Reproduction Test
advertisement

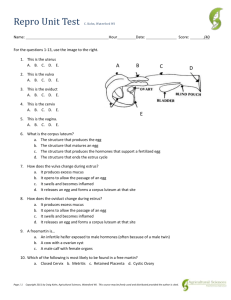
B142 Animal Science Animal Reproduction Test Name __________________________________ Date _____________ Using the terms below label the parts of the female reproductive system 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 1. ________________________ 5. ________________________ 2. ________________________ 6. ________________________ 3. ________________________ 7. ________________________ 4. ________________________ Uterine Body Vagina Oviduct Cervix Ovary Uterine Horn Vulva Match the following terms of the female reproduction to their correct definition. 9. ________ Occurs every 21 days when the ovaries produce a follicle and estrogen levels are high causing the female to be receptive to the male. 10. _______ Region at the base of the brain responsible for reproduction. 11. _______ Hormone produced by the hypothalamus 12. _______ Gland located near the base of the brain that produces follicle stimulating hormone and luteinizing hormone. 13. _______ Hormone responsible for the growth of follicles on the ovaries. 14. _______ Causes a mature follicle to rupture or ovulate and stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum. 15. _______ The primary reproductive organ where eggs are produced. 16. _______ Fluid filled blister like structures that contain developing eggs. 17. _______ Hormone produced by the follicle that causes the animal to come into estrus. 18. _______ When the follicle ruptures releasing the egg into the ovaduct. 19. _______ The site of fertilization. 20. _______ Forms in the crater left on the ovary after ovulation. 21. _______ Hormone that is produced by the corpus luteum which prepares the uterus for pregnancy and prevents the animal from returning to estrus by blocking the follicle stimulating hormone. 22. _______ Hormone that is produced by the uterus when no embryo is found. It causes the corpus lutieum to fade, allowing for the production of follicle stimulation hormone, which causes the animal to come back into heat. 23. _______ Membrane or sack that surrounds the developing embryo that attaches the uterus. This membrane stops the production of prostaglandin, maintaining the pregnancy. 24. _______ Where the uterus attaches to the placenta. 25. _______ Where the placenta attaches to the uterus. 26. _______ When eggs are flushed out of one cow, fertilized and placed in a surrogate mother to raise. 27. _______ When a cow is given hormones so that instead of producing one egg she produces many eggs. 28. _______ Taking a group of mature females and getting them to come into heat at roughly the same time. 29. _______ The act of giving birth. 30. _______ A term used to describe a difficult birth. 31. _______ The first milk produced by the mother. 32. _______ Calving difficulty. A. Hypothalamus B. Corpus Luteum C. Progesterone D. Gonadotrophin E. Pituitary gland F. Estrogen G. Prostaglandin H. Cotyledons I. Follicle J. Caruncles K. Ovaries L. Colostrum M. Estrus cycle N. Oviduct O. Ovulation P. Dystocia Q. Embryo transfer R. Super ovulation S. Parturition T. Estrus synchronization U. Luteinizing hormone V. Follicle stimulating hormone W. Placenta X. Distocia Match the following terms of the male reproduction to their correct definition. 33. _______ The male sex gland that produces sperm. 34. _______ The male sex cell that is responsible for fertilization. 35. _______ Small structures in the testicles that are responsible for sperm production. 36. _______ Sperm and additional fluids produced by several accessory glands. 37. _______ Cord that attaches to the testicle that is responsible for sperm maturing and final development. 38. _______ Tube that connects the epididymis with the urethra. 39. _______ Tube that carries urine from the bladder. 40. _______ Organs which contain fluids necessary for sperm survival. 41. _______ Gland that produces seminal fluid necessary for healthy sperm. 42. _______ A sack like structure designed to regulate optimal temperature for sperm production. A. Urethra B. Prostate Gland F. Seminiferous Tubules K. Sperm C. Vas Deferens D. Semen E. Seminal Vesicles G. Scrotum H. Sperm I. Testicle J. Epididymis Using the terms below label the parts of the male reproductive system. 42. _______________________ 43. _______________________ 42. 43. 44. 44. _______________________ 45. _______________________ 46. _______________________ 45. 47. _______________________ 46. 48. _______________________ 47. 48. 49. _______________________ 49. 50. _______________________ 49. 50. 51. 51. _______________________ 52. 52. _______________________ 49. 53. _______________________ 49. 45. 53. Sheath Seminal vesicle Testicle Seminiferous tubules Penis Cowpers gland Epididymus Sigmoid flexure Scrotum Retractor muscles Vas deferens Prostate gland Multiple Choice 54. It takes _____ days for sperm to completely mature. A.40 B.60 C.80 D.100 55. The estrus cycle in cows occurs every ______ days. A. 18 -24 days with 21 being average B. 16 to 16 days C. 45 to 60 days D. 8 to 12 days 56.The estrus cycle in cows lasts _______. A.3 to 5 hours B. 6 to 8 hours C.12 to 18 hours D. 2 to 3 days 57. Most cows should be bred ________ after the onset of standing heat. A. 3 to 6 hrs B. 1 to 2 days C. 18 to 24 hours D. 8 to 12 hours 58. Which of the following is considered the most important fertility indicator? A. Motility or the ability to swim B. Morphology or physical appearance C. Sperm count or concentration D. None of the above. 59. The targeted site to deposit the semen when artificially inseminating cattle is in the ______. A. Vagina B. Uterine body C. Uterine horn D. Cervix E. Ovaduct 60. The semen is deposited in the ______ when the cow is bred naturally. A. Vagina B. Uterine body C. Uterine horn D. Cervix E. Ovaduct 61. Liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and store semen and is stored at approximately ______ degrees F below zero. A. - 100 B. - 220 C. - 320 D. -460 62. A semen storage tank should be filled before the liquid nitrogen level drops below ______. A. 4 inches B. 2 inches C. 6 inches D. 1 inch 63. A tank with the outer jacket damaged and the vacuum gone will start to loose its insulating value and the nitrogen will boil off in less than ______ hours. A. 12 B. 24 C. 36 D. 48 64. Semen should be thawed at __________ degrees F for at least _______ seconds. A. 95 degrees, 45 seconds B. 100 degrees 60 seconds C. 45 degrees 95 seconds D. 99.8 degrees for 1 minute. 65. Never keep canes of semen raised out of the tank for more than ______ seconds. A. 5 B. 10 C. 30 D. 45 66. In 2002 there were over __________ embryo transfer calves registered in the United States. A. 5,000 B. 10,000 C. 15,000 D. 25,000 67. Most embryo transfer cows will produce ______ viable embryos. A. 5-7 B. 3-5 C. 8-10 D. 10-15 68. Embryo tranfers occur on day _____ because, prior to this time, the embryo is in the oviduct and has not traveled into the uterus where it can be non-surgically removed. A. 3 B. 7 C. 16 D. 21 69. Which of the following is not a method used to estrus synchronize cattle. A. Prostaglandin injection B. Gonadotropin injection C. MGA feed additive D. A vaginal implant E. These are all methods used to synchronize cattle 70. Which of the following methods of estrus synchronization is the simplest, the most common, and the most economical? A. Prostaglandin injection B. Gonadotropin injection C. MGA feed additive D. Vaginal implant 71. The major limitation of prostaglandin injection is that it does not affect animals that do not have a corpus luteum. Which of the following hormones is used in conjunction with prostaglandin to help minimize the differences in follicular development and produce a higher estrus response? A. Prostaglandin injection B. Gonadotropin injection C. MGA feed additive D. A vaginal implant 72. Which of the following methods of estrus synchronization is known to advance puberty in heifers? A. Prostaglandin injection B. Gonadotropin injection C. MGA feed additive D. Vaginal implant 73. Which of the following is not considered a visual sign of stage one labor in cows? A. The cow will often separate from the herd. B. The cow will stand up and lay down repeatedly. C. Vaginal discharge and uterine contraction are present. D. The water sack is present. 74. When does stage one labor end and stage two labor begin? A. When the calf is born B. When the calf enters the birth canal C. When no progress has been made over a 3 to 4 hour period. D. All of the above. 75. What takes place during stage three of labor? A. The calf is born B. The placenta is passed C. The calf enters the birth canal D. The water sack breaks. 76. Which of the following situations is a signal that birthing assistance is needed. A. The cow is in stage two labor, and has been straining for more than 30 minutes with no progress. B. The water sack is present for more than an hour and the animal has quit pushing. C. The animal is showing signs of severe stress and fatigue. D. It can be visually determined that the calf is coming in an abnormal way. E. All of the above. 77. Research has shown that calves born to mothers experiencing distocia are ____ times as likely to die than those born without difficulty. A. two B. four C. six D. eight 78. Pelvic area is _____ % heritable A. 35 B. 45 C. 55 D. 65 True False 79. ______ Bad health can affect the reproductive performance of the bull several months after the bull has recovered? 80. ______ Most males produce some sperm with physical abnormalities. 81. ______ When Artificial inseminating cattle one should always use the right hand inside the cow because most people are right handed and it is easier to manipulate the cervix. 82. ______ The squeeze shute is a convient and cost effective way of artificially inseminating cattle and is recommended by most A.I. professionals. 83. ______ When the semen is deposited in the reproductive tract, it is recommended that the plunger on the inseminating gun be quickly depressed to help the sperm cells travel up each uterine horn. 84. ______ The uterine lining is very thin and delicate and can easily be damaged if the technician is not careful when passing the inseminating gun through the cervix. 85. ______ Semen, if deposited correctly in the uterine body should travel up both uterine horns. 86. ______ The best indication that a semen tank has been damaged is a frost spot on the outside of the tank. 87. ______ To avoid frost bite on the skin, it is recommended that the AI technician wear cotton gloves when removing and handling semen out of a semen tank. 88. ______ When loading a straw of semen into a gun, the cotton plug end of the straw should be loaded into the gun first. The other end should be cut 1/4 of an inch back from the end of the straw. 89. ______ If the semen tank goes dry and is void of liquid nitrogen, the semen can be refrozen with minimal damage to the semen. 90. ______ Research has shown that the temperature of semen will change to the environmental temperature in about 30 seconds if held in an unprotected gun. 91. ______ To maintain the 95 degree temperature after thawing, the gun should be placed in a hot sterile wash cloth until you are ready to insert it into the cow. 92. ______ So the semen will thaw at a uniform rate, when removing a straw of semen from the storage tank and placing it in the thawing unit, the straw should not be touched with your fingers. 93. ______ When performing an embryo transfer, the recipient animal must be sychronized so that she comes into heat at approximately the same time as the donor animal, and the egg is implanted into the recipient animal between days 6 to 8 of their heat cycle. 94. ______ Because of the many benefits of estrus synchronization, it is generally cost effective whether you are breeding naturally or using artificial insemination. 95. ______ After the first week of the breeding season, breeding the natural heat cycle of cows only results in about 21% of the animals becoming pregnant. If estrus sychronization is used, 45 to 55 percent of the animals can be pregnant the first week. 96. ______ Research shows that almost 45% of cattle will come into heat between the hours of midnight and 6:00 am. 97. ______ Flexing or bending the limbs is the best way to tell if a calf is being born forward or backwards. Short Answer 98. Semen quality is evaluated on what three Criteria? A. B. C. 99. List five advantages of artificial insemination over natural breeding: A. B. C. D. E. 100. Explain how to check the level of liquid nitrogen in a semen storage tank. 101. List three advantages to embryo transfer: A. B. C. 102. List 4 advantages to estrus synchronization: A. B. C. D. 103. When pulling a calf that is forward, why is the calf rotated if it becomes hip locked in the pelvis of the cow? 104. Explain why a calf being delivered backwards may die if it is not delivered quickly? 105. What are the three most common mistakes made by people when helping their cows calve? A. B. C.