Drinking causes damage you can`t see……………
advertisement

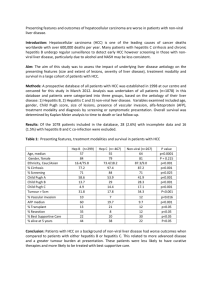
Transmission routes for Hepatitis B & C (blood borne viruses) Unprotected sex, wearing a condom forms a barrier between the condom and the mouth, vagina or anus. Condoms stop sperm and anything else getting in. Although pubic lice can still be transmitted as they live in the pubic region. Mother to child, blood borne viruses can be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her unborn child during pregnancy (the risk is usually higher the higher the viral load). Viruses can also be transmitted during childbirth, and some through breast feeding. Needles and syringes, used needles can have traces of blood on them. Therefore, sharing or re-using needles can cause the transmission of Hepatitis B & C. Needles are used for injecting drugs, vaccines, steroids etc…. . Syringes and filters can also have traces of blood on them and should never be shared or re-used. Tattooing and piercing, involves breaking of the skin, so there is a possible route of transmission. Blood borne viruses can be harboured in ink pots used to colour tattoos, so you insist on new ones. Any form of piercing including acupuncture has the potential to transmit blood borne viruses. Sharing piercing equipment and jewellery is also a potential risk. Blood & blood products are screened in the United Kingdom for HIV, Hepatitis C and Hepatitis B so are relatively safe. However, some countries do not have sufficient screening measures therefore could be potentially being infectious. Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis A Symptoms Symptoms Symptoms Jaundice, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, joint pain, diarrhoea, nausea & vomiting Jaundice, fatigue, dark urine, abdominal pain, nausea, loss of appetite Jaundice, fatigue, loss of appetite, fever, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea Transmission Transmission Transmission Infected blood or bodily fluids enter into another person, e.g. through unprotected sex, sharing needles (and other paraphernalia), mother to child, tattooing and piercing When infected blood or bodily fluid enters into another person, e.g. through unprotected sex, sharing needles (and other paraphernalia), mother to child, tattooing and piercing Is present in the faeces of people infected with the virus. Transmission occurs via the oral-faecal route; usually if someone has not washed their hands properly, resulting in other things becoming contaminated. Prevention Prevention Prevention Hepatitis A vaccine, Immunoglobulin can be used in the short term to offer some protection if exposed to the virus, always wash hands with soap & water after going to the toilet/changing nappies/before preparing food Hepatitis B vaccine Use condoms (inc use on sex toys), don’t share needles etc, use of sterile needles & equipment for tattooing/piercing, do not share razors or tooth brushes, immunoglobulin and vaccination of babies born to infected mothers, do not donate blood or blood products, do not donate breast milk No vaccine Do not share needles etc, use sterile needles for tattooing/piercing, do not share razors, do not share tooth brushes, always use condoms (including on sex toys), do not donate blood or blood products, do not donate breast milk Long term Long term Long term It is only an acute infection (less than 6mths, you can only have the virus once, 10% of those infected may experience symptoms for up to 1yr, it is more serious in the very young/elderly/those with an impaired immune system Only 10-15% of adults infected with the virus with have a long term chronic infection (there are treatments available), long term liver damage can cause fibrosis and cirrhosis (cell death and loss of liver function), 15% of those with chronic infection will die from liver disease 85% of adults infected with the virus with have a chronic infection, there are treatments available, long term liver damage can lead to cirrhosis and fibrosis (cell death & loss of liver function), 5% of those with chronic infection will die of liver disease