Diffraction Grating Activity
advertisement

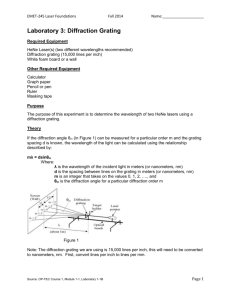
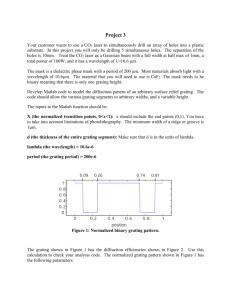
Diffraction Grating Activity Physics Name: Period: A diffraction grating is a series of thin, closely-spaced slits, which allow light waves to pass through. As the waves spread out on the other side of the grating, they can overlap so that they are in phases (with all of the different waves crests lining up) or out of phase (with the different waves lining up so that one’s crest matches another’s trough). Which one happens depends on where you and the difference in the distance between different slits. At the right angle, the waves coming from each slit are exactly one wavelength behind the waves coming from the next closer slit and those waves line up to produce constructive interference and a bright light. At other angles, the waves from one slit are exactly one-half wavelength behind the waves coming from the next closer slit and those waves combine to produce destructive interference and darkness. These regions alternate according to two simple formulae: Maxima: d sin = m where m is the number of the maximum 1 Minima: d sin = (m-2) where m is the number of the minimum In this lab we will investigate the diffraction pattern formed by different diffraction gratings and use it to find the wavelength of a laser pointer and the spacings of the slits in a pair of diffraction grating glasses. Materials Laser Pointer 5300 line/cm Grating Meter Sticks Clipboard Diffraction Grating Glasses Procedure: Part 1: Finding the Wavelength of Your Laser Pointer 1. Arrange your materials as shown in the diagram above. ·Your laser pointer should be resting flat, elevated off the table so that you can shine it through the diffraction grating that is right in front of the laser pointer. ·The diffraction grating should be standing perpendicular to the surface and square to the laser beam, oriented so that the maxima and minima in the diffraction pattern are to the side of the 0th order maximum, not above or below it. ·You should tape a piece of unlined, white paper onto the clipboard to use as a screen to observe that diffraction pattern. Hold the screen in landscape orientation and be sure that the screen is perpendicular to the tabletop and square to the oncoming laser beam. 2. On the diffraction grating slide, find the groove density and use that to calculate the spacing between grooves. Record your result in the space provided above the data table. 3. Turn on the laser pointer and aim it through the diffraction grating. Hold the screen in landscape orientation, as far away from the diffraction grating as you can get and still see two maxima on either side of the 0th maximum. Measure and record the distance from the diffraction grating to the screen. 4. Make a light pencil mark where each maximum appears on the screen. Be careful not to move the screen while you do this. 5. Turn off the laser pointer and remove the screen. Measure the distance from the 0th maximum to the 1st and 2nd maxima, which you marked on the paper. 6. Measure the distance from the 0th maximum to the 1st and 2nd minima. Take the minimum to be the spot exactly between the two adjacent maxima. 7. Based on your measurements, calculate the angle to each maximum and minimum. 8. Use the angle and the appropriate formula to calculate the wavelength of that light wave that created that dot. All of your measurements should agree, but don’t be surprised if they are not exact. 9. Take the average value of the wavelengths you calculated. 10. Find the value of the wavelength printed on your laser pointer and calculate the percent error between your average wavelength value and the manufacturer’s expected wavelength. Data Table: Finding the Wavelength of Your Laser Pointer Grating Spacing: d = Spot Length from Grating to Screen: Distance From Center Angle Wavelength () 2nd Maximum Left 2nd Maximum Right 2nd Minimum Left 2nd Minimum Right 1st Maximum Left 1st Maximum Right 1st Minimum Left 1st Minimum Right Part 2: Finding the Spacing of the Slits on a Diffraction Grating 1. Setup your materials, exactly the same as you did before, but replace the diffraction grating with a pair of toy glasses. 2. Repeat the procedure for Part 1. The only difference will be that the glasses will make a grid of dots (because it has grooves marked in it in both the horizontal and vertical direction). Pick the horizontal line of dots that includes the brightest dot and just use those dots. Ignore the other lines of dots. Data Table: Finding the Spacing of the Slits on a Diffraction Grating Wavelength: = Spot 2nd Maximum Left 2nd Maximum Right 2nd Minimum Left 2nd Minimum Right 1st Maximum Left 1st Maximum Right 1st Minimum Left 1st Minimum Right Length from Grating to Screen: Distance From Center Angle Groove Spacing (d)