An Introduction to SYSTAT
advertisement

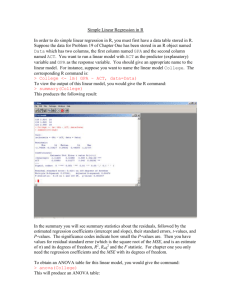
An Introduction to SYSTAT 1. Creating Data/Importing/Saving Data To create data, click File->New->Data, and enter the dataset. You can also import data by using File->Open->Data. The supported file formats for import include Excel, SPSS, SAS, MINITAB, and JMP. Once inputted, data can be saved in the SYSTAT file format. 2. The SYSTAT user interface The organization of the user interface is somewhat complicated. The command window is a .syc file that appears at the bottom of the screen. SYSTAT outputs the results of commands in a .syo file, which is accessible by clicking on a tab toward the top of the screen. Any graphics are also outputted to a separate tab. SYSTAT stores the results of user commands in the Workspace window on the left of the screen. The user has two options for analysis with SYSTAT: using the GUI, or using the command line. To run a command, right click in the .syc file. You then can choose to run the current line or to run the commands from the current line to the end. To specify a specific data set to use, type “USE FileName.extension”. Here’s an example of running commands on the SYTAT user interface. Figure 1: The SYSTAT user interface 3. Using the GUI in SYSTAT Basic statistics can be found under the Analyze tab. To analyze column variables, click Analyze>Basic Statistics. To analyze row variables, click Analyze->Row Statistics. You can also use the Analyze bar to get contingency tables, scatter plot matrices and correlation matrices, and stemand-leaf plots. To get basic graphs, use the Graph tab. Options include histograms You can also do a regression analysis using the GUI. Click Analyze->Regression and choose what type of regression you want to do. Options include least squares and logit regression. SYSTAT will output summary information, including residual plots. Some of the regression output will show up on in the Workspace window toward the left of the screen. You can tell SYSTAT to save the residuals. Other options include bootstrapping and normality tests. Figure 2: Using the GUI for Least Squares regression You can also do ANOVA using the GUI. Click Analyze->Analysis of Variance. 4. Basic command lines in SYSTAT Construct a qqplot Plot Y*X Sort by a variable QPLOT varname PLOT VarY*VarX SORT varname Normality test Ttest Bootstrap from a dataset Summary statistics CSTATISTICS varname/ ADTEST SWTEST TESTING TTEST var1 var2 USE Filename.extension SAMPLE BOOT(nsamples,sample_size)/MEAN MEDIAN CSTATISTICS variable1 variable2 CSTATISTICS varname 5. Linear Regression You have more control over your model form if you use the command line for regression. For example, to run a multiple linear regression including interaction and quadratics, you might type: REGRESS USE POP.syz MODEL GRADE=AGE RACE$ GOALS$ GENDER$ AGE*GOALS$ AGE*AGE ESTIMATE SYSTAT will automatically produce not only the standard estimates, but also interaction plots. To have SYSTAT choose a model using stepwise regression, you might type: REGRESS USE POP.syz MODEL GRADE=AGE RACE$ GOALS$ GENDER$ AGE*GOALS$ LOOKS MONEY LOOKS*MONEY START / FORWARD STEP / AUTO STOP SYSTAT will start with the variables in the model statement, run stepwise regression, and return the optimal model. If you want to save the residuals when running a regression analysis, type “SAVE RESIDS/ RESID DATA” before the ESTIMATE statement. 6. Logistic Regression Just add the keyword LOGIT before the MODEL statement; for example: USE Barley.syz LOGIT MODEL VAR_5=CONSTANT+Y1931 ESTIMATE SYSTAT will output the ROC curve 7. Fixed Effect ANOVA using SYSTAT A. One-Way ANOVA For a one-way ANOVA, you specify first the labels of the category, and then the dependent variable you want to consider. For example, if you wanted to know whether the price of whiskey depends on whether or not the company is a monopoly, you would type: ANOVA USE WHISKEY.syz CATEGORY POLICY$ DEPEND PRICE ESTIMATE The output includes the interaction plot. B. Two-Way ANOVA The format is basically the same for a two-way ANOVA; just add an extra variable to the CATEGORY statement. In SYSTAT, the ANOVA command automatically adds interactions to the model and tests for them. C. Options When Using ANOVA Add a covariate (goes before ESTIMATE statement) Estimate effects Specify type of Sum of Squares COVARIATE varname ESTIMATE ESTIMATE /SS=TYPE3 8. Random Effects As far as I can tell, to do a random effect ANOVA, you need to use the MIXED command. For example, suppose you wanted to see if barley yield depended on variety and site, and that site was considered a random effect. You would type: USE BARLEY.syz MIXED CATEGORY VARIETY$ SITE$ MODEL Y1932=VARIETY$ + SITE$ RANDOM SITE$ ESTIMATE 9. Manipulating datasets In some cases you may want to alter a dataset. I will give examples to illustrate how to do basic data manipulation. Create new variable Drop a data point Merge data sets IF SMOKING < 100 THEN LET SMOKERATE$='LOW' IF SMOKING==77 THEN DELETE MERGE Smoke2.syz Smoke1.syz Delete a column variable DELETE COLUMNS=SMOKING