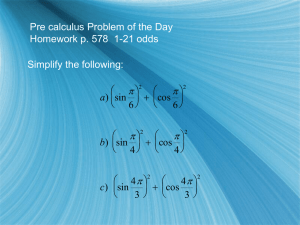
arcsin(x) = arctan(x/√(
advertisement

How to Solve Any Math By Hand and Some Algebra Everything on these pages are in radian mode. page 1 Floyd Nelson August 31, 2009 sin-1(x) is pronounced sine inverse of x. arcsin(x) or asin(x) is one of the infinite number of answers from sin-1(x). sinh(x) is pronounced hyperbolic sine of x. ln(x) stands for log natural of x. sign(7) = 1 sign(0) = sign(0) sign(-7) = -1 Degrees = π*Radians/180 = 10*Gradients/9 e ≈ 2.7182818284590452354 e ≈10.101101111110000101010001 Binary Code π ≈ 3.14159265358979323846264338327950288419716939937511 = 4*atan(1) π ≈ 11.00100100001111110110101 Binary Code cos(θ) = x/r = 1/sec(θ) = arcsin(x) = arctan(x/√(-x2+1)) cot(θ)/csc(θ) = sin(θ)/tan(θ) = 2 arccos(x) = arctan(x/√(-x +1))+π/2 sin(θ)*cot(θ) arcsec(x) = arctan(x/√(x2-1))+sign(sign(x)-1)*π/2 sin(θ) = y/r = 1/csc(θ) = arccsc(x) = arctan(x/√(x2-1))+sign(x)-1)*π/2 tan(θ)/sec(θ) = cos(θ)/cot(θ) = arccot(x) = arctan(x)+π/2 cos(θ)*tan(θ) sinh(x) = (ex-e-x)/2 = (ex-1/ex)/2 = (e2x+1)/(2*ex) = ex/2-1/(2*ex) tan(θ) = y/x = 1/cot(θ) = cosh(x) = (ex+e-x)/2 = (e2x+1)/(2*ex) = ex/2+1/(2*ex) sin(θ)/cos(θ) = sec(θ)*sin(θ) x -x x -x 2x 2x 2x tanh(x) = (e -e )/(e +e ) = (e -1)/( e +1) = 1-2/( e +1) sech(x) = 2/(ex+e-x) = 2/(ex+1/ex) sec(θ) = r/x = 1/cos(θ) = csc(θ)/cot(θ) = tan(θ)/sin(θ) = csch(x) = 2/(ex-e-x) = 2/(ex-1/ex) sec(θ)*cot(θ) -x x -x 2*x coth(x) = (e /(e -e ))*2+1 = 2/(e -1)+1 arcsinh(x) = ln(x/√(x2+1)) csc(θ) = r/y = 1/sin(θ) = sec(θ)/tan(θ) = cot(θ)/cos(θ) = arccosh(x) = ln(x+√(x2-1)) csc(θ)*tan(θ) 2 arctanh(x) = ln((1+x)/(1-x))/2 = (ln(1+x)-ln(1-x))/2 = ln(1-x )/2 arccsch(x) = ln(sign(x)*√(x2+1)+1)/x cot(θ) = x/y = 1/tan(θ) = 2 cos(θ)/sin(θ) = csc(θ)*cos(θ) arcsech(x) = ln(√(-x +1)+1)/x 2 arccoth(x) = ln((x+1)/(x-1))/2 = (ln(x+1)-ln(x-1))/2 = ln(x -1)/2 function continuous equation calculus equation domain of x sin(x) x-x3/3!+x5/5!-x7/7!+... ∑((-1)nx2n+1/(2n+1)!,n=0,∞) all real x cos(x) 1-x /2!+x /4!-x /6!+... ∑((-1) x /(2n)!,n=0,∞) all real x arctan(x) x-x3/3+x5/5-x7/7+... ∑((-1)nx2n+1/(2n+1),n=0,∞) -1<x≤1 ex 1+x/1!+x2/2!+x3/3!+x4/4!+... ∑(xn/n!,n=0,∞) all real x 2 4 2 3 6 4 ln(1+x) x-x /2+x /3-x /4+... π 4*(1/1-1/3+1/5-1/7+1/9-...) For ln(x+1) = ln(a) and -1<x≤1, if a≤0 then x = unidentified if 0<a≤1 then x = a-1 if 1<a then x = error sin(-x) = -sin(x) cos(-x) = cos(x) tan(-x) = -tan(x) csc(-x) = -csc(x) sec(-x) = sec(x) cot(-x) = -cot(x) ((-1)x/π+(-1)-x/π)/2 = cos(x) ((-1)x/π+(-1)-x/π)/(2i) = sin(x) atan(-x) = -atan(x) atan(|x|) = 90°-atan(1/|x|) n 2n ∑((-1) n+1 *x /n,n=1,∞) n -1<x≤1 4*∑((-1)n/(2*n+1),n=0,∞) For -ln(x+1) = ln(a) and -1<x≤1, if a≤0 then x = unidentified if 0<a then x = (1/a)-1 cos(θ) = cos(360°-θ) = cos(θ±360°) = cos(-θ) = sin(90°-θ) sin(θ) = sin(360°-θ) = sin(θ±360°) = sin(180°-θ) = cos(90°-θ) tan(θ) = tan(θ±180°) = cot(±90°-θ) sec(θ) = sec(360°-θ) = sec(θ±360°) = sec(-θ) = csc(90°-θ) csc(θ) = csc(360°-θ) = csc(θ±360°) = csc(180°-θ) = sec(90°-θ) cot(θ) = cot(θ±180°) = tan(±90°-θ) How to Solve Any Math By Hand and Some Algebra Everything on these pages are in radian mode. ∏(n,n=1,x) = x! x decimal x! 0 1 1 1 2 2 3 6 4 24 5 120 6 720 7 5040 8 40320 9 362880 10 3628800 11 39916800 12 479001600 13 6227020800 14 87178291200 15 1307674368000 16 20922789888000 17 355687428096000 18 6402373705728000 19 121645100408832000 20 2432902008176640000 page 2 8! = 1*2*3*4*5*6*7*8 binary x! Floyd Nelson August 31, 2009 0! = 1 1 1 10 110 11000 1111000 1011010000 1001110110000 1001110110000000 1011000100110000000 1101110101111100000000 10011000010001010100000000 11100100011001111110000000000 101110011001010001100110000000000 1010001001100001110110010100000000000 10011000001110111011101110101100000000000 100110000011101110111011101011000000000000000 1010000110111111011101110110011011000000000000000 10110101111101110110011001010011100110000000000000000 110110000001010111001001100000110100010010000000000000000 10000111000011011001110111110010000010101101000000000000000000 nPr(x,y) = x!/(x-y)! nCr(x,y) = nPr(x,y)/y! = x!/((x-y)!*y!) aloga(a)*b = ab logb(a) = ln(a)/ln(b) √(a*b) = √(a)* √(b) √(12) = √(4*3) = √(4)*√(3) = 2*√(3) ba=c ↔ a√(c)=b ↔ logb(c)=a 1/logb(a) = loga(b) -logb(a) = logb(1/a) = log1/b(a) loga(b) = logc(b)/logc(a) loga(b) + loga(c) = loga(b*c) loga(b) - loga(c) = loga(b/c) loga(bc) = c*loga(b) loge(a) = ln(a) 1/√(a) = √(a)/a a/√(a) = √(a) b/c c b -1 √(a*b) = √(a)*√(b) √(a/b) = √(a)/√(b) a = √(a ) a = 1/a a-b = 1/ab b c b+c b c b-c b d f b*f d*f b d f b*f d*f a *a = a a /a = a (a *c ) = a *c (a /c ) = a /c a1/b+c = b√(a)*ac ↑ Algebra ↑ ab+c = ab ac a0.5 = √(a) a0.25 = √(√(a)) a0.125 = √(√(√(a))) a0.0625 = √(√(√(√(a)))) 1/2 1/4 1/8 a1/b+c = b√(a)*ac a = √(a) a = √(√(a)) a = √(√(√(a))) a1/16 = √(√(√(√(a)))) In binary code: a0.1 = √(a) a0.01 = √(√(a)) a0.001 = √(√(√(a))) a0.0001 = √(√(√(√(a)))) 2*2*2*2 16 √(√(√(√(a)))) = √(a) = √(a) Here are examples of how to solve for fractional exponents by hand: a5 = a*a*a*a*a a5.78125 = a5*a0.78125 = a5*a0.5+0.28125 = a5*√(a)*a0.28125 = a5*√(a)*a.25+0.03125 = a5*√(a)*√(√(a))*a0.03125 = a5*√(a)*√(√(a))*√(√(√(√(a)))) In binary code a11.110101 = a*a*a*√(a)*√(√(a))*√(√(√(√(a))))*√(√(√(√(√(√(a)))))) To solve a√(b) by hand, use the formula b1/a. How to solve exponents by hand is shown above. There is an algorithm (method) to solve square roots by hand as shown on the next page. How to Solve Any Math By Hand and Some Algebra Everything on these pages are in radian mode. Floyd Nelson August 31, 2009 page 3 This shows how to find the square root of 28594.81 in decimal code. Each maximum x integer found is a part of the answer to the square root. The x in x2 has already been solved for. The other x’s have to be solved for. Each x integer, besides the first, is written in three places. 1 6 9. 1 √ 2 85 94. 81 x2 ≤ 2 12 = -1 ↓ ↓ ↓ 1 85 ↓ ↓ 2*10*x ≤ 185 2*10*6 = -1 20 ↓ ↓ 65 ↓ ↓ x2 62 = -36 ↓ ↓ 29 94 ↓ 2*160*x ≤ 2994 2*160*9 = -28 80 ↓ 1 14 ↓ x2 92 = -81 ↓ 33 81 2*1690*x ≤ 3381 2*1690*1 = -33 80 01 x2 12 = -1 0 To find the square root of 456872.651, organize the digits like this: 45 68 72. 65 10 This shows a simplified way of how to solve square roots in binary code. Arithmetic is always the easiest and most simplified when done in binary code. The red/blue numbers are crossed out if they are larger than the black number above them. If that is the case do not subtract and place a 0 for the answer of the square root, otherwise, if the numbers are capable of subtracting, place a 1 in the answer column, do not cross out the red/blue number, and subtract. 1 √10 - 01 1 - 1 1 01 ↓ 01 01 0 -11 -11 0 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 0 0 -11 -1 0. 11. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 11 01 11 00 11 10 11 -11 -1 0 10 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 10 01 10 00 10 00 1 10 1 -11 1 -1 0 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 00 00 11 00 11 00 11 10 1 -11 1 -1 1 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 11 01 11 00 11 00 10 00 10 10 -11 0 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 00 10 00 01 10 00 10 00 10 00 0 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 00 00 11 10 11 01 10 00 1 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 11 01 11 00 10 10 0 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 00 10 01 01 1 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 11 01 0 00 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 00 01 How to Solve Any Math By Hand and Some Algebra Everything on these pages are in radian mode. Decimal Base 10 Binary Base 2 Hexadecimal Base 16 .0078125 .015625 .03125 .0625 .125 .25 .5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 .0000001 .000001 .00001 .0001 .001 .01 .1 0 1 10 11 100 101 110 111 1000 1001 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110 1111 10000 10001 10010 10011 10100 .02 .04 .08 .1 .2 .4 .8 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F 10 11 12 13 14 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 10101 10110 10111 11000 11001 11010 11011 11100 11101 11110 11111 100000 100001 15 16 17 18 19 1A 1B 1C 1D 1E 1F 20 21 123589 11110001011000101 1E2C5 Floyd Nelson August 31, 2009 page 4 t Carry A B Carry+A+B = Z t Barrow A B Barr+A-B = Z 7 -1 1 0 0 7 1 0 0 1 6 0 1 1 0 6 -1 0 1 0 5 -1 0 0 1 5 0 1 0 1 4 1 0 0 1 4 0 0 1 1 3 1 0 1 0 3 -1 1 0 0 2 1 1 1 1 2 -1 1 1 1 312 = 28+25+24+23 = Binary: 100111000 985 = 3*162+13*161+9*160 = Hexadecimal: 3D9 Binary: 1101 0011 0101 1001 = Hexadecimal: D359 D 3 5 9 51042 = 5*104+103+4*101+2*100 Binary Subtraction Help for each digit of A-B=Z: Key: Barrowt + At - Bt = (Barrowt+1/2)+ Zt If the Barrow output is -2, then the next Barrow input is -1, because the next digit is 2* the value of the current digit. 0+0-0 = 0+0 0+0-1 = -2+1 0+1-0 = 0+1 0+1-1 = 0+0 -1+0-0 = -2+1 -1+0-1 = -2+0 -1+1-0 = 0+0 -1+1-1 = -2+0 Golden Ratio: 1/x = x-1 ≡ x = (1±√(5))/2 ≈ 1.618033988749895 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 How to Solve Any Math By Hand and Some Algebra Everything on these pages are in radian mode. Wikipedia page 5 Floyd Nelson August 31, 2009