PBS Islam - OrgSites.com
advertisement

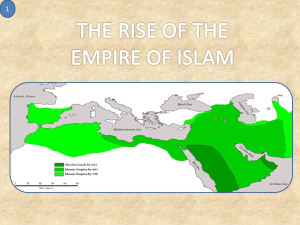
Islam: Empires of Faith Video Viewing Guide Video 1 3:45 Many cultures have been shaped by Islamic civilization How? Consider this as you view the film 4:00 Muhammad-early years 570 CE – Birth near Mecca into the Banu Hashim clan of the Quraysh tribe. His father died before his birth, and his mother died a few years later. Infancy – sent to live with Bedouin relatives. Bedouin culture involved strong kinship ties with clan and family. Fortunate to be raised by an uncle, Abu Talib, involved with trade. Without family ties, he wouldn’t have survived. 10:00 Bedouin belief system An oral culture - shared stories, recited poetry – poetry was the “sinew” that held the tribes together. This helped to express values. Words held a mystical importance. 10:45 The Ka’ba An ancient shrine in Mecca – wood, black stone, and cloth. Pre- Islamic site of a sanctuary in Mecca where tribal differences could be put aside. It was believed to be built by Abraham. Polytheistic beliefs centered around nature – water, wind, fire gods 11:35 Trade items Trade was facilitated by the Ka’ba. Mecca was the center for trade with a mix of cultures and religions. This allowed access to monotheistic ideas from Christians and Jews. Mecca was founded by the Umayyad clan of the Quraysh tribe. 13:40 Muhammad's characteristics Strong leader – able to propose solutions. This will be an important characteristic when he begins to spread the Islamic faith. Married Khadijah – the widow of a wealthy merchant. 15:10 Muhammad's vision Grew increasingly distracted and dissatisfied with material gain Spend time in the hills and wilderness surrounding Mecca. He had a profound and disturbing encounter with the Angel Gabriel 16:40 Muhammad's proclamation The first of many revelations was “There is no God, but God” emphasizing the indivisible divine unity of a single God. 18:00 With Islam came a new order, a new way of life Muhammad gained a small following and emphasized unity with no tribal divisions. He preached a strong social justice message with universal appeal 18:40 Verbal expression was the commanding cultural force The symbolic depth of pre-Islamic poetry and verbal expression of the Bedouin assisted Muhammad in conveying his message. 19:20 The Koran (Qu’ran) Revealed orally (Muhammad was illiterate), written down early on in Arabic to preserve the original message. It contains a revelation of spiritual, ethical, and social guidelines. Imagery is important paralleling traditional Bedouin poetry. The use of constantly shifting pronouns is present Images are not favored. 24:00 Unrest between tribal leaders and Muhammad The Umayyads felt threatened by Muhammad. They tried to run him out of town, planned an assassination. His uncle refused to start a tribal war and helped to remove Muhammad and his followers from Mecca. 26:10 A new tribe is formed He created a community of faithful believers – the umma. They were bound by faith not blood, transcended traditional Bedouin kinship ties. 27:50 New Muslim calendar – 622CE The escape to Yathrib (renamed “Medina” the city of the prophet) is known as the Hijira and marks year 1 on the Muslim calendar. Muhammad accepted other “people of the book” (became known as dhimmis) and accepted Moses and Jesus as prophets. The call to prayer is the first pillar of Islam “There is no God but God, and Muhammad is his Prophet.” 31:30 Enemies gather forces to wipe out Muslims Muhammad gathered arms and was greatly outnumbered 300 of his followers to 1000 heavily armed Meccans Held out for three years, and by 630 CE Muhammad prepared to return to Mecca – 10,000 strong. 37:30 Bedouin's response to the fall of Mecca Muhammad did not carry out bloody revenge. Instead he destroyed the idols and iconoclasm by smashing tribal gods into the dust. Symbollically wiping out the previous culture and uniting the tribes under the banner of Islam. 38:55 Muhammad dies 632 CE – the eleventh year of the Muslim calendar. Many of the tribes that initially converted renounced the new faith. 39:45 Who should succeed Muhammad A divergence of opinion arose. A new leader was designated as the caliph (political and religious successor to Muhammad). Abu Bakr was chosen. This decision led to a split between those who believed the successor did not have to be related to Muhammad – the Sunni branch of Islam and those who felt the successor should be a relative of Muhammad – the Shi’a branch of Islam. 40:45 Strength of Islam Again, universal appeal. Brought together a diverse group of people. Within 50 years, Islam spread rapidly. Within 200 years It spread from Spain to China connecting North Africa, the Middle East, and the northern portion of South Asia, encompassing the Sassanian (Persian) Empire, and taking over parts of the Byzantine Empire. 41:20 Muslim's lead a conquest of ideas Preserved and transmitted learning from the classical period. Took ideas from the Greek philosophers; the Indian numeral system which became Arabic numerals; Byzantine architecture. 42:45 Architectural accomplishments The Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem Great Mosque of Damascus in Syria