Ride The Convection Currents
advertisement

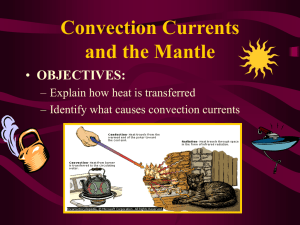
Name:____________________________________ Date:___________________ RIDE THE CONVECTION COASTER CONVECTION CURRENTS on e Did you know that the continents are moving a few centimeters every year? This supports the Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift. However, scientists are not always as smart as they think they are. Wegener’s theory did not provide reasons why the continents moved. There must be some reason for this phenomenon. In this investigation, you will identify the forces that cause the movement of the Earth’s crust. Objective: When you have completed this investigation, you should be able to analyze a convection cell model in order to explain the movement of Earth’s plates. Activity 1: Exploration 1. Pour three to five drops of liquid B into liquid A. 2. Briefly record your observation.____________________________________________________. 3. Pour three to five drops of liquid A into liquid B 4. Briefly record your observation ____________________________________________________. Activity 2: Teacher Demonstration 1. Observe the materials in the teacher demonstration. 2. Predict how the cold water will act when combined with the warm water. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Observe the teacher demonstration and record your observations in Figure 1. Figure 1: Teacher Demonstration Observations Warm Water Warm Water Cold Water The middle partition will be raised a few centimeters . ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ 4. Determine the accuracy of your prediction. Provide examples to support your response. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Activity 3: Understanding Convection Currents 5. Read pages 16 – 17 in Prentice Hall: Science Explorer: Inside Earth. 6. Complete the sentences in the paragraph below to explain how convection currents form within the earth to move earth’s plates. Use the words in the word bank to complete the paragraph. Some words (terms) are used more than once. WORD BANK asthenosphere convection convection currents core denser fluid magma plates Convection is the heat transfer by the movement of a heated ______________________. During _______________________, heated particles of ________________________ within the earth’s mantle begin to flow, transferring heat energy from one part of the mantle to another. Heat from Earth’s _______________________ is the source for convection currents in the earth. Hot columns of magma are heated by the core making them less dense. This material rises slowly through the __________________________, the upper part of the earth’s mantle. At the top of the asthenosphere, the hot material spreads out and pushes the cooler material out of the way. The cooler, _________________ material sinks back into the asthenosphere. Over and over, the cycle of rising and sinking occurs in the asthenosphere to create __________________________ ____________________. The convection currents produce movements that can cause the _____________________ to move. Now that you have an idea about convection currents within the earth, you need to apply this information to explain the demonstration in Activity 1. 7. Refer to the teacher demonstration in Activity 1. ESS - 114 8. Explain why the cold water behaved as it did in the warm water. Use evidence from the text to support your response. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Activity 4: Modeling Convection Currents…A Teacher Demonstration Materials portable burner 3 wooden splints pot water safety goggles Procedure: 9. Read the procedures, “Modeling Plate Movement.” Modeling Plate Movement A. B. C. D. Fill the pot ¾ of the way with water. Place the pot on top of the burner. Place the wooden splints in the water so that they are next to each other. Push the wooden splints together. Carefully let go. If the splints drift apart, gently move them back together again. E. Turn on the burner. F. Observe the two splints as the water heats up. G. Record your observations in the box below. Observations 10. Observe the investigation. ESS - 115 11. Identify how the materials used in the investigation represent the structures of the earth. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Analysis 1. On the diagram in Figure 2, “Cross Section of Earth,” sketch directional arrows showing the movement of the magma within the mantle. Figure 2: Cross Section of Earth crust mantle core 2. Explain how convection currents within the earth cause the crust and the continents to move. Use evidence from the investigation and the text to support your response. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ ESS - 116