Introduction
advertisement

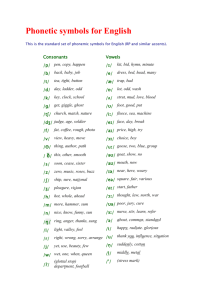
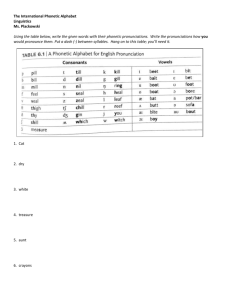
A Survey of Phonics & Phonetic Symbols On English Learning and Teaching 自然發音法與音標在英語教學之概述 Shu Yan Li Introduction Tracing back to our Chinese learning process ,we found that we listened and spoke it from age 1 to 6 . After 5 or 6 years of oral and listening acquisition ,we started to learn Chinese phonetic symbols , writing and reading . Then we could use it well .However , during junior high school ,we were forced to learn English alphabets, K.K. phonetic symbols ,spelling, reading and writing at beginning with few English inputs. That is why almost 40% learners fail to achieve English learning efficiency . From the experience of learning Chinese , we could find that pronunciation plays an important role on languages’ learning . Because it is the base of writing listening , and speaking. Phonics and phonetic symbols are not new tools for English learning in the U.S or in Taiwan, but how can they be fervently discussed in Taiwan? There are two reasons: one is English learning and teaching (E LT) scope lacks of consistent pronunciation teaching method. The second reason is, as EFL (English as foreign language) learners, we seems do not have thought them over with the learning problems before. Is there an easier approach to understand phonics and phonetic symbols? What is the simplest definition ? When is the appropriate time to teach and learn? How they are used in ELT? What are their functions in ELT ? These are the focus will be mentioned below. Definition Phonics is the knowledge about the letter-sound correspondence Relationship. “Phonics, which is the relationship between letters and their corresponding sounds, is very much a part of 1 learning how to read” (Lapp, 1997:696). As for teaching approach , “ Phonics instruction intended to help children to understand the fundamentally alphabetic nature of our writing system and, through that understanding, to internalize the correspondences between frequent spelling patterns and the speech patterns --- the words, syllables, and phonemes---- that those spelling represent” Adams, 1990). Thus, we knew that learners with the competence of spelling ,his concept of phonics must be completed and clear. Meanwhile, according to the basic ability, it is not hard to infer the easier language facility could be obtained. “Phonics method of teaching reading but is an essential ingredient of reading instruction” (Heilman,1985:17). Phonics aims to provide with a strategy for working out pronunciation of previously unseen words” (Stuart,1995:46). Phonetics symbols are set of symbols invented to transcribe the speech sounds by phoneticians to linguistic studies. They includes K.K. phonetic symbols (J.S. Kenyon and T. A. Knott) Knott), D.J. phonetic symbols and IPA (International Phonetic Alphabet).K.K. phonetic symbols are closer to IPA than to Webster's New World Dictionary (WNWD). IPA and K.K. phonetic symbols can not provide many clues of the spelling in the English words, but sometimes cause confusion to the learners. Taiwan, an EFL country, phonics as well as K.K. phonetic symbols are taken as two methods for teaching pronunciation. Application K.K. phonetic symbols has been widely used in Taiwan, such as mass media, textbooks and all kinds of exams for decades. The typical teaching method usually companies with the alphabets learning. “Phonetic symbols are taught in Taiwan for language learning’s sake, not for linguistic study.” (Hsu, 2000:21 ) Teaching English pronunciation through the phonetic symbols is a conventional teaching method in pronunciation teaching, through which the English sound and word pronunciation can be symbolized, and vise versa . Learners are asked to memorize all the symbols and spell words with practice in a short time. Usually they imitate the teacher’s pronunciation without efficient practice. Cause the schedule must be followed in school. Teachers don’t have much time to wait the learners who can not keep up with. But for well learners, like 2 “”Prof. H says, “K.K. phonetic symbols should act an assisting tool for language learning, because many adults, after a long period of language learning, can independently guess the pronunciation of a new word and need not check it up in the dictionary any more ”” (Hsu, 2000:51) Still phonetic symbols have their own values for the EFL learners. As far as the phonics, it has been used for a long period of time (more than ten years) in Taiwan. But there are no explicit or consistent guidelines for school teachers. At the beginning, it was conducted by cramming school for children English learning. Excellent effects could be found on these elementary students. Learners are taught to familiar with the rules that the combination of the alphabets how to pronounced with sufficient oral and listening inputs. “Teach children 44 sounds of English and how they are spelled. Then they can sound out each word from left to right and read it off the page” (Flesch, 1955: foreword). With the abounding inputs learners can know more words pronunciation and spelling by what they read and saw. “What effective readers do when they use the graphophonic cue system is (1)visually recognize known patterns of letters; (2) translate those patterns into the sounds they represent; and (3) blend the patterns together to see if it forms a sensible, recognizable word” (May, 1998:176). Learners can pronounce and spell well by practicing look-reading method from one- syllable to multi-syllable words. This approach follows the way of the native teaching method in the United States. According to the long-experienced observation, with the firm foundation of phonics about two years practice ; then to learn phonetic symbols, the complete English learning effects will be reached. When phonics collocate with phonetic symbols , learners can pronounce and listen words easily and correctly. If the long words they are not sure how to pronounce, they can rely on the K.K. phonetic symbols represented in the dictionary and sound it without wrongs. Through the process of consistent listening, spelling and reading training ,learners’ reading ability will be improved. The more vocabularies they knew, the more confidence they built . Thus, the long English learning journey can be keep going on . 3 Conclusion To practice continuously is the only simple way to facilitate the ability of spelling and pronunciation. As long as the learners own these basic competence , learning could start anytime ,anywhere ,with any topic. “Only through the real reading , the real learning begins.” Language is just a tool to help learners know more and communicate smoothly. With the definite way that teacher’s instruct, often learners get the most benefits from it. As ELF learners ,we have right to make some mistakes. Don’t be afraid but just try to speak it out bravely. Meanwhile, develop the persistent zeal and interest of learning, English would be a simple and easy stuff from now on. 【附錄一】字母音標發音 A B C D E F G H I R G K L M N O P Q S T U V W X Y Z S T U V W X Y Z 【附錄二】K.K.音標總表 單母音 母音 雙母音 無聲子音 有聲子音 子音 【附錄三】Phonics 發音規則略表 b bed bat book c cat can car d dog duck desk f fan fin fish g good girl green h hat happy hand 4 j k l m n p q r s t v w x y z jet king lap Mary net pen queen run sing top van win box yes zebra jar kick land Mom not pot quick rod song tin vine window fox you zero John cake look morning can up quit read stop take voice wind fax yet zerox Vowals 母音 a apple cat fan e pen bed jet i pin kick fish o pot box dog u duck umbrella up a...e name cake tale i...e bike kite tide o...e hole sole smoke u...e duke dispute mule Others 其他: 長母音(1) ea sea tea pea ee bee fee jeep ey key Jeffrey monkey 5 oo book cook oo (2) fool, cool pool, spool oa boat toad ai bait sailor ay pay say ou out loud ou touch enough ow cow bow ow low blow oi voice invoice oy toy joy Others 其他 (2) sh fish she ch chair church th thin thick th this there ng strong long pr pray proud br bring brown fl fly floor gl glad glamour ar bar jar er teacher firefighter ir girl bird or work humor ur blur fur air hair chair all wall ball old cold bold took spoon oak paid stay shout tough down row void annoy ship bench thirty those lung spring breed fleed glare tar smaller sir favor turkey pair small told 6 ing sing thinking understanding From自然發音教學淺談 文/Euchi Tai References 1.Yu, M.H..(1998). A Study of pre-service teacher-training programs for the teaching of English to children. Master thesis. Taipei: National Taiwan Normal University. 2.John Shefelbine, Scholastic Phonics Teacher’s Guide Level A,B,C, 2001 , California State University at Sacramento story Editor 3.Victoria Fromkin & Robert Rodman ,An Introduction to Language, Sixth Edition . Harcourt 4.Adams, M. J. (1990). Beginning to Read-- Thinking and learning about print.MA: MIT. 5.Adams, M.J. (1991). Beginning to Read: A critique by literacy professionals and a response by Marilyn Jager Adams. The Reading Teacher, 44(6), 370-95. 6.Flesch, R. (1955). Why Johnny can't read---And what you can do about it. New York: Harper &Row Publisher. 7.Flesch, R. (1983). Why Johnny stillcan’t read. New York: Harper &Row Publisher. 8.Funnell, E. & Stuart, M. (1995). Learning to read: Psychology in the classroom. Oxford: Blackwell. 9.Heilman, A. W. (1985). (5th Ed.) Phonics in proper perspective. Columbus: Merrill. 10.Hung, Shu-kui. (1998). A Comparison of two methods, K.K. phonetic symbols and phonics, in teaching English to children. Master thesis. National Kaohsiung Normal University. 11.Lapp, D., & Flood, J. (1997). Where is the phonics? Making the case (again) for integrated code instruction. The Reading Teacher, 10(5),696-700. 12.May, F. B. (1998). (5th Ed.) Reading as communication -- To help children write and read. NJ: Prentice Hall. 13.Chen, Tsai-er. (1998). The Teaching of English Pronunciation in Taiwan: A Review. The Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on English 14.Hsu, L S,(2000) . A Study on Phonics and Phonetic Symbols in ELT: National Taiwan Normal University 15.The Complete Book of Phonics. 1997. American Education Publishing 16.Practical English Readers Book One。1949。正中書局。 17.Practical English Readers Book Two。1949。正中書局。 18.Steven Pinker, The language instinct: how the mind creates language. HarperPereninial Publisher 中文參考資料 1.依筱雯。1997。Ears And Mouth 自然發音書。台北:敦煌書局。 2.林素娥、謝靜惠。1998。Learning To Read With Phonics 英語字母拼讀法。東西圖書。 3.Chou, Ch. T. (2000) 周中天。學Phonics 等於學好發音嗎?Cave English Teaching。24 期別冊,(14-15)。 7 4.Shen, Hs. Ch. (1993) 沈秀娟。如何用PHONICS 教單字— 以聲音為基礎的發音教學法。 5.Cave English Teaching,創刊號,(18-19)。 6.Yi, Hs. W.(1997) 依筱雯。字母拼讀法的運用。台北:敦煌。 7.Shih, Y. H. (2000) 施玉惠。發音不等於發「音」 。Cave English Teaching,24期別冊,(14-15)。 8.Hu, Ch. F. (1999) 胡潔芳。如何協助孩童發展英語音韻覺識。英語教學,23(3),(7-21)。 9.Chang, P. Y. (1993) 張寶燕。近數十年來英語發音教學理論與實際的簡介。英語教學, 18(2),(10-15)。 10.Mo, Ch. W. (1994) 莫君文。當KK 遇上PHONICS。Cave English Teaching,3 期,(14-15)。 11.Huang, Z. L. (1999) 黃自來。Phonics Instruction and Word Recognition 12.Huang, Ts. L. (1994) 黃翠蘭。KK 音標的基礎評量。Cave English Teaching 3 期, (15-16)。 13.Liou, M.L. & Chen, Ch. L. (1999) 廖美玲、陳秋蘭。嶄新而實用的英語教學﹍國小國中英 語教學指引。台北:敦煌。 14.Hsieh, Ch. Sh. (1997) 謝欽舜。暢談發音教學。Teaching Pronunciation。 15.台北:師德。 16.劉慶剛. 淺談Phonics 與英文發音 English Works 第4期,東西圖書 17.Jack Diao How to teach Phonics? English Works 第4期,東西圖書 18.李秀玲 打穩根基的第一年 Phonics教學. English Works 第4期,東西圖書 (21-23 ) 19.張芳琪,劉淑芬 Phonemic Awareness English Works 第11期,東西圖書(10-32) 8