Astronomy - Geneva 304
advertisement

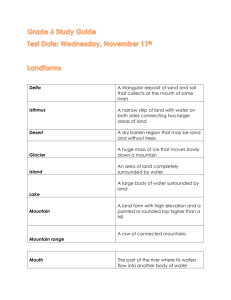
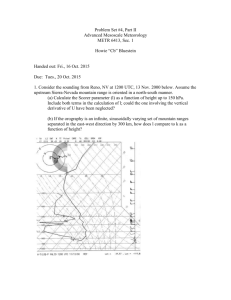
Earth Science Name_____________________________ Chapter 5 Period_____________________________ Worksheet Date______________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ Crustal Deformation Section 5.1 (0.10 point each) Deformation of the earth’s crust includes _ _ _ D _ _ _, T _ _ _ _ _ _, and _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ of the rock layers. The balancing of two forces on the Earth’s crust creates _ S _ _ _ _ _ Y. Pressure created by this bending causes rock in that area to _ E _ _ _ _. Plate movements or unequal weight distribution of the earth’s crust cab can cause S _ _ _ _ _ and S _ _ _ _ _. Three types of stress on rock layers are __________, __________ and __________. Section 5.2 See the photo of figure 5-3. What stress types would have created this folding? (0.25 points) In the diagrams below label which set of layers have been deformed into an anticline, syncline and monocline. (0.25 points) A B ____________ ____________ C _____________ Examine the block diagrams below. Label each with the name of the fault type. The types are NORMAL, REVERSE, THRUST, OR STRIKE SLIP. (0.25 points each) ____________ ____________ ____________ ____________ Section 5.3 (0.10 point each) The highest mountain above sea level on the entire Earth is ______________. It is part of the _____________ mountain range. In _____________ Mt. St. Helens, a ___________ is part of the _____________ mountain range. See figure 5-5. The Circum-pacific mountain belt in the chapter on volcanoes was called the ___________ of __________. Collisions between the continental and oceanic crust have created the __________ mountains. Collisions between ocean crust and oceanic crust have created the __________ mountains. Collisions between the continents have created the __________ mountains. Shown below are block diagrams illustrating four basic mountain types. One of the diagrams shows a combination of each of the types which is called Complex. Large mountain chains they are generally Complex. Label each block diagram with its type of formation, i.e. Folded, Faulted, Volcanic, Dome, and Complex. (0.20 points each) 1. Mountain type “A” Give an example 2. Mountain type “B” Give an example 3. Mountain type “C” Give an example 4. Mountain type “D” Give an example 5. Mountain type “E” Give an example