Supplemental Tables and Figure Legends
advertisement

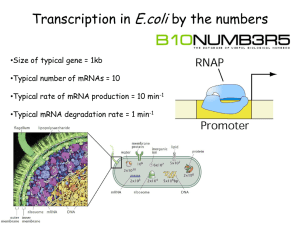
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Construction of the H(hsp/TP5) and H(hsp/TP6) transformation vectors. A PCR-amplified cassette containing the P element was inserted into a BamHI site (B) downstream of the Drosophila hsp70 promoter in a transitional plasmid. These PCRamplified cassettes spanned base pairs 38 to 2867 in the canonical P element (O’Hare and Rubin 1983). The hsp70/P fusions, flanked by NotI (N) sites, were then inserted into a NotI site in the 5’ portion of a hobo element in the transformation vector pHawN to produce the H(hsp/TP5) and H(hsp/TP6) constructs. Rectangles in the P elements are exons or portions of exons, and the darkened regions within them either are untranslated or are translated out of frame. Bent arrows indicate the direction of transcription from the P, hsp70 and hobo promoters. This schematic is not drawn to scale. Figure S2. RT-PCR analysis of expression of fully spliced germ-line mRNA from native (N) and transgenic (A-C) TP6 elements. The CP transgene, which expresses Ptransposase mRNA in the germ line, was used as a control. Samples with (+) and without (-) reverse transcription (RT) were analyzed by PCR amplification with primers P∆0/1-d and P∆2/3-u. This amplification generates a 1442 bp product from fully spliced germ-line CP mRNA and a 512 bp product from fully spliced germ-line TP6 mRNA. The 702 bp product detected in the transgene samples probably results from P∆2/3-u binding downstream of the 2/3 intron in TP6 cDNA and priming DNA synthesis through it. 1 Figure S3. RT-PCR analysis of expression of native (N) and transgenic (A-C) TP6 elements to detect mRNA that has retained the 2/3 intron. The CP transgene, which expresses P-transposase mRNA in the germ line, was used as a control. Samples with (+) and without (-) reverse transcription (RT) were analyzed by PCR amplification with primers P∆0/1-d and P2575-u. This amplification generates a 2039 bp product from CP mRNA that has lost the 0/1 and 1/2 introns, but that has retained the 2/3 intron., and it generates an 1109 bp product from TP6 mRNA that has lost the 0/1 intron but that has retained the 2/3 intron. Products that would indicate loss of the 2/3 intron are not distinctly visible in this gel; thus, fully spliced cDNA is much less abundant than cDNA that retains the 2/3 intron. Figure S4. RT-PCR analysis to compare P-element mRNA levels in flies carrying the CP transgene and either native (N) or transgenic (A-D) TP5 elements. Samples with (+) and without (-) reverse transcription (RT) were analyzed by PCR amplification with appropriate primers. Each experimental set consisted of eight independently isolated RNA samples, four from flies carrying the native TP5 element and four from flies carrying a TP5 transgene. These samples were randomly paired to compare P mRNA levels between native and transgenic genotypes. (A) Amplification using primers Aub-d and Aub-u to detect aubergine mRNA. (B) Amplification using primers TP5-d and P∆2/3-u to detect germ-line mRNA from the TP5 elements. The expected product is 471 bp long; the 661 bp product probably arises from P∆2/3-u binding downstream of the 2/3 intron in unspliced TP5 cDNA and priming DNA synthesis through it. (C) Amplification using primers P∆0/1-d and P∆2/3-u to detect germ-line P-transposase mRNA from the 2 CP transgene. The expected product is 1495 bp long. The 1685 bp product is probably due to P∆2/3-u binding downstream of the 2/3 intron in partially spliced CP cDNA and priming DNA synthesis through it. (D) Amplification using primers P∆0/1-d and P2075-u to detect CP mRNA that retains the 2/3 intron, i.e., that is not specific to the germ line. The expected product is 1592 bp long. 3 Table S1. Primers used in PCR analysis of RT products. Name Sequence Aub-d 5’-(1937)TACGGGAATGACGGACGCTATG(1958)-3’ Aub-u 5’-(2967)GTGTTCGTTTACGGTGGAGAAGTAG(2943)-3’ P318-d 5’-(318)GCACCTGCAAAAGGTCAG(335)-3’ P∆0/1-d 5’-(426)GGGAGTACACAAACAGA(442)/(501)GTCCT(505)-3’ TP5-d 5’-(424)GTGGGAGTACACAA(437)/TG/(1524)TCATT(1528)-3’ P1828-d 5’-(1828)CAAGCCGTCTCAACCAAG(1845)-3’ P∆2/3-u 5’-(2168)CCCGAATTTCTTAACATTTCTGTATTCCTGG(2138)/CTATTAT(1941)-3’ P2075-u 5’-(2075)CACAATAGACAGCACATAACTACC(2052)-3’ P2575-u 5’-(2575)CAACATCGACGTTTCGCGCTG(2555)’-3’ Nucleotide positions within the aub gene and P element are given in parentheses. Intron and deletion breakpoints are indicated by a slash and nucleotides inserted at deletion breakpoints are given between slashes. Sequences that prime DNA synthesis downstream in the gene or element are denoted with the letter d; sequences that prime DNA synthesis upstream are denoted with the letter u. The concentration of all primer stock solutions was 20 ng/l except for P∆2/3-u, which was 40 ng/l; 1.9 l each primer was added to each PCR. The temperature profile for all the PCRs involving the P∆2/3-u primer was 3 min at 92o C, 2 min at 63o C, 3 min at 72o C for the first cycle and 1 min at 4 92oC, 2 min at 63o C, 3 min at 72o C for the subsequent 22 or 29 cycles. For all other PCRs, the annealing temperature was lowered from 63o C to 60o C. 5 Table S2. Gonadal dysgenesis in the offspring of reciprocal F1 hybrids between TP or H(hsp/P) stocks and the M5B#1 strain (experiment 1). Cross I TP or H(hsp/P) Stocka present in F2 Cross II F1 Stock x M5B#1 No. of F2 %GD + SEb Stock x M5B#1 F1 No. of F2 %GD + SEb yw - 500 100.0 + 0.0 467 99.8 + 0.2 TP5-N + 265 34.7 + 4.1 203c 82.3 + 3.9 - 241 46.7 + 5.5 186c 83.9 + 3.8 + 424 1.9 + 0.8 317 65.1 + 4.9 - 418 1.9 + 0.7 315 67.0 + 5.6 + 339 98.7 + 0.9 109 100.0 + 0.0 - 345 100.0 + 0.0 89d 100.0 + 0.0 + 410 99.0 + 0.5 179d 99.6 + 0.4 - 410 98.6 + 0.7 202 99.4 + 0.4 + 380 99.0 + 0.6 200 100.0 + 0.0 - 364 99.8 + 0.2 190 99.2 + 0.8 + 360 99.7 + 0.3 130 98.8 + 0.9 - 326 100.0 + 0.0 120 99.7 + 0.3 + 328 99.5 + 0.4 360 100.0 + 0.0 - 350 99.8 + 0.2 335 100.0 + 0.0 + 351 99.2 + 0.4 236 100.0 + 0.0 TP6-N SP-B KP-3 TP5-C TP6-A TP6-B TP6-C 6 - 357 100.0 + 0.0 270 100.0 + 0.0 Except where indicated, the data in each group came from 25 replicate vials. a y w is an M strain. TP5-N and TP6-N are strains with the native telomeric P elements on the X chromosome; other entries are strains with H(hsp/P) transgenes that contain the indicated P element. b Unweighted mean percentage of GD + SE c These flies came from 16 replicate vials. d These flies came from 15 replicate vials. 7 Table S3. Gonadal dysgenesis in the offspring of reciprocal F1 hybrids between TP or H(hsp/P) stocks and the M5B#1 strain (experiment 2). Cross I TP or H(hsp/P) Stocka present in F2 Cross II F1 Stock x M5B#1 No. of F2 %GD + SEb Stock x M5B#1 F1 No. of F2 %GD + SEb yw - 457 100.0 + 0.0 362 99.7 + 0.3 TP5-N + 327 46.5 + 5.2 321 83.1 + 4.2 - 283 58.9 + 5.1 279 87.4 + 3.5 + 310 3.8 + 1.5 252 64.6 + 5.3 - 267 1.2 + 0.8 221 68.1 + 6.0 + 299 99.5 + 0.5 121 100.0 + 0.0 - 304 100.0 + 0.0 122 100.0 + 0.0 + 379 99.4 + 0.4 262 100.0 + 0.0 - 257 100.0 + 0.0 159 99.5 + 0.5 + 173 99.5 + 0.5 211 99.6 + 0.4 - 160 100.0 + 0.0 179 100.0 + 0.0 + 204c 98.4 + 1.3 214 95.9 + 1.9 - 210c 99.7 + 0.3 184 93.3 + 2.1 + 276 98.5 + 1.1 48d 100.0 + 0.0 - 279 99.7 + 0.3 59d 96.9 + 3.1 + 298 99.2 + 0.5 118 100.0 + 0.0 TP6-N SP-A KP-7 KP-14 TP5-A TP5-B TP5-D 8 - 257 99.6 + 0.4 108 99.5 + 0.5 Except where indicated, the data in each group came from 24-25 replicate vials. a y w is an M strain. TP5-N and TP6-N are strains with the native telomeric P elements on the X chromosome; other entries are strains with H(hsp/P) transgenes that contain the indicated P element. b Unweighted mean percentage of GD + SE c These flies came from 23 replicate vials. d These flies came from 13 replicate vials. 9 Table S4. Gonadal dysgenesis in the offspring of reciprocal F1 hybrids between strains with the native telomeric P elements (TP5-N and TP6-N) and the M strain Samarkand (experiment 2). Cross I TP present Stock TP5-N TP6-N Stock x M Cross II F1 Stock in F2 No. of F2 %GD + SEa No. of F2 %GD + SEa + 414 97.8 + 0.9 247 94.6 + 2.9 - 434 98.6 + 0.5 219 100.0 + 0.0 + 398 89.2 + 2.5 294 99.1 + 0.5 - 391 90.3 + 2.2 291 98.5 + 0.8 The data in each group came from 24-25 replicate vials. a x M F1 Unweighted mean percentage of GD + SE 10 Table S5. Gonadal dysgenesis in the offspring of the stocks used to analyze the effects of the native telomeric P elements (TP5-N and TP6-N) on germ-line transposase mRNA levels. Stock No. of vials No. of %GD + SEa M cytotype 25 471 99.8 + 0.4 TP5-N 25 472 6.2 + 1.9 TP6-N 24 459 64.3 + 6.9 a Unweighted mean percentage of GD + SE 11