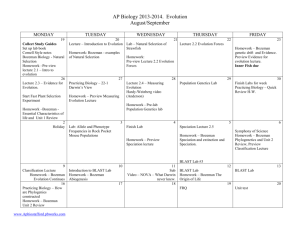
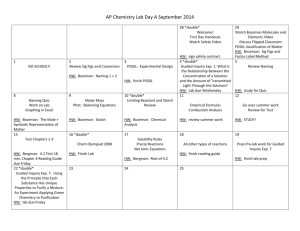
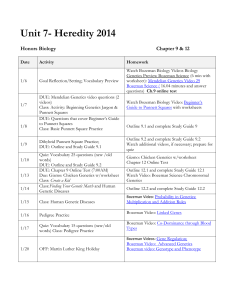
Evolution main ideas
advertisement

Evolution main ideas: All living things are united through evolution. Evolution describes both the similarities and diversity of life. What are some commonalities between (conserved processes among) all living organisms? BOZEMAN 005 There are different types of evidence for evolution BOZEMAN 004 - fossil record – including transitional fossils - anatomy – homologous structures, vestigial structures - biochemistry – analysis of DNA or protein sequences - embryology - biogeography/geology Individuals do not evolve, POPULATIONS EVOLVE. How can a population evolve? – 5 mechanisms (causes) of evolution 1 natural selection BOZEMAN 001 BOZEMAN 002 (Variation, overproduction, fitness, adaptation over time) 2 genetic drift BOZEMAN 003 3 mutation 4 gene flow 5 sexual selection How can we measure if a population is evolving or not? – Hardy Weinberg Equation – used to estimate the allele and genotype frequencies in a large population. A population is evolving if the allele and genotype frequencies are changing. In order for H-W EQUILIBRIUM (population not evolving), 5 qualifications must be met. Notice that these are the opposite of the 5 mechanisms of evolution. If a population is evolving, it could lead to speciation – the creation of a new species. The 5 causes of microevolution can lead to macroevolution (speciation). 2 main causes of speciation – geographic isolation & reproductive isolation BOZEMAN 007 BOZEMAN 008 Cladograms/phylogenetic trees show speciation and how different species are related to each other. BOZEMAN 006 Populations continue to evolve. Evolution is still occurring. BOZEMAN 009 The origin of life on earth. BOZEMAN 010 BOZEMAN 011 Evolution main ideas: All living things are united through evolution. Evolution describes both the similarities and diversity of life. What are some commonalities between (conserved processes among) all living organisms? BOZEMAN 005 There are different types of evidence for evolution BOZEMAN 004 - fossil record – including transitional fossils - anatomy – homologous structures, vestigial structures - biochemistry – analysis of DNA or protein sequences - embryology - biogeography/geology Individuals do not evolve, POPULATIONS EVOLVE. How can a population evolve? – 5 mechanisms (causes) of evolution 1 natural selection BOZEMAN 001 BOZEMAN 002 (Variation, overproduction, fitness, adaptation over time) 2 genetic drift BOZEMAN 003 3 mutation 4 gene flow 5 sexual selection How can we measure if a population is evolving or not? – Hardy Weinberg Equation – used to estimate the allele and genotype frequencies in a large population. A population is evolving if the allele and genotype frequencies are changing. In order for H-W EQUILIBRIUM (population not evolving), 5 qualifications must be met. Notice that these are the opposite of the 5 mechanisms of evolution. If a population is evolving, it could lead to speciation – the creation of a new species. The 5 causes of microevolution can lead to macroevolution (speciation). 2 main causes of speciation – geographic isolation & reproductive isolation BOZEMAN 007 BOZEMAN 008 Cladograms/phylogenetic trees show speciation and how different species are related to each other. BOZEMAN 006 Populations continue to evolve. Evolution is still occurring. BOZEMAN 009 The origin of life on earth. BOZEMAN 010 BOZEMAN 011