Wk 2 Homework - English for Chemistry & Materials Science
advertisement

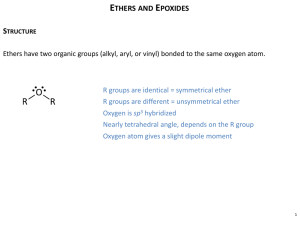
Wk 2 Homework: Paraphrasing Legitimately Task 1: Read the following text and the accompanying paraphrase, jot down all the devices the author employed in order to paraphrase the text (5 points) and evaluate its efficacy (3 points). Ether Functional Group: Original source The ether functional group is R1OR2, where R1 and R2 are alkyl or aryl groups which may or may not be the same. The central part of the ether molecule is C-O-C, and because the oxygen atom is attached only to carbons and not to a hydrogen atom the ethers are relatively unreactive. If a hydrogen atom was attached to the oxygen many of the properties would be similar to those of the alcohols. Instead the relative unreactivity is more closely related to the alkanes. One of the main uses of ethers are as organic solvents. The oxygen atom of an ether functional group has two lone pairs of electrons. This is important in solutions of high hydrogen ion concentration where one of these pairs of electrons can form a dative covalent bond (where one of the two atoms involved contributes both electrons) with a hydrogen ion. This gives a positively charged oxonium ion. In this reaction the oxygen atom is behaving the same way as it does in a water molecule. In aqueous solutions free hydrogen atoms are not encountered because they join with water molecules to give hydroxonium ions, H3O+. Some ether compounds have the oxygen atom from the functional group attached to carbon atoms which are cyclic in nature, that is they are part of a ring structure. This is an example of a heterocyclic compound. Due to the greater number and stronger bonds that are present the boiling point of these cyclic ethers is higher than might be anticipated from their chemical formula. For example ether is C2H5OC2H 5 and it has a boiling point of 94°F (34.5°C). The cyclic ether tetrahydrofuran, which has a chemical formula of C2H4OC2H 4, has a boiling point of 149°F (65°C). This difference in the boiling point of these two very similar molecules is due to the cyclic nature of the latter and the greater energy needed to break some of the hydrogen bonds which are formed. One class of compounds with the ether functional group that are an exception to the rule of unreactivity of ethers are the epoxides. Originally epoxides were named as oxides of alkenes. Ethylene oxide is an example of an epoxide ether. It has the chemical formula CH 2OCH2 with the C-O-C forming a ring structure. Ethylene oxide has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name of epoxyethane or oxirane. The C-O-C functional group when present in an epoxide has a far greater reactivity towards nucleophiles. The basic mode of action is to make the cyclic structure a straight chain molecule. For example ethylene oxide is added to the strong nucleophile water in the presence of the catalyst sulfuric acid at 140°F (60°C) to produce ethylene glycol (antifreeze). The ether functional group is generally very unreactive except when found in the form of an epoxide. The oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons which make ethers very powerful organic solvents. Retrieved from http://www.bookrags.com/sciences/chemistry/functional-group-woc.html (11-09-09) Ethers: paraphrase A common functional group in Ethers is ROR, in which each R designated either represents an alkyl or an aryl group. The main attribute of ether is its tendency to be rather inert. This inertness accounts to the dynamics of the oxygen atom arrangement; Not being attached to Hydrogen atoms but only to carbon atoms, oxygen avoids the formation of ( OH ) - hydroxyl groups, featured in alcohols. What renders ethers dominant organic solvents is the lone-pair electron found in the oxygen atom. Forming a covalent bond, oxygen reacts with a hydrogen ion to yield an oxonium ion. Ethers exhibit a ring arrangement of heterocyclic compounds. Depending on the behaviour of the ring and the energy required to cleave the hydrogen bonds formed, the boiling point of each ether shows some discrepancy. Unlike to common ones, when formed as epoxides, ethers can also be highly reactive with nucleophiles. Epoxides are also dubbed as oxides of ether or according to convention as epoxyethane or oxirane. Task 2: Paraphrase legitimately the text Carbon Monoxide Poisoning in the following link (7 points): http://cfpub2.epa.gov/ncea/cfm/recordisplay.cfm?deid=65703