Unit 3: ecology and energy flow
advertisement

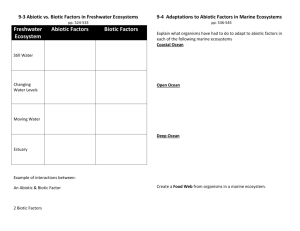
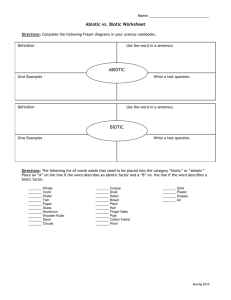
Unit 3: ecology and energy flow 4.2.A o As energy flows through the ecosystem, all organisms capture a portion of that energy and transform it to a form they can use o Illustrate and describe the flow of energy within a food web o Explain why there are generally more producers than consumers in an energy pyramid o Predict how the use and flow of energy will be altered due to changes in a food web 4.2. B o Matter is recycled through an ecosystem o Explain the processes in the recycling of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon through an ecosystem o Explain the importance of the recycling of nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon within an ecosystem 1.1.I o Mass is conserved during any physical or chemical change o Compare the mass of the reactants to the mass of the products in a chemical reaction or physical change (e.g., biochemical processes, carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle, nitrogen cycle, decomposition and synthesis reactions involved in a food web) as support for the Law of Conservation of Mass 1.2.F Energy can be transferred within a system as the total amount of energy remains constant (i.e., Law of Conservation of Energy) Classify the different ways to store energy (i.e., chemical, nuclear, thermal, mechanical, electromagnetic) and describe the transfer of energy as it changes from kinetic to potential, while the total amount of energy remains constant, within a system (e.g., biochemical processes, carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle, nitrogen cycle, food web) 3.2Fc Explain how water is important to cells (e.g., is a buffer for body temperature, provides soluble environment for chemical reactions, serves as a reactant in chemical reactions, provides hydration that maintains cell turgidity, maintains protein shape) Sequence: Read chapter 2 (section 2.2 and 15.2) Topic: food webs Assmt: vocabulary Intro to food webs Le: pyramids Pyramid Le: types of food webs Assmt: food web Le water Le: variables Case studies from student food webs Le nutrient cycles Le: variables Biology I Ecology and flow of energy Outline I. Food webs A. Trophic levels all begins with the ___ ___ ___ 1. producers aka _____________trophs a. their job is to convert abiotic ___________ and energy from the __________ into biotic ___________, usually using ______________________ b. examples: ________________, ______________ 2. consumers aka _________________trophs a. their job is to convert biotic __________________ into biotic ________________________, usually using __________________________ b. types a. primary (1st order) aka ________________ examples are ________________, _______________ b. secondary (2nd order) aka ________________ examples are _______________, ________________ c. tertiary (3rd order) , quaternary (4th order) d. omnivores 1-4+ 3. recyclers a. their job is to convert dead biotic __________________ into abiotic and biotic ________________________, usually using __________________________ b. types a. decomposers examples are _________________ and ________________ b. scavengers examples are __________________ and _______________ B. 10% rules 1. 10% rule and the energy pyramid states ____________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. An example of this is __________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 2. 10% rule and the biomass pyramid states __________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. An example of this is __________________________________ ____________________________________________________ 3. numbers ‘pyramid’ states _______________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________. An example of this is __________________________________ ____________________________________________________ C. Types 1. terrestrial a. are principally located on ________________. b. An example is ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ c. Some major advantages are _________________________ ________________________________________________ 2. aquatic a. are principally located in the _______________________. b. An example is ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ c. Some major advantages are _________________________ ________________________________________________ d. Special properties of water that support life (internal as well as external) a. Buffer for body _______________ because of high ______________ heat. Ex: ___________________ __________________________________________ b. Buffer for _______________ because of its ability to be an _________________ or ______________. Ex: _____________________________________ c. Helps to dissolve and transport nutrients because of ________________. Ex: _____________________ _________________________________________ d. Place for ____________ _____________ to occur. Ex:_______________________________________ 3. hybrid- of course all food webs depend on __________________ D. Variables 1. No food web is __________________. One change results in at least _______________ and sometimes many more. 2. examples: a. a decrease in sun results in ________________________ ______________________________________________ b. an increase in rain _______________________________ ______________________________________________ c. a decrease in grass _______________________________ ______________________________________________ d. an increase in predator populations___________________ _______________________________________________ II. Nutrient cycles A. 1st law of thermodynamics- ____________ can neither be _____________ nor ___________________. So it must be _________________________ B. Types 1. Water cycle a. Exists primarily as _____________ b. processes a. condensation/precipitation (biotic/ abiotic)_________ __________________________________________ b. evaporation (biotic/ abiotic) _________________________ __________________________________________________ c. combustion (biotic/ abiotic) _________________________ __________________________________________________ d. respiration (biotic/ abiotic) __________________________ __________________________________________________ e. transpiration (biotic/ abiotic) ________________________ __________________________________________________ f. aids in chemical reactions (biotic/ abiotic) ____________ __________________________________________________ 2. Carbon cycle a. Exists primarily as _____________________________ _____________________________________________ b. Major processes a. photosynthesis(biotic/ abiotic) ____________________ _______________________________________________ b. combustion(biotic/ abiotic) _______________________ _______________________________________________ c. respiration/ cellular respiration(biotic/ abiotic) ______ ________________________________________ d. consumption(biotic/ abiotic) ________________________ __________________________________________________ e. decomposition(biotic/ abiotic) _______________________ __________________________________________________ 3. Nitrogen cycle a. Exists primarily as _____________________________ _____________________________________________ b. processes a. nitrogen fixation(biotic/ abiotic) _____________________ __________________________________________________ b. denitrification(biotic/ abiotic) _______________________ __________________________________________________ c. nitrification(biotic/ abiotic) __________________________ __________________________________________________ d. consumption(biotic/ abiotic) _________________________ __________________________________________________ e. denitrification(biotic/ abiotic) _______________________ __________________________________________________ f. decomposition(biotic/ abiotic) _______________________ _________________________________________________ C. Variables 1. No nutrient cycle is __________________. One change results in at least _______________ and sometimes many more. 2. examples: a. an increase in carbon dioxide results in ______________ ______________________________________________ b. an increase in rain _______________________________ ______________________________________________ c. a decrease in evaporation __________________________ ______________________________________________ d. an increase in lightening ___________________________ _______________________________________________