File
advertisement

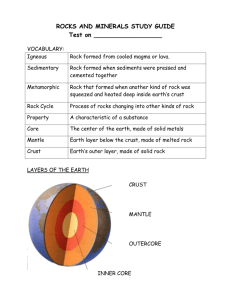
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST GEOLOGY FINAL Learning Goal 30 Minerals I can explain that rocks are made of minerals and describe the properties of common minerals 1. Minerals that break in irregular, round breaks have a. Cleavage b. Hardness c. Fracture d. Metallic luster 2. True or False: The 7 mineral tests cannot be used on rocks that are a mixture of minerals a. True b. False 3. All of the following are tests for properties of a mineral except for a. Hardness b. Texture c. Element d. Streak Color 4. What are rocks mostly made up of? a. Organic material b. Fossils c. Dirt d. Minerals 5. What is a characteristic of all minerals? a. Minerals have a crystalline structure b. Minerals are hard c. All minerals are the same color d. Minerals contain organic matter Learning Goal 31 Minerals I can group rock samples as sedimentary igneous, and metamorphic. I can draw the rock cycle and explain the energy involved in each rock type being made. 6. What produces igneous rocks? a. Pressure and Heat b. Earthquake c. Melting and Cooling d. Weathering and Deposition 7. What rock types do not form by the transfer of heat? a. Sedimentary rock b. Metamorphic rocks c. Igneous rocks d. All three rock types use heat energy to be made Use this chart to answer #5 Metamorphic Igneous Sedimentary Mineral Shiny Air holes X X X Flat layers X X X Fossils Particles stuck together X X Glassy Crystals X X X X X X 8. (Use the chart above)This rock has particles that are stuck together and has flat layers. According to the key above it is . . . a. Sedimentary b. Mineral c. Metamorphic d. Igneous 9. (Use the chart above) If a rock has a glassy surface, crystals and is shiny it could be either an igneous rock or a mineral. What should I look for to find out if it is igneous or not. a. Flat layers b. Fossils c. Particles stuck together d. Air Holes 10. What events must happen for a rock to change from igneous to sedimentary? a. Melting, cooling b. Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementation c. Heat, pressure d. Erosion, heat, melting 11. What events must happen for a rock to change from an igneous rock to a metamorphic rock? a. Melting, cooling b. Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementation c. Heat, pressure d. Erosion, heat, melting Learning Goal 32 Earth’s Surface Changes I can use a model to demonstrate and explain how erosion, weathering and gravity change the earth’s surface slowly over time. 12. What term describes the movement of rock particles? a. Erosion b. Deposition c. Weathering d. Cementation 13. Which of the following is the breakdown of rocks into smaller pieces? a. Cementation b. Melting of rock c. Weathering d. Heat and pressure 14. Rivers and streams start from a high location and move to a lower location. The earth’s surface can change dramatically over time because rivers and streams cut into the surface of the earth. What type of force is responsible for this? a. Gravity b. Chemical c. Heat d. Balanced forces 15. How is gravity involved in changing the earth’s surface? a. Gravity pulls only water down: example creating rivers b. Gravity creates tilted layers: example tilting c. Gravity doesn’t change the earth’s surface only weathering does that. d. Gravity pulls everything down: example flattening/eroding mountains 16. Which of the following is a model for cementation? a. Running water down an inclined tray of dirt b. Using a hair dryer to blow sand across a box c. Gluing pieces of sand together d. both a & b Learning Goal 33 Rock Layer & Dating I can explain how rock layers are made and how you can tell which are younger and older and how this relates to the organisms in younger rocks look most like organisms today. 17. How are sedimentary rock layers formed? a. Rock layers are formed whenever magma flows outward from Earth. b. Rock sediments melt into flat layers c. Sediments deposit and cement on top of old sediment layers d. Heat and pressure cause sediments to flatten out into sheets. 18. Choose the best selection to finish the statement. “Fossils that are found _________usually look more like the organisms that are alive today.” In the top layers Near a volcano Close to an earthquake In the bottom layers a. b. c. d. 19. Scientists use relative dating to tell which fossils and rock layers are older than others. Which statement best summarizes relative dating? A. Dating a relative b. Comparing different things to decide which item is older than another c. Using chemicals to find the exact year a rock was formed d. Using the color of a rock to determine the age 20. True or False: Organisms can be put in chronological order (from youngest to oldest) if you know what sedimentary rock layer they were discovered in? a. True b. False Use the diagram to the right to answer question #4 21. Finish the sentence: The fossil of the organism in layer A would look _____________________. 1. Similar to organisms in layer C 2. Similar to organisms like dinosaurs 3. Similar to organism in layer D 4. Similar to organisms today Learning Goal 34 Rock disconformities I can explain faulting and folding in sedimentary layers Use the diagram to answer questions #1 22. What event made it so that the layers have bent? a. b. c. d. Erosion A Fault line Folding Intrustion of igneous rock (lava) For #3 and #4 match the pictures with the correct type of disturbance to the rock layers. A. B. 23._______Folding 24._______Fault 25. What types of disturbances can cause the layers to become “messed up” where the older layers may end up higher than the younger? a. Weathering b. Erosion c. Cementation d. Folding/Faulting 26. In the diagram above it shows examples of both folding and faulting. Of all the layers, which one is the youngest? a. b. c. d. 27. F D B H In the diagram, the layers D, E, F and G have clearly been dis-conformed before the x/y change happened. What happened to these layers first? a. the layers have been dis-conformed by faulting first b. the layers have been dis-conformed by folding first Learning goal 35 Fossils I can explain how fossils are formed and how they show us about the history of the earth. 28. What must happen for an organism to be fossilized? a. It must be decomposed completely b. It must be buried quickly to prevent decomposition c. It must have died at an early age d. It must be in a desert at the time of death 29. In a region of Wyoming covered by rolling hills, and desert a petrified shark’s tooth was found. Since sharks live in salt water what does this fossil indicate about the geological history of this region? a. it was once covered with a vast freshwater lake. b. it was once covered by a swamp or marshland. c. it was once covered by an ocean. d. it has always had the same geography as it has today. 30. What is the process by which a fossil is formed? a. Organism buried→ death→ uplift→ minerals replace bone materials b. Organism dies→ Lava covers organism→ uplift c. Organism dies→ buried quickly so it doesn’t decompose→ pressure→ minerals replace bone material→ uplift d. Organism dies→ organism decomposes →buried→ pressure→ minerals replace bone material→ uplift 31. Which of the following situations is most likely to form a fossil? a. A forest fire occurs b. Dies and floats out to sea c. Lava covering a recently dead organism d. A mudslide covering a recently dead organism 32. After a bone has been fossilized and becomes a fossil what is different about it? a. It is no longer bone, the minerals changed the bone into rock b. Nothing changed it is perfectly preserved bone from prehistoric animals. c. The bone is genetically different once it is fossilized. d. It turns into wood after it is fossilized. 33. What is the last thing that must happen in order to be considered a fossils? a. Turned into stone b. Buried in sediment c. Die quickly d. Put under pressure Learning Goal 36 Earthquakes and Volcanoes I can describe how energy from inside the earth causes earthquakes and volcanoes and how they change the earth’s surface 34. Which of the following is an example of an event that would change the Earth's surface quickly? a. Explosive volcano b. Weathering & Erosion c. Sedimentary rock formation d. Glacier flow 35. What kind of energy is transferred during a volcano? a. Chemical and Kinetic b. Light and Kinetic c. Electricity and Kinetic d. Heat and Kinetic 36. The energy of an earthquake travels as ________________. a. light waves b. heat waves c. chemical rays d. seismic waves 37. How do earthquakes change the earth’s surface? a. Build up of magma makes rivers b. Makes a volcanic cone c. Raise or lowers the surface of the land d. Build up of magma makes new land 38. How do volcanoes change the earth’s surface? a. b. c. d. Causes new land Causes valleys to form Causes dirt to form Causes rivers to form Learning Goal 37 Geologists & Building I can discuss why sometimes people build structures in areas where geologist have discouraged building because of earthquakes, mudslides, etc. 39. A family wishes to build a house on a steep hillside. They call a geologist to ask if this is a good idea. What will the geologist probably suggest to the family? a. Windstorms will affect the house and yard. b. The hillside may erode and damage the property. c. That hills are perfect places to build homes because of the great view d. Earthquakes are more likely on a steep hillside 40. Which of the following places would be the best place to build a home based on geology. a. a beautiful cliff side by the beach b. a dry river bed c. a solid rock foundation d. a sandy hill by a river 41. Which of the following is a way that people try to control the effect of gravity on the Earth’s materials? a. Building retaining walls to stop soil from sliding downwards b. Designing bridges to span wide rivers during floods c. Finding new ways to construct airplanes for transportation d. Constructing roads that will go around hills, not over them. 42. A home builder wishes to build a development of homes on an earthquake fault where the view is beautiful. What is the role of a geologist in this situation? a. geologist would offer and sell earthquake hazard insurance b. the geologist would determine if homes could or could not be built there because he makes the laws c. the geologist would engineer the homes so that they could be protected against the earthquake hazards d. the geologist would explain the earthquake hazards and warn against building there. 43. Why would a building company chose to build structures even though a geologist warned against it? a. because they like to make scientists mad b. because the area has a great view and that will easily sell the buildings c. because buildings don’t need to be built on solid surfaces d. because they have built many structures and always know best