Supplementary Table 1 Table 1 Bacterial strains and plasmids used
advertisement

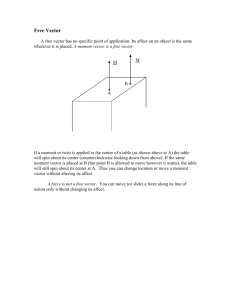
Supplementary Table 1 Table 1 Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study Strains/Plasmids Relevant Characteristics Source ZM4 Wild-type Zymomonas mobilis ZM4 ATCC 31821 JM110 Streptomycin resistant Escherichia coli strain Stratagene used as cloning host for preparation of nonmethylated plasmids. ZM6014 ZM4 adapted for acetic acid tolerance (Chen et al. 2009) ZM4 ∆XR ZM4 with a ZMO0976 knock out This study ZM6014 ∆XR ZM6014 with a ZMO0976 knock out This study pTeasy Commercial vector containing ampicillin Promega resistance cassette and ColE1 ori pTspecXR pTeasy vector containing spectinomycin This study resistance (SpecR) cassette and homologous regions flanking ZMO0976 pSTV28 pSTlsXR Commercial plasmid containing chloramphenicol TaKaRa resistance cassette and p15A ori (Japan) pSTV28 containing SpecR and homologous This study Bio Inc. regions flanking ZMO0976 pZMETX Plasmid containing xylose metabolic genes (Agrawal et al. 2011) obtained from A1 pZMETX* Mutated pZMETX containing xylose metabolic genes obtained from A3 (Agrawal et al. 2011) Supplementary Materials and Methods Knockout of XR-gene (ZMO0976) in Z. mobilis XR-gene knockout was carried out in Z. mobilis according to a published procedure (Viitanen et al. 2011). pTspecXR was constructed for this purpose (Supplementary Fig. 1). pTeasy backbone of the plasmid pTspecXR was obtained by EcoRI and SphI double digestion of a plasmid pTadh-fba. pTadh-fba has an ~2 kb operon Padh-fba ligated to the commercial pTeasy vector (Promega) using A-T cloning. Sequence of spectinomycin resistance (SpecR) cassette which includes the promoter was obtained from GenBank (accession # X03043). Synthetic DNA was used for SpecR cassette (Genscript). SpecR cassette was ligated to pSTV28 vector at BamHI site to obtain plasmid pSTVls. The 5’ homologous region (HR) for XR was cloned from ZM4 genome using TAATGCAAGCATGCCCTTATATGGTCTGACGTTG-3’) primers and – (5’(5’- GCGATTCGTCGACTGATATTGATACCAAGATCAATC-3’). Restriction sites are indicated in bold underlined fonts. The 5’ homologous region extends from 1 kb upstream to 0.2 kb downstream of the 5’-end of ZMO0976. 5’ HR was ligated to pSTVls vector at SalI and SphI restriction sites to get pSTls5’XR. Similarly the 3’ HR was cloned using primers – (5’ATATTACCCGGGCTATCCGCTGGATGTTGGAG-3’) and (5’- ATTATTGAATTCGGACGGACGATCAGAGAAGCG-3’). The 3’ HR extends from 0.2 kb upstream to 1 kb downstream of the 3’-end of ZMO0976. 3’ HR was ligated to pSTls5’XR vector at XmaI and EcoRI restriction sites to get the suicide vector pSTlsXR. EcoRI and SphI were used to double digest pSTlsXR to obtain two DNA fragments of size 3.0 and 3.4 kb. The 3.4 kb DNA fragment consisted of the SpecR cassette flanked by homologous regions of ZMO0976. This fragment was ligated to the EcoRI and SphI digested pTeasy backbone mentioned above to obtain the suicide vector pTspecXR (Supplementary Fig. 1). JM110 was used as cloning host so that methylation-free plasmids can be obtained for efficient electroporation in Z. mobilis ZM4. Several primers were used to confirm the knockout of ZMO0976 from ZM4 genome. Primers (5’- GCTATTGACGGTACCATGAACACTTCTACGCAAAAACC-3’) and (5’- TATTCGTACTAAGCTTTTATTTATCGCGTGGCGGGGGTG-3’) bind to the ends of ZMO0976 and amplify the entire ZMO0976 gene. GCCATCAAAGGTCAACGCGATAATTTGATTATTGCG-3’) Primers and - (5’(5’- CCAGATAATGTTCAAAGCGCGGTTTCTGGAATTTC-3’) amplify the middle 526 bp portion of the ZMO0976 gene. Primers (5’-AAAGAAACCAATCCCGTTGTTGTCAAAGCCAAAGTC-3’) and (5’- CCATTGAAGAATGGCATGCTTTGACCGATGAAGC-3’) amplified the genomic region flanking ZMO0976. Supplementary Fig. 1 Upstream of XR 1 5'-end of XR R Amp pTspecXR SpecR 6397bp ColE1 3'-end of XR Downstream of XR Plasmid map of pTspecXR, a pTeasy derived suicide vector for knockout of XR-gene