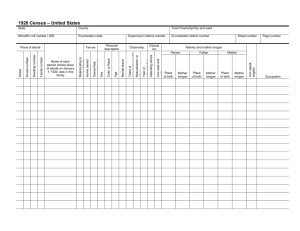
Lesson Plan-1 Date: 2012/2013 Lesson Title: Finding a job
advertisement

Lesson Plan-1 Date: 2012/2013 Lesson Title: Finding a job. Teaching Discipline(s): English as a Foreign Language Instructor Name: Przemysław Jackowski Instructor Country: Poland 1. 2. 3. 4. Learning Objectives (Please identify 1-2 objectives of this lesson-- focus on a daily lesson and the goals you hope students will achieve) Students will be able to present their opinions and justify them. Students will employ correct grammatical phrases referring to agreeing and disagreeing to somebody’s opinion. Students will cooperate to reach consensus within a group. Students will be able to present right arguments during a group-discussion session. Accessories / Teaching Aids Required Students will be given opinion, agreeing and disagreeing cards – with useful phrases during a group-discussion session. Students will be presented with materials to make notes – each group a different colour paper. Students will be given written instructions from the teacher. Reference Material (if any public materials are used, please list the sources of these materials here) Micro - Lesson Outline (please describe the activity, strategy, topic you will demonstrate to the “student” group) Procedure: 1. As a warm-up activity (lead-in stage) the teacher asks students a few questions about work: At what age do people usually begin to work in your country? At what age do people usually retire in your country? At what age would you like to be financially independent? The teacher assumes that students have some previous knowledge referring to job experience. 2. Pre-Communicative Activity (4 minutes): Students are divided into groups of 4. The teacher at random distributes little cards among students with numbers; 1, 2, 3 and 4 on them. 1s form one group, 2s the next, 3s and 4s respectively. Each group is given cards containing a few questions about aspects which are usually taken into account while deciding on a particular king of a job. Students decide on 3 aspects the most important ones. Afterwards, the leader of each group reads the answers. Which of the following benefits are most important to you in a job and why? Name 3 the most important. Good working conditions A high salary Promotion prospect A good relationship with your boss No overtime The opportunity to use skills and knowledge you have acquired Workplace near your home The opportunity to travel Flexible working hours 3. Communicative Activity (8 minutes): Students are given cards with information about different people applying for a job. Students are asked to write down on a piece of paper their choice and justification. Suppose your group is in charge of hiring a new employee for your firm. You have to decide between four people. - person A Mr. Jackowski is a man in his 40s, has little experience in your company’s business. He has some financial problems because he has just lost his job as a CEO in a big company. But he claims he is willing to learn and has previous experience in management. - person B Mr. Adams is with many years of experience in a company very similar to yours who has only a high school education. - person C Miss Johnson is a recent university graduate with a degree in a field closely related to your company's business. - person D Mrs. Brown is a woman who has been looking for a job for the last 3 months. She has some experience in your company business and if she doesn’t find a job soon she will have a lot of problems with paying the bills and her only 6-year-old daughter might be taken away by a social worker. Which person would you choose and why? One representative from each group - the leader - is invited to tell classmates which person they have chosen and why. 4. Recapitulation / Consolidation – debriefing ( 2 minutes): Students are invited to share their feelings during this activity and how they have reached consensus. Assessment (please describe how you will assess learning during this mini-lesson): Formative assessment-activities are used to provide feedback, evaluating learning progress in order to motivate students to higher levels. Please describe what best teaching practices this lesson will demonstrate: Group work, reaching decision. This lesson uses methods of cooperative learning. Lesson Plan-2 Date: 2012/2013 Lesson Title: Problem behaviour and what to do about it? Instructor Name: Przemysław Jackowski Teaching Discipline(s): English as a Foreign Language Instructor Country: Poland 5. 6. 7. 8. Learning Objectives Students will be able to present their opinions and justify them. Students will brainstorm ideas connected with problem behaviour at school. Students will use the vocabulary (mainly verbs) they know to complete their tasks. Students will be able to present right arguments during a group-discussion session. Accessories / Teaching Aids Required Each group of students will be given a piece of paper to write; each group a different colour of paper. Group A (yellow – WHY PROBLEMS OCCUR), Group B (green – PREVENTING PROBLEM BEHAVIOUR), Group C (blue – REACTING TO PROBLEM BEHAVIOUR). Students will be given written instructions from the teacher. Micro - Lesson Outline Procedure: 1. As a warm-up activity (lead-in stage) the teacher introduces the topic: Problem behaviour and what to do about it? The teacher asks students what forms problem behaviour can take. For example, disruptive talking, inaudible responses, sleeping in class, poor attendance, tardiness, failure to do homework, cheating in tests, insolence to the teacher or damaging the school property... 2a. Communicative Activity (4 minutes): Students are divided into groups of 5. Groups will be created by random assignment with special consideration given to mixing abilities. Students will be sitting in a circle. Each group is given a piece of colour paper with a task – Group A: Why the problem behaviour occurs, Group B: How we can prevent it, Group C: What to do if it arises. Students are asked to write down answers on their piece of paper. 2b. Communicative Activity (6 minutes) – cooperative learning: Once each group has finished the task, new groups of 3 students are formed. The new group of three students consists of one student from group A, one from B and one from C. Each group is given a piece of paper with a table: WHY PROBLEMS OCCUR, PREVENTING PROBLEM BEHAVIOUR, REACTING TO PROBLEM BEHAVIOUR. Students present their answers to other students within the new group. The members of each group can add additional items. Then the leader of the group is asked to present findings. A class discussion might follow. Recapitulation / Consolidation – debriefing ( 3 minutes): Students are invited to share their feelings during this activity and how they reached decisions, if they had any problems within a group, how they solved the problems. Was there anybody who didn’t want to take part in a discussion. Assessment (please describe how you will assess learning during this mini-lesson): Formative assessment-activities are used to provide feedback, evaluating learning progress in order to motivate students to higher levels. Please describe what best teaching practices this lesson will demonstrate: Group work, reaching decision. This lesson uses active learning technique. Lesson Plan-3 Date: 2012/2013 Lesson Title: WISHES and REGRETS Teaching Discipline(s): English as a Foreign Language Instructor Name: Przemysław Jackowski Instructor Country: Poland 9. 10. 11. 12. Learning Objectives Students will use wish + past tense verb form to express a hypothetical (imaginary) situation. Students will write reasons why some sentences are true for them. Students will use vocabulary (mainly verbs in past tense) they know to complete their tasks. Students will be working in pairs using the target grammar to complete their tasks. Accessories / Teaching Aids Required Students will be given written instructions from the teacher. Each student will be given a paper with 20-wish sentences. Micro - Lesson Outline Procedure: 1. As a warm-up activity (lead-in stage) the teacher introduces the topic: WISHES and REGRETS The teacher elicits the right grammatical form of the verb in I wish structure. For example, the teacher says: “I don’t like the job” and stars the new sentence from “I wish I....” and asks students to complete the sentence. It is assumed that the student is already familiar with this structure. 2a. Communicative Activity (4 minutes): Students read through the sentences and check five which are true for them. The students are asked to write the reason why the sentences are true for them. 2b. Communicative Activity (6 minutes): The students now have to walk around the class and find people who have the same wishes and once they have found the student they compare their reasons. Be sure to model a conversation using the target grammar. For example: A: Do you wish you didn’t have to start school at 7.20? B: Yes, I do. A: Why do you wish you had more money? B: Well, I want to buy a bike. Recapitulation / Consolidation – debriefing ( 3 minutes): Students share their feelings during this activity, if they had any problems with grammar, how they solved the problems. Assessment (please describe how you will assess learning during this mini-lesson): Formative assessment-activities are used to provide feedback, evaluating learning progress in order to motivate students to higher levels. Please describe what best teaching practices this lesson will demonstrate: pair work. This lesson uses active learning. WISHES * I wish.......... 1 I wish I didn't have to start school at 7.20. 2 I wish I knew how to use google docs. 3 I wish I had a sister. 4 I wish I went to the gym on Monday. 5 I wish I were a doctor. 6 I wish I lived in the country. 7 I wish I learned Chinese. 8 I wish I were still 12-year-old. 9 I wish I had more time to read English books. 10 I wish I could go no holiday to Spain. 11 I wish my friends didn't lie to me. 12 I wish I were taller. 13 I wish I were more creative. 14 I wish I were more easy-going. 15 I wish I were a business-person. 16 I wish I had more money. 17 I wish I were more hard-working. 18 I wish I had more patience. 19 I wish I my parents were more tolerant. 20 I wish I lived on my own. 5 sentences which are true for me People who have the same wishes Lesson Plan-4 Date: 2012/2013 Instructor Name: Przemysław Jackowski Lesson Title: Body organs-functions-idioms. Teaching Discipline(s): English as a Foreign Language Instructor Country: Poland Learning Objectives (Please identify 1-2 objectives of this lesson-- focus on a daily lesson and the goals you hope students will achieve) 13. Students will name body organs, provide their functions. 14. Students will work in teams to name and draw as many organs as possible. 15. Students will cooperate within a group to come up with body idioms. Accessories / Teaching Aids Required Students will be provided with big sheets of paper to draw Human Body Frame. Students will get markers to draw the inner organs of the body. Students will be given written instructions from the teacher. Micro - Lesson Outline 1. As a warm-up activity (lead-in stage) the teacher asks students a few questions about body organs: The teacher introduces students to Body Organs vocabulary. This can be done by using a student as a model and pointing to a body part and asking students, “What do you call this?” The teacher assumes that students have some previous knowledge referring to anatomical body structure. 2. Communicative Activity: Part one (3 minutes): Students are divided into two teams of 4-5 students. Each team chooses a Model. One student in each team draws a body outline. Both teams attach the full-scale-drawing to the board. Part two (2 minutes ): Students are to draw as many body organs as possible on the full-scale-drawing sheet within 2 minutes. Part three (2 minutes ): Students are to choose 3 body organs and explain their functions within 2 minutes. Part three (3 minutes ): Students are to write down as many as possible body-organ idioms within 3 minutes. Meantime the class assess both teams. The students act as experts. Students are given cards with information about body organs. 4. Recapitulation / Consolidation / Debriefing: Students are invited to share their feelings during this activity and how they have reached consensus. Assessment (please describe how you will assess learning during this mini-lesson): Formative assessment-activities are used to provide feedback, evaluating learning progress in order to motivate students to higher levels. Please describe what best teaching practices this lesson will demonstrate: Group work, reaching decision. This lesson uses active methods. ORGAN Appendix (wyrostek robaczkowy) Brain Bladder Diaphragm Gall bladder (pęcherzk żółciowy) Heart Intestines: small intestine Intestines: large intestine + colon FUNCTION Traditionally, there are no known appendix functions. It controls each and every part of the body. It is the organ where the excreted urine by the kidneys is collected before begin disposed off by urination. Respiration It helps in digestive process and the bile produced in the liver is stored in the gall bladder. Heart pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body through blood vessels. The small intestine is responsible for absorbing most of the nutrients found within your food. Its principle function is to reabsorb water and maintains the fluid balance of the body. Certain vitamins are also taken in through the large intestinal wall. Kidney Larynx (krtań) Liver Lungs Oesophagus (przełyk) Pancreas Spleen (śledziona) Stomach Tongue Trachea (windpipe) Thymus gland (grasica) Thyroid gland (tarczyca) The function of the kidneys is regulation of electrolytes, regulation of blood pressure, production of urine. Voice production, control of airflow (breathing) and swallowing. Detoxification of blood, production of biochemicals for digestion and protein synthesis. Transport atmospheric oxygen into the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere from the blood. Swallowing The pancreas produces the most important hormones like insulin and digestive enzymes. The function of the spleen is to remove old red blood cells and recycle iron. The stomach is the primary organ of the digestive system that is involved in the second phase of food digestion. Digestive function Allows passage of air to the lungs Production of T-lymphocytes that are very important for adaptive immune system. They produce hormones and control the amount of calcium in the blood and within the bones. ORGAN IDIOM The most important part or aspect of a situation is Heart of the matter called the heart of the matter. If someone has a change of heart, they change Change of heart their attitude or feelings, especially towards greater friendliness or cooperation. A person who has their heart in their mouth feels Have one's heart in one's extremely mouth anxious or nervous faced with a dangerous or unpleasant situation. Have one's heart in the A person who has their heart in the right place has right kind feelings and good intentions, even if the results place are not too good. Someone who has their heart set on something Have one's heart set on sth wants it very much. If your heart sinks, you feel very unhappy and Your heart sinks despondent If you wear your heart on your sleeve, you allow Wear your heart on your others sleeve to see your emotions or feelings. Someone who has a heart of stone is a cold person Heart of stone who shows others no understanding, sympathy or pity. If you put your heart (and soul) into something, Put your heart into you are very something enthusiastic and invest a lot of energy and hard work in something. If you shout at the top of your lungs, you shout as At the top of one's lungs loudly as you possibly can. Bite your tongue Hold your tongue Keep a civil tongue Tongue-tied Slip of the tongue On the tip of your tongue Tongue in cheek Jump down someone's throat butterflies in one's stomach have the stomach for something one's eyes are bigger than one's stomach way to a man's heart is through his stomach on an empty stomach vent your spleen beat one's brains out blow someone's brains out pick someone's brain(s) If you bite your tongue, you try not to say what you really think or feel. If you hold your tongue, you stay silent and say nothing. People who keep a civil tongue express themselves in polite terms. If you are tongue-tied, you have difficulty in expressing yourself because you are nervous or embarrassed. A slip of the tongue refers to a small spoken error or mistake. To say that a word or an answer is on the tip of your tongue means that you're sure you know it but have difficulty finding it. If you describe a remark as tongue in cheek, you mean that it is not meant to be taken seriously; it is meant to be funny or ironic. If you jump down someone's throat, you suddenly start shouting at them in a very angry manner. A nervous feeling To have the courage or resolution to do something One has taken more food than one can eat. If you want a man to love you, you should feed him good food. When you have not eaten anything To express anger (often + on ) To try very hard to do something To kill someone with a gun. To talk with sb. to find out information about sth. rack one's brain(s) a brain drain be out of your brain be the brains behind something have something on the brain To try very hard to think of something. The movement of people with education and skills from their own country to another country. To be very drunk. To be the person who plans and organizes something, especially something successful. To not be able to stop thinking or talking about one particular thing.