The Ecosystem Concept - Humanities and Social Studies Education

NAG 301:
SOIL AND VEGETATION ECOLOGY
DR. K. CHATTERJEA
What is Biogeography?
A study of the distribution of biological materials over the earth’s surface and the factors responsible for the observed spatial variations.
Source of energy : Solar radiation activates biospheric activities.
Central themes : usually drawn from the plant world.
-- a study of spatial relationships, distribution, and adaptations of various plant species and plant communities.
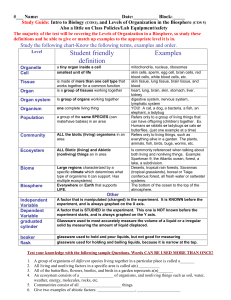
The ecosystem concept : includes both organic and inorganic parts of the biosphere.
Structure of ecosystems:
LIVING ORGANISMS
EXCHANGE OF MATERIALS
NON-LIVING
SUBSTANCES
Autotrophic (self-feeding) component:
Heterotrophic (other-feeding) component
1
Ecosystem’s basic components:
1) ABIOTIC substances
2) PRODUCERS
3) CONSUMERS
4) DECOMPOSERS
ENVIRONMENTAL VARIABLES :
The distribution of a species population is a function of its resource requirements for growth and reproduction and its ability to exploit available environmental resources.
Four interacting groups of factors directly/ indirectly affect vegetation:
1) Abiotic (Physical)
2) Biotic (excluding human)
3) Anthropogenic
4) Evolutionary
Abiotic: All plants and animals are directly/ indirectly dependent.
Two most important limiting factors: temperature and water. These provide the opportunities.
Soil controls the exploitation of such factors.
GAIA CONCEPT
The Gaia hypothesis assumes that the living world (the biosphere) and the global environment form A SINGLE INTERACTIVE SYSTEM. It serves to focus attention on the nature of the biosphere , the evolution and spatial variation of the diverse forms of life that occupy it and the implications of the increasing human impact on them.
Readings:
Pears, Nigel (1985), Basic Biogeography
Tivy, Joy, (1993), Biogeography nag301_ecosystem_introduction.doc
2