Cell Theory Timeline Cards and Facts 2012
advertisement

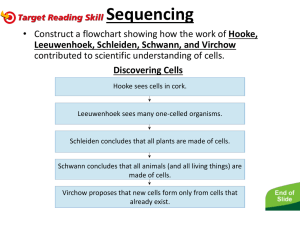
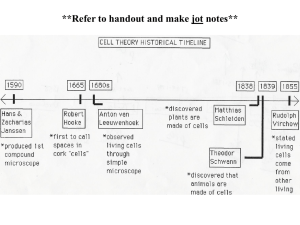
Robert Brown Botanist (1773-1858) In 1831, Robert Brown named the cell nucleus. Robert Hooke Philosopher and Architect (1635-1703) In 1665, Robert Hooke named the cell as the basic component of living organisms. Anton van Leeuwenhoek Microbiologist (1632-1723) The Father of Microbiology Anton van Leeuwenhoek improved the microscope and was the first to observe and describe single celled organisms in 1676. He originally called them animalcules! We now call them microorganisms. Theodor Schwann Physiologist (1810-1882) Theodor Schwann developed cell theory in 1837 with Matthias Schleiden. Louis Pasteur Chemist and Microbiologist (1822-1895) Louis Pasteur was one of the founders of microbiology. He introduced “germ theory” in 1862 which explained that microorganisms (bacteria) infected animals and humans cause disease. Matthias Schleiden Botanist (1804-1881) Matthias Schleiden is a co-founder of cell theory. In 1883, he proposed that plants are composed of cells. Rudolf Virchow Physician/Doctor (1821-1902) Rudolf Virchow is known as the Father of Modern Pathology. In 1858, he published his work on cells and cell division in which he stated “every cell originates from another existing cell like it”. Zacharias Janssen Spectacle maker (1580 - 1638) Dutch spectacle-maker from Middelburg associated with the invention of the first optical telescope. Jansen is sometimes also credited for inventing the first truly compound microscope. Francisco Redi Doctor/Naturalist / Poet (1626- 1698) He disproved the theory of spontaneous generation by performing experiments to observe if rotting meat changed to flies. In his experiment he had 6 jars, 3 covered with fine gaze and 3 were left uncovered. John NeedhamBiologist / Roman Catholic Priest (1713 -1781) He did experiments with spoiled wheat, in containers. In the experiment a broth mixture was briefly boiled, then the mixture was allowed to cool in an open container to room temperature. Later, the flasks would be sealed, and microbes would grow a few days later. These experiments seemed to show that there was a life force that produced spontaneous generation. Today, it is know that he did not boil the broth long enough to kill all the microbial and leaving the flasks open exposed the broth to microbial contamination. Lazzaro SpallanzaniBiologist/ Catholic Priest (1729 – 1799) He tried several variations on the experiments done by John Needham. He discovered that soup that was kept sealed did not contain the micro organisms that appeared in soup open to the air. He determined that micro organisms get into the soup from the air. Casper Wolff German Biologist / Embryologist (1733 – 1794) He wrote a paper that saying that cells start off the same, then divide becoming specialized tissue and that tissue that becomes organs. Lorenz Oken Nnaturalist/ philosopher (1779 -1851) It is reported that in 1805 Oken stated that "All living organisms originate from and consist of cells" ... 1590 - Zacharias Janssen invent the world's first compound microscope. 1665 - Robert Hooke of England looks through a microscope at a sliver of cork. He notices what he calls cells or pores. He believes the cells contained the noble juices or fibrous threads of the tree when it was alive. He is the first person to use the word cell to describe microscopic structures. 1668 - An Italian physician, Francesco Redi, performed an experiment to see if rotting meat changed into flies. He discovered that only flies to could make more flies, thus disproving the theory of spontaneous generation. 1674 - Anton Van Leeuwenhoek, of Holland, used microscopes to view many things including pond organisms, bacteria and blood cells. He made careful sketches of what he observed. 1745 - John Needham, a naturalist and clergyman in Scotland, discovered that soup that had been exposed to the air contained micro organisms. He theorized that a life force was present in all inorganic matter including air and oxygen that could cause spontaneous generation. 1759 - C. F. Wolff of Germany comes up with a generalized cell theory. 1765 - Lazzaro Spallanzani, a biologist and abbot in Italy tried several variations on the experiments done by John Needham. He discovered that soup that was kept sealed did not contain the micro organisms that appeared in soup open to the air. He determined that micro organisms get into the soup from the air. 1805 - Lorenz Oken a German naturalist, renown philosopher and thinker of the 29th century. It is reported that in 1805 Oken stated that "All living organisms originate from and consist of cells" ... 1831 - Robert Brown discovers the nucleus of the cell. He stresses its importance in fertilization. 1839 - Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann create cell theory. The theory states that all living things are made up of one or more cells. Schleiden publishes his cell theory applying it to plants, while Schwann publishes his applied to animals. Theodor Schwann discovers special cells that form a sheath around nerve axons. They are now called Schwann cells. He conducts experiments to help disprove spontaneous generation once and for all. 1855 - Rudolf Virchow writes and publishes his aphorism omnis cellula e cellula, which means every cell stems from another cell. He theorizes that all forms of disease come from changes in normal cells. Robert Remak discovers a method to isolate the membrane of the cell and proves that it divides a cell. 1857 -Rudolf Virchow heartily endorses cell division and the role it plays in pathology. 1864 - Louis Pasteur repeated the soup experiment, determining that soup spoiled when exposed to air only if the air was not filtered or if the container had an opening allowing micro organisms to enter. He stated that flasks with long S shaped necks protected the soup because the micro organisms settled in the neck instead of the soup.