Math Unit 2 gr 5 whole numbers
advertisement

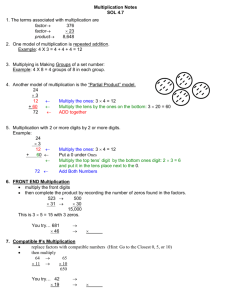
Unit 2 Whole Numbers – grade 5, Learning Goals 1. Recognize and read numbers from 1 to 999 999 2. Read and write numbers in standard form, expanded form, and written form 3. Compare and order numbers 4. Use place value to represent numbers 5. Recall basic multiplication and division facts 6. Count by 11s and 12s 7. Estimate sums, differences, products, and quotients 8. Add, subtract, and multiply numbers mentally 9. Add and subtract 4-digit numbers 10. Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number 11. Divide a 4-digit number by a 1-digit number 12. Pose and solve problems using whole numbers 13. Solve problems with more than one step. 14. Use patterns in a table to make predictions p.26 Whole Numbers Key Words (5TB27) Compensation= Adding an amount to one term that you subtract from another. 27 + 53 = (27 + 3) + (53 – 3) = 30 + 50 = 80 Dividend = the number to be divided. In the division sentence 77 divided by 11 = 7, the divident is 77. Divisor = the number by which another number is divided. In the division sentence 77 divided by 11 = 7, the divisor is 11. Quotient = the number obtained by dividing one number into another. In the division sentence 77 divided by 11 = 7, the quotient is 7. Compatible numbers = pairs of numbers you can easily divide mentally Lesson 1 – Representing, Comparing, and Ordering Numbers Standard Form = 4027 Words = four thousand twenty-seven Expanded form = 4000+ 20 + 7 Base ten blocks = 4 cubes 10x10 2 sticks 1x10 7 single blocks Place-Value Chart Thousands hundreds tens ones 4 0 2 7 NOTE: When we write numbers with more than 4 digits in standard form, we put a space between the hundreds digit and the thousand digits. Lesson 2 – Using Mental Math to Add (5TB31) Strategy: I estimate when I don’t need an exact answer. (4 ways below!!!) 1. Use front-end estimation. Add the first digits of the numbers (3438 + 4279 is about 3000 + 4000, or 7000) 2. For a better estimate, round each number to the nearest hundred. 3438 rounded to the nearest hundred is 3400 4279 rounded to the nearest hundred is 4300 3400+ 4300 = 7700 3438 + 4279 is about 7700 3. Use compensation 2180 + 6432 =--? 2180 + 20 = 2200 6432 – 20 = 6412 The sum of 2200 + 6412 is equal to the sum of 2189 + 6432. 2200 + 6412 = 8612 Thus 2180 + 6432 = 8612 To compensate, I took 20 away from one number and added 20 to the other one! 4. Use the strategy of adding-on 2625 + 432 Start with the greater number, 2625 There are four hundreds to add -> 2725 2825 2925 3025 There are 3 tens to add, count on by 10 three times 3025, 3035, 3045, 3055 Then add 2 3055 + 2 = 3057 Your answer 2625 + 432 = 3057 Lesson 3 – Adding 3- and 4-digit Numbers (5TB34) Use Base Ten Blocks on a place-value mat to add. 10 ones can be traded for 1 ten! 10 hundreds can be traded for 1 thousand. Use expanded form to add 738 + 1 452 700 + 30 + 8 1000 + 400 + 50 + 2 1000 + 1100 + 80 + 10 =2100 + 90 = 2190 Use place value to add (see book p. 35 for an example) Lesson 4 – (5TB37) Adding Three Numbers 2 strategies: 1. Add 2 numbers first, then add the third one to the sum of the 2 first ones 2. Use place value to add (p. 38) NOTE: Estimate to check the answer is reasonable! Lesson 5 –Using Mental Math to Subtract (5TB41) 3 strategies: 1. Round each number to the nearest hundred and then subtract 2. Make a friendly number 3. Think of the number in expanded form. Subtract each number in turn. Lesson 6 –Subtracting with 4digit numbers (5TB44) 3 strategies: 1. Use Base 10 Blocks on a place-value mat to subtract 2. Use place value to subtract (p. 45) NOTE: Estimate to check the answer is reasonable! Lesson 7 – Multiplication and Division Facts to 144 (5TB47) Most multiplication facts have: One related multiplication fact (8x8=64 64:8=8) Two related multiplication facts 9 x 8 = 72 8 x 9 – 72 72/9 = 8 72/8=9 Factors are numbers you multiply to get a product. 9 and 8 are factors of 72. 2 Strategies to help you multiply: 1. Use known facts to multiply. To find 12 x 8, you use 10 x 8 (80) and 2 x 8 (16) and then you add the 2 (80 +16 = 96 2. Use patterns to remember multiplication facts with 11. A strategy to help you divide: Use related multiplication facts to find the quotient. To find 77/11 think 11 times which number is 77? You know 11 x 7 = 77, so 77/11= 7 The divisor is 11. The dividend is 77. The quotient is 7. Lesson 8 – Multiplying with Multiples of 10 (5TB52) Every multiple of 10 has 10 as a factor. These are multiples of 10 100 1000 30 300 3000 Do you remember??? Factors are numbers you multiply to get a product. 9 and 8 are factors of 72. 1. Use place value to multiply by 10, 100, and 1000. (p. 53) When you multiply a whole number by 10, the digits move 1 place to the left. When you multiply a whole number by 100, the digits move 2 places to the left. When you multiply a whole number by 1 000, the digits move 3 places to the left. 2. Use basic facdts and place-value patterns to multiply by 10, 100, and 1000. (p. 53) When you multiply a whole number by a multiple of 100, the digits in the product of the related basic fact move 2 places to the left. When you multiply a whole number by a multiple of 1 000, the digits in the product of the related basic fact move 3 places to the left. Lesson 9 – Using Mental Math to Multiply (5TB55) Lesson 10 – Multiplying 2-digit Numbers (5TB58) Tools: base ten blocks/ grid paper Lesson 11 – Estimating quotients (5TB61) Estimate. Look for compatible numbers. Compatible Numbers are pairs of numbers you can divide mentally. Estimate. Use front-end estimation. Find out how many digits the quotient will have. Break the number into 2 numbers you can easily divide by the number you are dividing into (336 divided by 4, think 336= 320 + 16, since it is easier to divide both 320 and 16 by 4) Lesson 12 – Dividing with Whole Numbers (5TB64) Think multiplication (inverse operation) Use place value Use short division Lesson 13 – Solving Problems (with more than 1 step!) (5TB68) Lesson 14 - Strategies Toolkit Strategies Make a table Use a model Draw a diagram Solve a simpler problem Work backward Guess and check Make an organized list Use a pattern Draw a graph Use logical reasoning (5TB72) Unit 2 – Show what you know! 5TB74 Unit Problem – On the Dairy Farm (5TB76) Check List: Your work should show: That you can choose the correct operation to solve problems All calculations in detail A challenging story problem using whole numbers A clear explanation of how you solved your story problem