Higher Human Biology: Thickened nuchal
advertisement
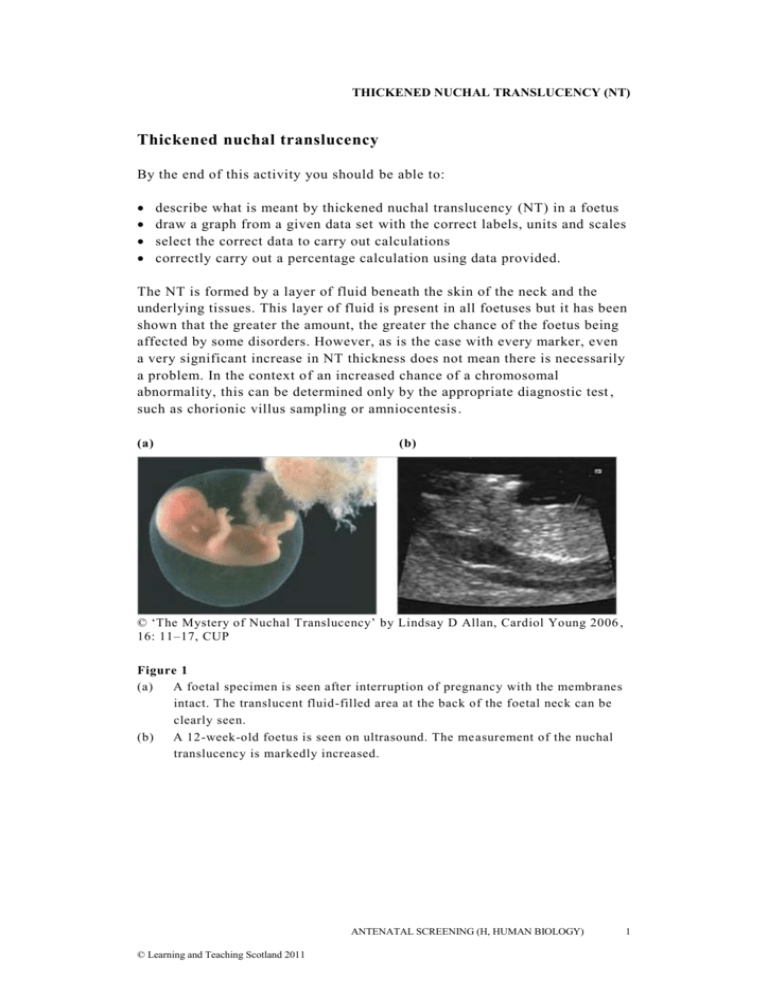
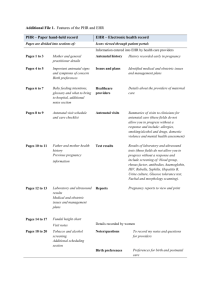
THICKENED NUCHAL TRANSLUCENCY (NT) Thickened nuchal translucency By the end of this activity you should be able to: describe what is meant by thickened nuchal translucency (NT) in a foetus draw a graph from a given data set with the correct labels, units and scales select the correct data to carry out calculations correctly carry out a percentage calculation using data provided. The NT is formed by a layer of fluid beneath the skin of the neck and the underlying tissues. This layer of fluid is present in all foetuses but it has been shown that the greater the amount, the greater the chance of the foetus being affected by some disorders. However, as is the case with every marker, even a very significant increase in NT thickness does not mean there is necessarily a problem. In the context of an increased chance of a chromosomal abnormality, this can be determined only by the appropriate diagnostic test , such as chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis . (a) (b) © ‘The Mystery of Nuchal Translucency’ by Lindsay D Allan, Cardiol Young 2006 , 16: 11–17, CUP Figure 1 (a) A foetal specimen is seen after interruption of pregnancy with the membranes intact. The translucent fluid-filled area at the back of the foetal neck can be clearly seen. (b) A 12-week-old foetus is seen on ultrasound. The me asurement of the nuchal translucency is markedly increased. ANTENATAL SCREENING (H, HUMAN BIOLOGY) © Learning and Teaching Scotland 2011 1 THICKENED NUCHAL TRANSLUCENCY (NT) Questions The following table shows the incidence of chromosomal defects according to foetal NT in a screening study involving 96,127 singleton pregnancies. 1. Complete the table then draw a bar graph of the results and describe the trend. NT (mm) Total number Number of chromosomal defects <3.4 95,086 315 3.5–4.4 568 120 4.5–5.4 207 69 5.5–6.4 97 49 >6.5 166 107 Percentage of chromosomal defects 2. The following table gives the results of a study on the pregnancy outcome of foetuses with increased NT. The study measured the NT thickness in 1930 pregnancies. An enlarged NT thickness was discovered in 27 foetuses. 2 ANTENATAL SCREENING (H, HUMAN BIOLOGY) © Learning and Teaching Scotland 2011 THICKENED NUCHAL TRANSLUCENCY (NT) (a) Which result from the table best supports the statement that even a very significant increase in NT thickness does not diagnos e a foetal problem? Justify your answer. (b) What percentage of foetuses had an enlarged NT measurement? (c) What was the mean enlarged NT thickness? (d) What percentage of foetuses with an enlarged NT measurement had an adverse outcome? (e) What percentage of foetuses with a normal karyotype were found to have anomalies discovered at ultrasound examination? ANTENATAL SCREENING (H, HUMAN BIOLOGY) © Learning and Teaching Scotland 2011 3 THICKENED NUCHAL TRANSLUCENCY (NT) Answers 2. 4 (a) The result that shows a thickened NT measurement of 9.3mm. This is the largest NT measurement yet there was a live birth with no fetal anomalies. (b) Number with enlarged NT = 27, total number studied = 1930 . Percentage with increased NT thickness = 27/1930 × 100 = 1.4% (c) Total NT thickness of 27 results in the table = 136.3. Mean = 136.3/27 = 5.05mm (d) 27 foetuses had an enlarged NT measurement. Only 10 were normal so 17 had an adverse outcome. 17/27 × 100 = 62% (e) 6 out of the 17 foetuses who had abnormalities discovered by ultrasound had a normal karyotype. 6/17 × 100 = 35% ANTENATAL SCREENING (H, HUMAN BIOLOGY) © Learning and Teaching Scotland 2011