REVIEW SHEET – ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
advertisement

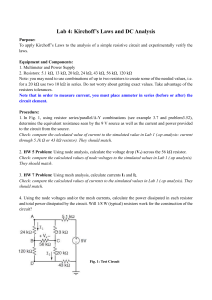
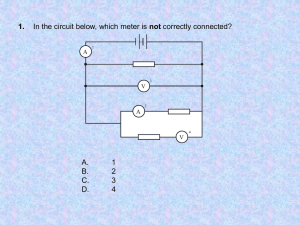
Review Sheet – Electric Circuits 1. Read chapters 19 and 20. 2. Terms to know: circuit, alternating current, direct current, electron flow, conventional current, drift velocity, conduction electrons, voltage drop, potential difference, Ohmic device, non-Ohmic device, power, charge, energy, schematic, variable resistor, series circuit, parallel circuit, fuse, circuit breaker, ground, short circuit, open circuit, equivalent resistance, junction, ammeter, voltmeter, multimeter. 3. Define: a) resistance b) electric current 4. State Ohm’s Law. 5. a) What is the difference between direct current and alternating current? b) What is the difference between electron flow and conventional current? c) What is the source of DC? d) What is the source of AC? 6. a) If a circuit has a one amp current flowing through it, how many coulombs of charge pass a given point in one second? b) How many electrons pass that point in one second? 7. a) What is the cause of resistance in a wire? b) What four factors affect the resistance of a wire? How do they affect it? c) What type of wire is the best conductor? d) What type of wire has the most resistance? 8. What is the difference between an Ohmic device and a non-Ohmic device? Give an example of each. 9. a) What are the formulas for mechanical power? b) What are the formulas for electrical power? 10. Be able to sketch graphs for power, resistance and current. 11. Be able to read and draw schematic diagrams for simple circuits as well as series and parallel circuits, including meters. 12. a) How is an ammeter connected into a circuit? b) How much internal resistance does an ideal ammeter have? c) How is a voltmeter connected into a circuit? d) How much internal resistance does an ideal voltmeter have? 13. What are some common uses of variable resistors? 14. a) What is the equivalent resistance of two 50 Ω resistors connected in series? b) What is the equivalent resistance of two 50 Ω resistors connected in parallel? 15. A series circuit consists of a 100 Ω and a 50 Ω resistor connected to a battery. a) Which resistor, if either, has a greater voltage drop? b) Which resistor, if either, has more current running through it? c) Which resistor, if either, dissipates more power? 16. A parallel circuit consists of a 100 Ω and a 50 Ω resistor connected to a battery. a) Which resistor, if either, has a greater voltage drop? b) Which resistor, if either, has more current running through it? c) Which resistor, if either, dissipates more power? 17. Adding an extra resistor to an existing series circuit will cause the total current to (increase/decrease/remain the same) while the total resistance will (increase/decrease/remain the same). The voltage drops across the remaining resistors will (increase/decrease/remain the same). 18. Adding an extra resistor to an existing parallel circuit will cause the total current to (increase/decrease/remain the same) while the total resistance will (increase/decrease/remain the same). The voltage drops across the remaining resistors will (increase/decrease/remain the same). 19. What is the purpose of a fuse and a circuit breaker in your household electrical system? What is the difference between the two? 20. A kilowatt-hour is a unit of : power energy current voltage resistance time Comparison between Series and Parallel Circuits Characteristic Voltage Current Resistance Power Light Bulbs Series Circuit Parallel Circuit Quantity Resistance Potential Difference (Voltage) Charge Current Energy Power Resistivity Length Crosssectional Area Variable Unit Name Unit Symbol Vector or Scalar Formulas