Object oriented programming - Milestone International College
advertisement

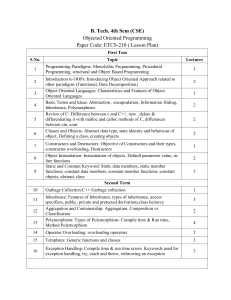
Object Oriented Programming Software Evolution:Every after decade a new software technology emerged Since the invention of the computer many programming approaches have been tired to handle the increasing complexity in: Modular programming Top-down approach Bottom-up approach Structured programming Object oriented programming is an approach to program organization and development that attempts to eliminate some of the pitfalls of conventional programming methods by incorporating the best of structured programming features with powerful new concepts What is Object Orientation? The field of object orientation is to represent the objects that we find in the real world in software. These objects may be of various types, ranging from physical to the more conceptual Object oriented analysis method identify five types of objects Tangible things Physical objects eg- car, train etc Roles Of people or organization eg account holder, employee etc Incidents Something happening at a particular time eg- flight transaction etc Interactions A link between objects eg electrical connection, contract etc Specifications A definition of a set of other objects eg- a description of a particular type of stock item etc What is an Object? Object are the elements through which we perceive the world around us. In other word objects are the combination of data and function in a single unit. We naturally see our environment as being composed of things which have recognizable identifies and particular behaviors. All objects have these characteristics of identify and behavior which enable us to recognize them as discrete things Objects also exhibit state, which means that we can describe what an object is? What it does? And what it is called? It is instinctive to classify individual objects according to their common characteristics; we recognize. For example that all cats are of a single type . Although we may also identify individual different between specific cats. Our perception is that all individual cats belong to a general class which we call cat. We know about all cats because we recognize what they have in common Some object are composed of other objects or contain other objects .A house object is composed of other objects such as bricks, windows, doors, tiles etc. Why we use objects in programs? The world is composed of interacting, classifiable and identifiable objects and therefore programs too, can usefully be structured in this way. Since all software application serve people living in the real world, then that software should mirror the real world as closely as possible, both in its workings and in its underlying design. Hence object- oriented programming is more natural way to program then procedural programming The object oriented programming approach to software is that it unifies inside objects two things that have traditionally been separated in programming paradigms Data Process Object= (private) date + public (process) Object Oriented Programming Compiled by K@pil Sh@rma Page 1 The linking of these two aspects of programming is known as Encapsulation and allows the implementation of information hiding Objects have a private part of hidden internal detail (state data and internal processes) and a public interface which clearly defines the set of possible behaviors of the objective (the message to which it can respond). This separation of the public interface of an object and its internal implementation allows us to treat the two as separate parts of the programming process Why do we need object oriented programming? Object-oriented programming technique was developed because limitations were discovered in earlier procedural approaches to programming In procedural approaches new methods in programming were introduced called structured programming, breaking a program or list of instructions into functions. These functions or list of instructions into functions. These functions can be further extended by grouping a number of functions together into a module. As programs grow ever larger and more complex even the structured programming approach begins to show signs if strain. The reasons for the failures reveals that there are weakness in the procedural paradigm. In a procedural language, the emphasis is on doing things or action. The subdivision of a program into functions continues this emphasis. Functions do things just as single program statements do. But the data, which is an important part of the program, is given second class status in the organization of procedural languages. ( the important part of an inventory program isn’t a function that displays the data or a function that checks for correct input , it’s the inventory data itself) The data that was probably reads from a disk file or standard input are kept in the computer memory and treated as a variable: these variable could be declared as global or local depending upon the nature of the programming Features or elements of Object Oriented Language: Objects: Object are the elements through which we perceive the world around us. Object are the combination of data and function in a single unit. Objects can interact without having to know details of each other’s data or code. We naturally see our environment as being composed of things which have recognizable identifies and particular behaviors. All objects have these characteristics of identify and behavior which enable us to recognize them as discrete things Objects also exhibit state, which means that we can describe what an object is? What it does? And what it is called? It is instinctive to classify individual objects according to their common characteristics; we recognize. For example that all cats are of a single type. Although we may also identify individual different between specific cats. Our perception is that all individual cats belong to a general class which we call cat. We know about all cats because we recognize what they have in common Some object are composed of other objects or contain other objects .A house object is composed of other objects such as bricks, windows, doors, tiles etc. Class: Class is a blue print of an object. In other word class is a collection of objects, where user can define data and related functions to manipulate the data. For example manager, peon is the object of the class employee and car, bus is the object of the class vehicle. It specifies what data and functions will be included in objects of that class. Defining class doesn’t create an object but class is the description of object’s attributes and behaviors Class: person Attributes: Name, sex, age etc Behaviors: Speak ( ), Listen ( ), Walk ( ) When class is defined, objects are created as <Class name><object name>; If employee has been defined as a class, then the statement Object Oriented Programming Compiled by K@pil Sh@rma Page 2 Employee manager; Will create an object manager belonging to the class employee. Each class describes a possibly infinite set of individual objects, each object is said to be an instance of its class and each instance of the class has its own value for each attribute but shares the attribute name and operations with other instances of the class. The following points give the idea of the class: A class is a template that unites data and operations. A class is an abstraction of the real world entities with similar properties A class is an implementation of abstract data type. Inheritance Inheritance is the process by which objects of one class inherits the characteristics of another class as part of its definition. It supports the concept of hierarchical classification Inheritance is appropriate when one class is a kind of other class (text window is a kind of window) In OOP, the concept of inheritance provides the idea of reusability; we can add additional features to an existing class without modifying it. This process, deriving a new class from the existing one is called inheritance Once a class has been written and debugged, it can be distributed to different programmers for reuse, which is called reusability in object-oriented programming. A programmer can take class and without modifying it, can add new features and create a new class according to the requirements. This can be done by deriving a new class from the existing one. The new class will inherit the capabilities of the existing one, but it is free to add new features of its own. Code reusability is one of the major advantages of inheritance. Polymorphism The word polymorphism is derived from Latin words ‘poly’ means many and ‘morphos’ means form.So, polymorphism means “having many forms”. The polymorphism allows different objects to respond to the same message in different ways, the response specific to the type of objects. Polymorphism is important when object oriented programs dynamically creating and destroying the objects in run time. Example of polymorphism in OOP is operator overloading, function overloading. For example:- operator symbol ‘+’ is used for arithmetic operation between two numbers, By overloading same operator ‘+’ can be used for concatenation of strings. Data Abstraction and Encapsulation: - The wrapping up of data and function into a single unit is called encapsulation. Encapsulation is the most striking feature of a class . The data is not accessible from outside of class. Only member function can access data on that class. The prevention of data from direst access by the program is called data hiding. That data can be hidden making them private so that it is safe from accidental modification. Abstraction is the representation of all the essential features (state and behaviors) of an object without including the details or explanations. The classes use the concept of data abstraction, so they are known as abstract data types (ADT) Applicatons of OOP OOP has become one of the programming buzzword today Applications of OOP are beginning to gain importance in many areas The most popular application of OOP has been in the area of user interface design such as windows. There are hundreds of windowing systems developed using OOP techniques Real-business systems are often much more complex and contain many more objects with complicated attributes and methods (member functions). OOP is useful in this type of applications because it can simplify a complex problem Object Oriented Programming Compiled by K@pil Sh@rma Page 3 The promising areas for application of OOP includes: Games Expert system Object-oriented databases Artificial Intelligence AI and expert systems Most important areas of application is design of user interface such as window Computer based training and educational systems OO technology is going to change the way software engineers will think, analysis, design and implement systems in future Comparison between Procedural and OO programming Procedural Date type Variable Function/Procedure Function calls Problem is divided into different functions 6. Follow top down approach 7. Emphasis is given on procedures rather than data 8. It allow data to move freely by declaring data globally 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Object- oriented Abstract data type/ class Object/Instance Method/ Operation/ Service Message passing Problem is divided into different objects 6. Follow bottom up approach 7. Emphasis is given on data rather than Procedure 8. It does not allow data to move freely by making data private 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Important features of Object-Oriented Programming are as follows:1) Emphasis is given on data rather than procedures 2) Programs are divided into different groups known as objects 3) Data structures are designed such that they characterize the objects 4) Functions and data are tied together 5) Data is hidden and can’t be accessed by external function 6) Functions are communicated between each other through objects. 7) New data and function can easily be added 8) Follow Bottom up approach Important features of procedure-oriented programming are as follows:1) Emphasis is on doing things rather than data 2) Large programs are divided into smaller programs know as function 3) Data move freely around the program from function to function 4) Function transforms data from one form to another 5) Employs top-down approach in program desi Advantages and disadvantages Object-Oriented Programming:OOP contributes greater programmer productivity Better quality of software and lesser maintenance cost. The main advantages are:1) Making the use of inheritance, redundant code is eliminated and the existing class is extended 2) Through data hiding programmer can build secure programs that cannot be invaded by code in other parts of the program Object Oriented Programming Compiled by K@pil Sh@rma Page 4 3) System can be easily upgraded from small to large systems 4) Software complexity can be easily managed 5) Message passing technique for communication between objects makes the interfaces description with external system much simpler 6) Code reusability is much easier than conventional programming language Disadvantage of OOP 1) Compiler and runtime overhead. Object oriented program required greater processing overhead demands more resources 2) An object’s natural environment is in RAM as dynamic entity but traditional data storage in files or databases 3) Requires the mastering in software engineering and programming methodology 4) Benefits only in long run while managing large software projects Object Oriented Programming Compiled by K@pil Sh@rma Page 5