharmacotherapeutic group: Analgesics; Other analgesics and antipyretics; Pyrazolones ATC Code: N02BB02 Dipyrone is a pyrazolone derivate and has analgesic, antipyretic and minor antiphiogistic as well as spasmolytic properties. Among the pyrazolone derivates it has the strongest analgesic effect. Similar to other analgesics, the mechanism of action is not known in detail. Among other things, metamizole sodium inhibits the prostaglandin synthesis (PGE I and PGE2) and reversibly the aggregation of thrombocytes. It inhibits the cyclooxygenase and affects the effect of the arachidonic acid. At the same time there seems to be a central component of action. For the analgesic active component, an attenuation of the central pain perception by Action activation of neurons in the pain inhibition Optalgin is a non-narcotic Pharmacological system is also under consideration. analgesic and antipyretic. properties The antipyretic effect is mediated by central attack on the hypothalamic heat regulation center, supported by increased heat dissipation via the periphery. The exudations-inhibiting and vessel-sealing properties of metamizole sodium are the bases of the antiphlogistic effect that at least partly can be explained by an inhibition of the endogenous prostaglandin synthesis. Pharmacokinetic properties After oral administration, dipyrone is rapidly and virtually completely absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and is rapidly split to 4-methylaminoantipyrine (MAA) via a non-enzymatic hydrolysis. The subsequent metabolism process leads to the formation of 4- acetylaminoantipyrine (AAA) via the active 4-aminoantipyrine (AA). Another route of degradation consists of the incomplete oxidation of MAA to 4-formylaminoantipyrine (FAA). Only 6570% of the applied dose can be detected via these metabolites. Maximum plasma concentrations (with respect to all metabolites) can be detected after approx. 30-90 min. After oral administration of 1 g metamizole sodium, the maximum plasma concentration Cmax of MAA is 10.5 +/-2.8 µg/ml, after rectal administration of I g dipyrone it is 6.1 +/1.9 µg/mI. The degree of plasma protein binding is 57.6 % for MAA, for 47.9 % for AA, 17.8 % for FAA and 14.2 % for AAA. The pharmacokinetic behavior of the metabolites seems to be different depending on the dose. The excretion is primarily (approx. 90%) renal with the main metabolites AAA and 10% is excreted biliary with a half life of approx. 10 h. In the elderly, the elimination half life of MAA rises from 2.6 h (12 probands, 2 1-30 years) to 4.5 h (9 probands, 73-90 years). Following an intramuscular injection, the metabolites of metamizole sodium show a similar behavior. Action Optalgin is a non-narcotic analgesic and antipyretic. Preclinical Safety Data Acute toxicity See Overdosage Subchronic/chronic toxicity There are studies available on the subchronic and chronic toxicity in various animal species. Rats were orally administered metamizole sodium in doses of 100-900 mg/kg bw for 6 month. In the highest dose group (900 mg/kg bw), an increase of reticulocytes and Heinz bodies was observed after 13 weeks. Dogs were administered dipyrone in doses of 30-600 mg/kg bw for 6 month. Depending on the dose, a hemolytic anemia as well as functional kidney and liver alterations were observed at doses from 300 Preclinical Safety Data mg/kg bw upwards. Mutagenic and Carcinogenic Potential Dipyrone has not been sufficiently tested for mutagenicity. There are both indications of mutagenic effects of dioyrone as well as negative results. Long term studies in rats showed no evidence of a carcinogenic potential. In 2 of 3 long term studies in the mouse, liver cell adenomas were increasingly observed at high doses. ReproductiveToxicity Embryotoxicity studies in rats and rabbits have shown no evidence of teratogenic effects. Embryolethal effects were observed in rabbits from a maternally subtoxic daily dose of 100 mg/kg bw upwards. In rats, embryolethal effects at doses in the maternal toxic range were observed. Daily doses above 100 mg/kg bw in rats led to a prolongation of the gestation period and to an impairment of the birth process with increased mortality of mother and young. Fertility tests showed a slightly decreased pregnancy rate in the parent generation at a dose above 250 mg/kg bw per day. The fertility of the FI generation was not affected. Notes The dose should be reduced in elderly patients as well as inpatients with reduced general condition or limited creatinine, since the excretion of the metabolic products of dipyrone may be retarded. Currently there is no sufficient information regarding the long term administration of dipyrone in patients with seriously impaired liver and kidney function Duration of Treatment The duration of administration depends on thenature and severity of the medical condition. Adults and Adolescents over from 15 years old (over 53 kg body weight) Optalgin Caplets/Tablets 1-2 caplets or 1-2 tablets up to 4 times Optalgin Caplets/Tablets 1-2 caplets or 1-2 tablets up to 4 times daily. Do not exceed 8 caplets or 8 Dosage and tablets daily. Administration Optalgin Drops 25-50 drops up to 4 times daily. daily. Do not exceed 8 caplets or 8 tablets daily. Depending on the maximum daily dose, the single dose can be taken in intervals of 6 to 8 hours. The caplets/tablets should be taken with sufficient liquid. (e.g a glass of water). Optalgin Drops The oral drops are taken with a little bit of water. Adults and adolescents From 15 years (>53 kg) 25-50 drops up to 3 4 times daily. Infants and Children For all age groups except babies, 8-16 mg of dipyrone (metamizole) per kg body weight can be administered as a single dose. The table below shows the recommended single dose and the maximum daily dose as a function of body weight or age. Age Body weight (kg) Dose (No of drops) 3-11 months 5-8 2-5 drops up to 3 times daily 1-3 years 9-15 4-12 drops up to 3 times daily 4-6 years 16-23 6-19 drops up to 3 times daily 7-9 years 24-30 10-25 drops up to 3 times daily 10-12 years 31-45 13-14 years 46-53 12-37 drops up to 3 times daily 19-44 drops up to 3 times daily The table below shows the recommended single dose in miligrams of dipyrone and the maximum daily dose in milligrams , as a function of body weight and age: Body Single Dose Maximum Weight in in Drops Daily Dose Kg (Dose in in Drops (Age) mg) (Max daily dose in mg) 5-8 2-5 drops 11-15 drops (3-11 (40-100 mg) (220-300 months) mg) 9-15 4-12 drops 21-37 drops (1-3 years) (80-240 mg) (420-740 mg) 16-23 6-19 drops 37-56 drops (4-6 years) (120- 380 (740-1120 mg) mg) 24-30 10-25 drops 57-75 drops (7-9 years) (200-500 (1140-1500 mg) mg) 31-45 12-37 drops (10-12 (240-740 73-112 drops years) mg) (14602240 mg) 46-53 19-44 drops 110-131 (13-14 (380-880 drops years) mg) (2200-2620 mg) Overdosage Manifestations : In connection with acute overdose, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pains, impaired kidney fUnction/acute kidney failure (e.g. with signs of an interstitial nephritis) and — more rarely — central nervous symptoms (vertigo, somnolence, coma, spasms) and a drop in blood pressure up to a shock and tachycardia were observed. After administration of very high doses, the excretion of rubazonic acid may cause a red discoloration of the urine. Treatment No specific antidote is known for dipyrone. If dipyrone was only recently administered, it can be tried to limit the absorption in the body by means of absorption reducing measures (e.g. activated carbon). The main metabolite (4-Nmethylaminoantipyrine) can be eliminated by means of hemodialysis, hemofiltration, hemoperfiision or plasma filtration. The treatment of the intoxication as well as the prevention of severe complications, may Overdosage require general and special intensive medical monitoring and treatment. Treatment of Severe Anaphytactic Reactions (Shock): Emergency measures according to the current guidelines must be initiated. לצרכן – אופטלגין® טבליות/קפליות בעלון לצרכן בעלון אופטלגין® טיפות פרטים על השינוי/ים המבוקש/ים פרק בעלון טקסט נוכחי טקסט חדש פעילות רפואית לשיכוך כאבים ולהורדת חום. התרופה מיועדת לשיכוך כאבים בנוניים עד חזקים כגון כאבי ראש ,שיניים וכאבי וסת ולהורדת חום גבוה שאינו מגיב לאמצעי טיפול אחרים. מתי אין להשתמש בתכשיר אל תשתמשי בתרופה כאשר הינך בהריון או מניקה. אין להשתמש בתרופה זו אם ידועה רגישות לאחד ממרכיביה. אין להשתמש בתרופה למיחושים קלים. אל תשתמש/י בתרופה זו אם ידוע לך על חוסר באנזים "( G6PDרגישות לפול"). אין להשתמש בתרופה זו אם הינך סובל/ת מפורפיריה חדה או אם קיים דיכוי של מח העצם. אל תשתמשי בתרופה כאשר הינך בהריון או מניקה. אין להשתמש בתרופה זו אם ידועה רגישות לחומר הפעיל דיפירון (מטאמיזול),פרופיפנאזון,פנאזון,פנילבוטאזון או לאחד ממרכיביה הבלתי פעילים של התרופה. אין להשתמש בתרופה זו למיחושים קלים. אל תשתמש/י בתרופה זו אם ידוע לך על חוסר באנזים "( G6PDרגישות לפול"). אין להשתמש אם הינך סובל/ת מליקוי במערכת הדם. אין להשתמש בתרופה זו אם הינך סובל/ת מפורפיריה כבדית חריפה חדה (מחלה תורשתית בה קיים ייצור מוגבר והצטברות של פורפירין ,הגורמים להפרעות למשל במערכת העצבים). אין להשתמש בתרופה אם קיים דיכוי של מח העצם (כגון לאחר טיפול כמותרפי). אין להשתמש בתרופה מבלי להיוועץ ברופא לפני התחלת הטיפול אם הינך סובל/ת או סבלת בעבר מליקוי בתיפקוד מערכת הנשימה (כגון אסתמה) הכבד, הכליה ,מערכת הדם (כגון קרישה או אנמיה). יש להקפיד לדווח לרופא במידה ויש לך נטיה לרגישות יתר ,כגון אם הינך סובל(ת) מגנחת הסימפונות (אסתמה) או סרפדת (אורטיקריה) כרונית (פריחה מגרדת בעור) או מפורפיריה ( מחלה תורשתית בה קיים ייצור מוגבר והצטברות של פורפירין ,הגורמים להפרעות עוריות או במערכת העצבים). אזהרות אין להשתמש בתרופה זו לעיתים קרובות או תקופה ממושכת בלי להיוועץ ברופא. אם הינך רגיש/ה למזון כלשהו או לתרופה כלשהי ,עליך להודיע על כך לרופא לפני נטילת התרופה. רגישות יתר לתרופה זו עלולה לגרום ללויקופניה (מיעוט תאי דם לבנים) ,טרומבוציטופניה (מתבטאת בעליה בנטיה לדמומים) או לאגרנולוציטוזיס (פגיעה טוקסית בכדוריות דם לבנות) ושוק .תגובה זו עלולה להופיע לעיתים נדירות והיא מתבטאת בעייפות או חולשה במשך 3-2ימים ולאחר מכן מופיעים חום וכאב גרון .עם הופעת אחד הסימנים הנ"ל ,העלולים להופיע אחרי 2-1ימים של נטילת התרופה ,יש להפסיק מיד נטילת התרופה ולהיוועץ עם הרופא שלך. בהיוועצך ברופא ,יש להודיעו אם נטלת תרופה אחרת בו-זמנית עם אופטלגין. תרופה זו עלולה לגרום לצבע אדום בשתן חומצי. בתופעה זו אין מקום לדאגה. נטיה לרגישות יתר למשככי כאבים ,ותרופות לטיפול בדלקות פרקים ולתרופות אחרות. תסמינים הקשורים לאלרגיה:במצבים כאלה,הסיכון לשוק אנאפילאקטי עולה (ראה/י סעיף תופעות לוואי). אם הינך סובל/ת מנטיה לאלרגיות :כגון אלרגיה למזון ,משקאות אלכוהלים ,בע"ח, חומר משמר ,צבעי שיער ,תרופות שונות, אלרגיה הגורמת לאסתמה או פריחה כרונית בעור ( - - )urticariaיש ליטול אופטלגין רק בהשגחה רפואית. ליקויים בתיפקוד הכבד ,הכליה ,מערכת הדם (כגון קרישה או אנמיה). אם את/ה סובל/ת ממחלות שנלווית אליהן ירידה בכדוריות דם לבנות. ליקויים בתיפקוד מערכת הנשימה (כגון אסתמה) אם אתה סובל מגנחת הסימפונות (אסתמה) או מזיהומים כרוניים של דרכי הנשימה. נטיה לרגישות יתר ,כגון אם הינך סובל(ת) מגנחת הסימפונות (אסתמה) או סרפדת (אורטיקריה) כרונית (פריחה מגרדת בעור). דיפירון עלול לגרום לתופעות נדירות אך מסכנות חיים של שוק אנאפילקטי ו/או אגרנולוציטוזיס(.ראה/י תופעות לוואי). אין להשתמש בתרופה זו לעיתים קרובות או תקופה ממושכת בלי להיוועץ ברופא. אם הינך רגיש/ה למזון כלשהו או לתרופה כלשהי ,עליך להודיע על כך לרופא לפני נטילת התרופה. רגישות יתר לתרופה זו עלולה לגרום לעיתים נדירות ללויקופניה (מיעוט תאי דם לבנים) ,טרומבוציטופניה (מתבטאת בעליה בנטיה לדמומים) או לאגרנולוציטוזיס (פגיעה טוקסית בכדוריות דם לבנות) ושוק .תגובה זו מתבטאת בעייפות או חולשה במשך 3-2 ימים ולאחר מכן מופיעים חום גבוה, צמרמורות ,כאב גרון ,קשיי בליעה ודלקות בחלל הפה ,באף ,או באברי המין .עם הופעת אחד הסימנים הנ"ל ,העלולים להופיע כבר בשעה הראשונה לאחר נטילת התרופה אחרי 2-1ימים של נטילת התרופה ,יש להפסיק מיד נטילת התרופה ולהיוועץ עם הרופא. בהיוועצך ברופא ,יש להודיעו אם נטלת תרופה אחרת בו-זמנית עם אופטלגין. רופה זו עלולה לגרום לצבע אדום בשתן חומצי. בתופעה זו אין מקום לדאגה. תגובות בין תרופתיות אם הינך נוטל/ת תרופה נוספת או אם גמרת זה עתה הטיפול בתרופה אחרת ,עליך לדווח לרופא המטפל כדי למנוע סיכונים או אי-יעילות הנובעים מתגובות בין תרופתיות ,במיוחד לגבי תרופות מהקבוצות הבאות :תרופות נגד קרישת דם, ציקלוספורין (להשתלות) -תיתכן ירידה ברמת ציקלוספורין או כלורפרומזין (תרופה אנטי- פסיכוטית). נהיגה השימוש בתרופה זו במינונים גבוהים מהמומלץ עלול לפגום במהירות התגובה,ביכולת לנהוג ולהפעיל מכונות ועל יש להימנע במנהיגה ברכב, הפעלת מכונות ובכל פעילות המחייבת עירנות, הסיכון עולה אם התרופה נלקחת בשילוב עם אלכוהול. נהיגה תופעות לוואי תרופות נגד דלקת שאינן סטרואידיות ( )NSAIDSכגון אספירין. תרופות נגד קרישת דם (וורפרין). ציקלוספורין (להשתלות) -תיתכן ירידה ברמת ציקלוספורין. כלורפרומזין (תרופה אנטי-פסיכוטית). בנוסף לפעילות הרצויה של התרופה ,בזמן השימוש בה עלולות להופיע השפעות לוואי. תופעות המחייבות התייחסות מיוחדת בחילה או גירוי בקיבה. שוק אנפילקטי -תופעה של רגישות יתר המתבטאת בזיעה קרה ,סחרחורת ,קוצר נשימה ,בחילה ,או דופק מהיר (נדיר) הפסק/י הטיפול ופנה/י לרופא מיד! התקפים חריפים של פורפיריה ( ראה/י "אין להשתמש בתרופה מבלי להיוועץ ברופא לפני התחלת טיפול") (נדיר) :הפסק/י הטיפול ופנה/י לרופא מיד! כאבי ראש מתמשכים ,הפרעה זמנית בתפקודי כליות בחולים עם עבר של מחלות כליה או תגובה אלרגית בעור כגון פריחה או שלפוחיות ריריות (נדיר) :הפסק/י הטיפול ופנה/י לרופא מיד! תופעות הלוואי העיקריות של התרופה הם תופעות של רגישות יתר .הן כוללות: שוק אנאפילקטי ואגרנולוציטוזיס .אלו הן תופעות נדירות אך מסכנות חיים .הן יכולות להתרחש אפילו אם בעבר נטלת את התרופה ללא סיבוכים .הן יכולות להתרחש כבר בשעה הראשונה לאחר נטילת התרופה ,אך גם מס' שעות לאחריה. שוק אנפילקטי -תופעה של רגישות יתר חריפה המתבטאת בזיעה קרה ,בפריחה חמורה בכל הגוף,נפיחות של העור או של הלוע,שלפוחיות ריריות ,סחרחורת ,קוצר נשימה חמור ,בחילה,הקאה ,גירוי בקיבה,דופק מהיר ,הרגשת לחץ בחזה וירידה חדה בלחץ הדם., (נדיר) הפסק/י הטיפול ופנה/י לרופא מיד! והזעק עזרה רפואית מיד! בינתיים עד הגעת הרופא יש להשכיב את החולה על גבו ,להרים את רגליו .רצוי לחמם את גופו ע"י שמיכה. רגישות יתר לתרופה זו עלולה לגרום לעיתים נדירות ללויקופניה (מיעוט תאי דם לבנים) ,טרומבוציטופניה (ירידה בטסיות הדם המתבטאת בעליה בנטיה לדמומים) או לאגרנולוציטוזיס (פגיעה טוקסית בכדוריות דם לבנות) . הסיכון לאגרנולוציטוזיס עולה אם התרופה ניטלת מעבר ל 7ימים. תגובה זו מתבטאת בחום גבוה, צמרמורת ,כאב גרון ,קשיי בליעה ודלקות בחלל הפה ,באף ,או באברי המין .הרעה בהרגשה הכללית (כגון עייפות או חולשה). אם הנך נוטל/ת במקביל אנטיביוטיקה- יתכן והסימנים הנ"ל יהיו חלשים יותר. עם הופעת אחד הסימנים הנ"ל ,יש להפסיק מיד נטילת התרופה ולהיוועץ עם הרופא, תופעות עוריות או ריריות: במקרים בודדים ייתכן: Stevens-johnson syndromeאו – Lyell's syndromאלו הם תגובות עוריות חריפות ומסכנות חיים כגון פריחה או שלפוחיות ריריות - .הפסק הטיפול ופנה לרופא מייד! כאבי ראש מתמשכים, במקרים נדירים ,בעיקר במצבים של ירידה בנפח הדם,בחולים עם עבר של מחלות כליה ובמקרים של מינון יתר,יתכן: הפרעה זמנית בתפקודי כליות בחולים עם עבר של מחלות כליה ,בתפקודי כליה כגון ירידה או חוסר במתן שתן ,דלקת כליות ,או הפרשה של חלבון בשתן .או תגובה אלרגית חריפה בעור כגון פריחה או שלפוחיות ריריות (נדיר) :הפסק/י הטיפול מיד ופנה/י לרופא! בחילה או גירוי בקיבה. התקפים חריפים של פורפיריה ( ראה/י סעיף " 2לפני השימוש בתרופה") (נדיר) :הפסק/י מינון יתר בחילה ,הקאות ,כאב בטן,פגיעה בתפקודי כליה, ובמקרים נדירים יותר :סחרחורת,עוויתות ,חוסר הכרה ,ירידה בלחץ הדם ,שוק ,הפרעות בקצב הלב. בנטילת מינון מאד גבוה של התרופה ,צבע השתן עלול להפוך לאדום לצרכן – אופטלגין טיפות למתן דרך הפה בעלון לצרכן בעלון פרטים על השינוי/ים המבוקש/ים פרק בעלון מינון טקסט נוכחי טקסט חדש 3-11חודשים 6-2 :טיפות ,עד 4 פעמים מיום. 3-1שנים 12-4 :טיפות ,עד 4פעמים ביום. 6-4שנים 11-6 :טיפות ,עד 4פעמים ביום. 9-7שנים 22-11 :טיפות ,עד 4פעמים ביום. 12-11שנים 37-12 :טיפות ,עד 4 פעמים ביום. 14-13שנים 44-11 :טיפות ,עד 4 פעמים ביום. יש ליטול את המינון המתאים כפי שמופיע בטבלה מטה. יש ליטול התרופה במרווחי זמן של 6-8שעות. מומלץ לתת את המינון לפי משקל הילד בהתאם לטבלה. רק במקרה שלא ידוע משקל הילד -יקבע המינון על פי גיל הילד. אין ליטול מנה יותר מ 3-פעמים ב 24-שעות. הטיפות אינן מיועדות לתינוקות מתחת לגיל 3חודשים או במשקל נמוך מ 5-ק"ג. מבוגרים ומתבגרים מעל לגיל 15שנה (מעל משקל גוף של 53ק"ג): 21-22טיפות עד 4עד 3פעמים ביום . תינוקות וילדים: משקל גוף (ק"ג) 5-8 גיל 3 - 11 חודשים 1 - 3שנים 9 - 15 4 - 6שנים 16 - 23 7 - 9שנים 24 - 30 10 - 12שנים 31 - 45 13 - 14שנים 46 - 53 מבוגרים ומתבגרים מעל לגיל 12 שנה: מעל 23 מינון ( מס' טיפות) 2 -5טיפות עד 3 פעמים ביום 4 - 12טיפות עד 3 פעמים ביום 6 - 19טיפות עד 3 פעמים ביום 10 - 25טיפות עד 3פעמים ביום 12 - 37טיפות עד 3פעמים ביום 19 - 44טיפות עד 3פעמים ביום 22-21טיפות עד 3 פעמים ביום לצרכן – אופטלגין טבליות/קפליות בעלון לצרכן בעלון מינון מבוגרים ומתבגרים מעל לגיל 15שנה ומעלה: מבוגרים ומתבגרים מעל לגיל 15שנה: 2 - 1קפליות/טבליות ,עד 4פעמים ביום ,במרווחי זמן של 6- 2 - 1קפליות/טבליות ,עד 4פעמים ביום. 8שעות. אין ליטול יותר מ 8 -קפליות/טבליות ליום. הטבליות ו/או הקפליות אינן מיועדות בדרך אין ליטול יותר מ 8-קפליות/טבליות ליום. אין לעבור על המנה המומלצת. כלל לתינוקות ולילדים. הטבליות ו/או הקפליות אינן מיועדות בדרך כלל לתינוקות אין לעבור על המנה המומלצת. אם החום נמשך יותר מ 3-ימים או הכאבים ולילדים .להם ניתן לתת את התרופה בצורת טיפות. נמשכים יותר מ 11-ימים למרות השימוש אם החום נמשך יותר מ 3-ימים או הכאבים נמשכים יותר מ- 7 11ימים למרות השימוש בתרופה ,יש לפנות לרופא .הסיכון בתרופה ,יש לפנות לרופא. ל לאגרנולוציטוזיס עולה אם הטיפול נמשך מעבר ל7- ימים(.ראה/י סעיף תופעות לוואי). בקשישים ,או בחולים עם הרגשה כללית ירודה ,או בחולי כליה – יש להתייעץ עם הרופא .יתכן ויידרש מינון נמוך יותר של התרופה. יש להתייעץ עם הרופא או עם הרוקח אם הנך מרגיש/ה שההשפעת התרופה חלשה או חזקה מידי.