perception freud
advertisement
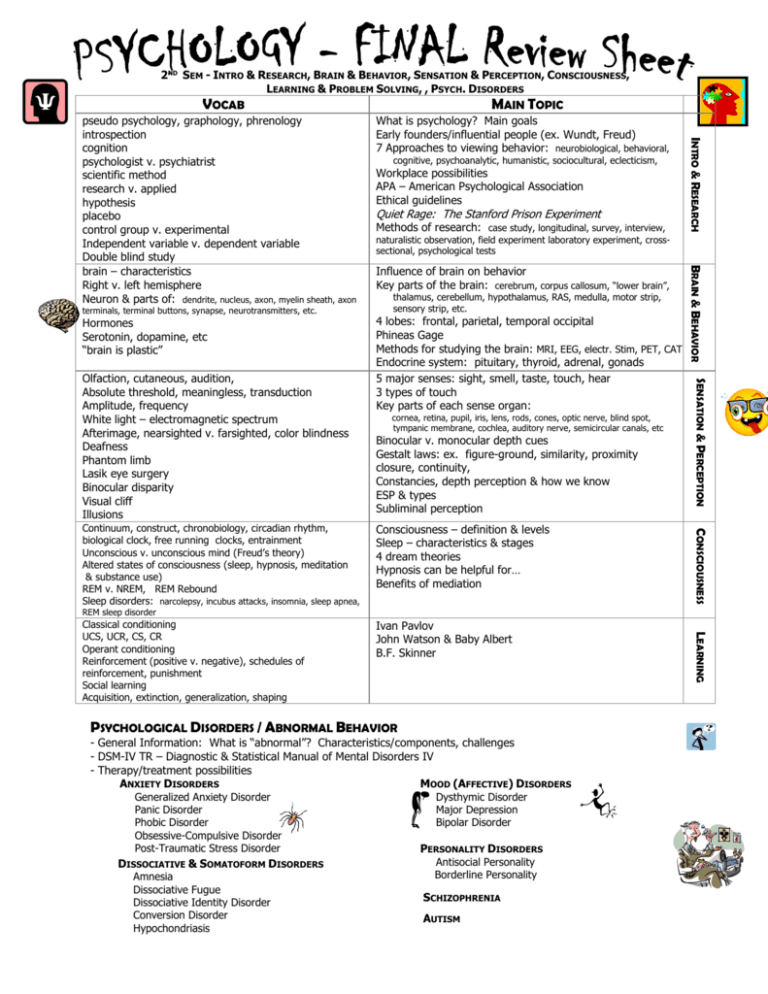
2ND SEM - INTRO & RESEARCH, BRAIN & BEHAVIOR, SENSATION & PERCEPTION, CONSCIOUSNESS, LEARNING & PROBLEM SOLVING, , PSYCH. DISORDERS VOCAB Hormones Serotonin, dopamine, etc “brain is plastic” Methods of research: case study, longitudinal, survey, interview, naturalistic observation, field experiment laboratory experiment, crosssectional, psychological tests Influence of brain on behavior Key parts of the brain: cerebrum, corpus callosum, “lower brain”, thalamus, cerebellum, hypothalamus, RAS, medulla, motor strip, sensory strip, etc. 4 lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal occipital Phineas Gage Methods for studying the brain: MRI, EEG, electr. Stim, PET, CAT Endocrine system: pituitary, thyroid, adrenal, gonads 5 major senses: sight, smell, taste, touch, hear 3 types of touch Key parts of each sense organ: cornea, retina, pupil, iris, lens, rods, cones, optic nerve, blind spot, tympanic membrane, cochlea, auditory nerve, semicircular canals, etc Binocular v. monocular depth cues Gestalt laws: ex. figure-ground, similarity, proximity closure, continuity, Constancies, depth perception & how we know ESP & types Subliminal perception Consciousness – definition & levels Sleep – characteristics & stages 4 dream theories Hypnosis can be helpful for… Benefits of mediation CONSCIOUSNESS Continuum, construct, chronobiology, circadian rhythm, biological clock, free running clocks, entrainment Unconscious v. unconscious mind (Freud’s theory) Altered states of consciousness (sleep, hypnosis, meditation & substance use) REM v. NREM, REM Rebound Sleep disorders: narcolepsy, incubus attacks, insomnia, sleep apnea, Quiet Rage: The Stanford Prison Experiment SENSATION & PERCEPTION Olfaction, cutaneous, audition, Absolute threshold, meaningless, transduction Amplitude, frequency White light – electromagnetic spectrum Afterimage, nearsighted v. farsighted, color blindness Deafness Phantom limb Lasik eye surgery Binocular disparity Visual cliff Illusions cognitive, psychoanalytic, humanistic, sociocultural, eclecticism, Workplace possibilities APA – American Psychological Association Ethical guidelines BRAIN & BEHAVIOR terminals, terminal buttons, synapse, neurotransmitters, etc. MAIN TOPIC What is psychology? Main goals Early founders/influential people (ex. Wundt, Freud) 7 Approaches to viewing behavior: neurobiological, behavioral, INTRO & RESEARCH pseudo psychology, graphology, phrenology introspection cognition psychologist v. psychiatrist scientific method research v. applied hypothesis placebo control group v. experimental Independent variable v. dependent variable Double blind study brain – characteristics Right v. left hemisphere Neuron & parts of: dendrite, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, axon REM sleep disorder Ivan Pavlov John Watson & Baby Albert B.F. Skinner PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDERS / ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR - General Information: What is “abnormal”? Characteristics/components, challenges - DSM-IV TR – Diagnostic & Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders IV - Therapy/treatment possibilities ANXIETY DISORDERS MOOD (AFFECTIVE) DISORDERS Generalized Anxiety Disorder Panic Disorder Phobic Disorder Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder DISSOCIATIVE & SOMATOFORM DISORDERS Amnesia Dissociative Fugue Dissociative Identity Disorder Conversion Disorder Hypochondriasis Dysthymic Disorder Major Depression Bipolar Disorder PERSONALITY DISORDERS Antisocial Personality Borderline Personality SCHIZOPHRENIA AUTISM LEARNING Classical conditioning UCS, UCR, CS, CR Operant conditioning Reinforcement (positive v. negative), schedules of reinforcement, punishment Social learning Acquisition, extinction, generalization, shaping