Year 2 Teaching Sequence xxx
advertisement

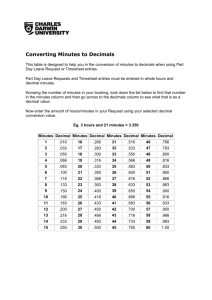
Year 5 Teaching Sequence Spring 2 – Ordering and rounding decimals (two days) Prerequisites: Understand decimal notation for tenths and hundredths in context e.g. length, converting 125cm to m (see Year 4 spring teaching sequence 1 and oral and mental starter bank 2) Recognise the equivalence between tenths written as vulgar fractions (1/10) and decimal fractions (0.1), and between hundredths written as vulgar and decimal fractions (see Year 5 spring teaching sequence 10 and oral and mental starter bank 2) Round three-digit numbers to the nearest 100 (see oral and mental starter bank 2) Overview of progression: Children place numbers with one decimal place on a number line, then do the same for numbers with two decimal places. They use this experience to order a mixed set of numbers with one or two decimal places. Numbers with one or two decimal places are rounded to the nearest whole number, and the reasons for doing so discussed. Note that children should be able to use their knowledge of placing two-digit numbers on a 0-100 line to place decimals with two places between neighbouring whole numbers. Watch out for children who think that 1.75 is greater than 1.8 because 75 is more than 8. Watch out for children who write 0.3 as 0.30 - they correctly see this as equivalent to 30 hundredths but incorrectly add a zero as we do in money, e.g. £0.30. © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y5 Maths TS2 – Spr – 2days Objectives: Order numbers with one and two decimal places and place them on a number line Round a number with one or two decimal places to the nearest whole number Whole class Group activities Paired/indiv practice Resources Show chn a 100 bead bar and say that one end represents 0 and the other 1. Each bead represents one hundredth. How can we write this? Write 1/100 and 0.01 on the board. What does each group of ten beads represent? Talk to your partner. How can we write this? Write 10/100, 1/10 and 0.1 on the board. Ask chn to come up and hang tags to show 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, and 0.9. See how 0.5 comes half way along the beads. What’s another way to write 0.5? What number comes half way between 0.2 and 0.3? Write 0.25 on a tag and hang it after the 25th bead. What does the 2 in 0.25 represent? And the 5? Write down two other numbers that come between 0.2 and 0.3. Show a counting stick and say that one end presents 0 and the other 1. Point to 0.35. What number goes here? And here? (Pointing to 0.75, then 0.49 and 0.51). Now say that one end represents 2 and the other 3. Count from 2 to 3 in steps of 0.1. Point to 2.2 and 2.3. Write three numbers on your whiteboards that go between 2.3 and 2.4. Choose three whiteboards showing different numbers and ask children to help you to put them in order. Group of 4-5 children Sketch a line from 0 to 1 on the flipchart. Mark but do not label where 0.63 comes to. I’m thinking of a number on this line. You can suggest a number and I will tell you whether my number is more or less than that number. Take several numbers and say whether the number you are thinking of is more or less. You can now ask me to mark on two different tenths, e.g. 0.1 and 0.2 to help you to guess my number. Which tenths do you think would be useful? Mark on the tenths they suggest (e.g. 0.6 and 0.7). Children continue to suggest numbers and you say where the secret number is more or less until they guess it. Repeat. Easier: Mark on 0.5 to begin with, and suggest neighbouring tenths if necessary. Harder: Ask a pair of children to take your place in thinking of a number the second time you play the game. Ask chn to place numbers with two decimal places on number lines, which are ‘empty’ between neighbouring whole numbers (see resources). They then order a set of given decimals. Easier: Children’s lines have tenths marked (but not labelled). 100 bead bar and wipeon/wipe-off tags (or pieces of card and paperclips) (perhaps borrowed from a year 2 or 3 teacher) or use ITP Ordering numbers, choosing 100 beads Counting stick Activity sheets (see resources) © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y5 Maths TS2 – Spr – 2days Show chn a counting stick and say that one end represents 2 and the other 3. Count from 2 to 3 in steps of 0.1. Point to 2.3. Is 2.3 nearer to 2 or 3? So if we are rounding to the nearest whole number 2.3 rounds to 2. What other numbers with one decimal place might round to 2? Point to 2.7. Is 2.7 nearer to 2 or 3? So 2.7 rounds to 3. Write another number with one decimal place that rounds to 3 on your whiteboards. Point to 2.5. What about this number? What multiple of 10 would you round 25 to? 30. So we round 2.5 up to 3. Point to 2.2 and 2.3. Write a number on your whiteboards that goes between 2.3 and 2.4. You've written different numbers but which whole number is closest to all of them? So they all round to 2. Think of another number with two decimal places that will round to 2. Point to 2.8 and 2.9 and repeat. Which whole number do all your numbers round to? Write another number with two decimal places that will round to 3. Can you think of a number greater than 3 with two decimal places that will round down to 3? Later this term we learn to add numbers with decimal places, and rounding will help us to make an estimate. Write 2.23 + 5.89 on the board. What do you think the answer will be to the nearest whole number? How did you work that out? Sometimes we don’t round to the nearest whole number, but round up. For Group of 4-5 children Draw a three by two grid on your whiteboards, and write six numbers between 0 and 10 with one decimal place. Ring a number if it rounds to 5. Which numbers have you rung? Which are rounded down, and which rounded up? Ring a number if it rounds to 9. Repeat until a child has rung six numbers. Repeat, this time asking children to write down six numbers between 0 and 10 with two decimal places. Easier: Children mark their six numbers on a 0-10 line (see resources) rather than writing them on a grid. Chn mark on numbers with one and two decimal places on blank number lines and round each to the nearest whole number (see resources). Easier: Children’s number lines have tenths marked (but not labelled). Harder: If children work well, ask them to choose four numbers with two decimal places to round to the nearest tenth. © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Counting stick 0-10 number line with tenths marked Activity sheets (see resources) Y5 Maths TS2 – Spr – 2days example, If I’m buying material for some new curtains, and have worked out that I need a length of 3.2 metres to make my curtains, it wouldn't be very helpful if I only bought 3 metres of material! My curtains would be too short! If the shop sold material only by the metre, I’d have to buy 4 metres and have some left. Perhaps I could make matching cushion covers! © Original teaching sequence copyright Hamilton Trust, who give permission for it to be adapted as wished by individual users. Y5 Maths TS2 – Spr – 2days