ELDAS User Requirements Document
advertisement

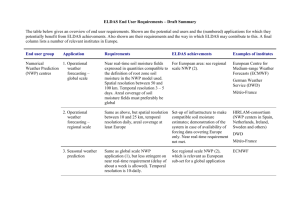
ELDAS URD (draft) 1 ELDAS User Requirements Document (DRAFT) Project ID EVG2-2001-00013 Date of preparation 12-2-2016 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Identification of sectors 3. List of institutions & requirements ELDAS URD (draft) 2 1. Introduction As a first iteration of the ELDAS User Requirements Document (URD) an inventory of potential types of institutions (companies, governmental services, research institutions, …) that has a potential interest in ELDAS products has been compiled in section 2. This compilation is based on the experience of members of the ELDAS team, who represent a wide range of potential users of soil moisture fields at regional European scale. Section 3 provides a list of potential institutions and their specific requirements with respect to the ELDAS product. This section is to be completed in a later stage of the ELDAS project. 2. Identifications of sectors ELDAS aims at the design and test of an infrastructure for soil moisture assimilation at the regional to global scale. During the project period, a prototype system will be designed and implemented, and experiments will be carried out addressing the validation and application of the soil moisture fields produced with the ELDAS system. The motivation of this project is based on a number of potential impacts of regional scale soil moisture: Short- and medium-range Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) is shown to be sensitive to the treatment of soil moisture in the prediction models. The land surface routines used in these applications are necessarily simplifications of reality and suffer from systematic shortcomings. NWP forecasts need to be kept on a realistic track by means of corrections derived from available routine observations. ELDAS is designed to be highly compatible with this data correction practice, by its choice of spatial and temporal resolution, type of data used and algorithms applied. Seasonal predictions by these NWP-centers are known to be sensitive to the hydrological memory of the soil water reservoir. In particular the occurrence of persistent droughts is related to systematic interaction between the soil moisture reservoir and the atmospheric hydrological cycle. ELDAS products are assumed to contain potentially useful information on the soil moisture conditions that can be related to the hydrological cycle on a seasonal time scale, and may therefore serve as indicator for seasonal weather prediction, including the prediction of droughts. Surface floodings is partially dependent on the state of the soil moisture reservoir at the moment of excessive precipitation events. An accurate monitoring of soil moisture evolution by a system similar to ELDAS may help in assessing the risk of these floodings when excessive precipitation is expected. Future climate predictions using numerical climate models show a wide range of hydrological conditions for a given greenhouse gas scenario. This is partially related to differences between (and uncertainties of) land surface and soil moisture parameterization schemes used in these climate models. ELDAS products may help in the creation of a soil moisture database compatible to the quantity that is actually simulated in these climate models, and serve as verification material to assess and improve the quality of climate models. Emphasis of the ELDAS system design is the application of soil moisture assimilation at a regional to continental scale. Methodologies developed and implemented for this ELDAS URD (draft) 3 spatial scale may well be applicable at smaller scales (individual small river catchments or agricultural regions), but this is not explicitly addressed by the ELDAS consortium. Summarizing this discussion, the following sectors may be identified as potential users of ELDAS products: National and European centers for Numerical Weather Prediction and Seasonal Prediction Hydrological services monitoring soil moisture evolution in areas sensitive to floodings after strong precipitation events Climate modeling institutions with expertise on land surface modeling and evaluation of land surface models, in particular the soil hydrological components of these land models. These sectors all require soil moisture fields that extend over spatial scales varying from large river basins to the global scale. The required spatial resolution depends on the application, and varies from order 5 5 km for flood forecasting and mediumrange NWP applications to 252 km2 for seasonal and climate modeling applications. In these large scale applications, temporal resolution is determined by the memory of the soil water reservoir. Updates once per week are deemed sufficient. For short term flood and weather forecasting daily updates of soil moisture fields are necessary. 3. List of institutions and requirements To be compiled ELDAS URD (draft) 4 ELDAS End User Requirements – Draft Summary The table below gives an overview of end user requirements. Shown are the potential end users and the (numbered) applications for which they potentially benefit from ELDAS achievements. Also shown are their requirements and the way in which ELDAS may contribute to this. A final column lists a number of relevant institutes in Europe. End user group Application Numerical 1. Operational Weather Prediction weather (NWP) centres forecasting – global scale 2. Operational weather forecasting – regional scale Requirements ELDAS achievements Examples of institutes Near real-time soil moisture fields For European area: see regional expressed in quantities compatible to scale NWP (2). the definition of root zone soil moisture in the NWP model used. Spatial resolution between 50 and 100 km. Temporal resolution 3 – 5 days. Areal coverage of soil moisture fields must preferably be global European Centre for Medium-range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) Same as above, but spatial resolution between 10 and 25 km, temporal resolution daily, areal coverage at least Europe HIRLAM-consortium (NWP centers in Spain, Netherlands, Ireland, Sweden and others) Set-up of infrastructure to make compatible soil moisture estimates; demonstration of the system in case of availability of forcing data covering Europe only. Near real-time requirement not met. German Weather Service (DWD) Météo-France DWD Météo-France ELDAS URD (draft) End user group Hydrological services Climate research groups 5 Application Requirements ELDAS achievements Examples of institutes 3. Seasonal weather prediction Same as global scale NWP application (1), but less stringent on near real-time requirement (delay of about a week is allowed). Temporal resolution is 10-daily. See regional scale NWP (2), which is relevant as European sub-set for a global application ECMWF 4. Flood forecasting Root zone soil moisture content in big river catchments at 1 – 10 km resolution for estimation of infiltration-excess and flood peak timing and intensity ELDAS-infrastructure may be applied here, but typical ELDAS resolution (20 km) probably too coarse for application UK Environmental Agency, Dept. of Flood Prediction 5. Routine monitoring Near real-time daily precipitation and evaporation estimates at 10 – 20 km resolution Demonstration data bases of evaporation and precipitation fields are produced within ELDAS, but near real-time requirement not met same as above 6. Development and evaluation of climate models Weekly – monthly fields of evaporation, runoff, soil moisture and precipitation at 50 – 100 km resolution, covering at least Europe and preferably global (retrospective analysis possible) Products of ELDAS system compatible with climate model requirements. Analysis of potential value of ELDAS products Laboratoire de Météorologie Dynamique (LMD) Netherlands Institute for Inland Water Management (RIZA) Rossby Centre Sweden