Luciana S. Amaral1, Taicia P. Fill1, Edson Rodrigues Filho1
advertisement

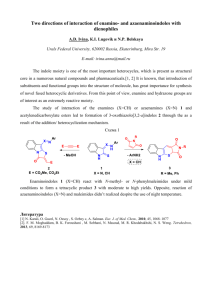
Sociedade Brasileira de Espectrometria de Massas – BrMASS Natural Products “Mass spectrometry as an important toll to study the influence of media composition in the cytochalasin´s production by endophytic fungus isolated from Cupressus lusitanica” Luciana S. Amaral1, Taicia P. Fill1, Edson Rodrigues Filho1 lu_samaral@yahoo.com.br, edson@dq.ufscar.br Laboratório de Bioquímica Micromolecular de Micro-organismos (LaBioMMi) – Departamento de Química - UFSCar The cytochalasins are a class of fungal metabolite well known for their distinctive biological activities [1]. Chemically, the cytochalasins are characterized by a highly substituted perhydroisoindol ring system which is turn linked to a C16-C18 polyketide ring system. The biosynthesis of cytochalasins involves the formation of an acetyl- and methionine-derived polyketide chain and the attachment of an amino acid such as phenylalanine, leucine, or tryptophan[2]. During our studies on the chemistry and biochemistry aspects of plant microorganism’s interactions, we isolated an unidentified endophytic fungus from leaves of Cupressus lusitanica which demonstrate a great ability to produce cytochalasins in Czapeck media enriched with yeast extract. We isolated and identificated the cytochalasin D (1), a mixture of cytochalasins C (2) and Q (3), and detected some others, which contain a phenylalanine moiety. The ESI-MS of cytochalasin D showed the ion [M+H]+ at m/z 508 and the MS/MS analyses of this was carried out in order to obtain diagnostic product ions. The CID of the m/z 508 generated ions at m/z 490, 448, 430, 412 and 120, due to losses of water, acetic acid, and the poliketide ring indicating the diagnostic ion related to phenylalanine moiety. It is known that media composition can have a great impact on the production of microbial products. Than, to verify the production of cytochalasins in this strain, we screened a panel of extracts prepared from 5 different media (Czapeck, and Czapeck supplemented with phenylalanie, tyrosine, alanine, tryptophan) and compared with the extract from Czepck media enriched with yeast extract. In order to verify the presence of the cytochalasins biosynthesized with the phenylalanine moiety in these different media, we employed the LC/MS/MS precursor ion experiment, using the diagnostic ion at m/z 120. The precursor ion at m/z 120 in the chromatogram showed the production of the cytochalasins with a phenylalanine moiety in all different media. However the media supplemented with phenylalanine showed more chromatographic peaks than the others. We conclude that the MS is a powerfull toll to study the influence of media composition on the fungal production of these secondary metabolites. OH (1) HN OH HN HN OOAc OH O (3) O (2) OOAc OH O OOAc OH O Referências [1] Feng, Y.; Blunt, J. W.; Cole, A. L. J.; Munro, M. H. G.; J. Mat. Prod. 2002, 65, 33 - 38. [2] Lin, Z.; Zhu, T.; Wei, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Gu, Q.; Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 3045-3051 3º Congresso BrMass – 12 a 15 de Dezembro de 2009