The Sun
advertisement

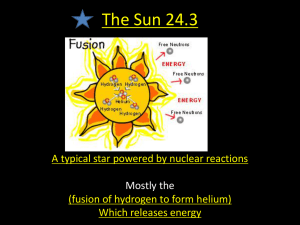
UCCS Astronomy Lab I 1. 6000K / 15 million K 11000K / 27 million K. Depleted / to explode all of the above The fusion of neutrinos into helium. The fusion of positrons into hydrogen. The fusion of hydrogen into helium. Electric currents generated in its core. What is the specific 3-step energy generating process in the Sun called? A) B) C) D) 7. Electrostatic forces between ions in its interior. Gas pressure. Its gravitational force. Nothing: the Sun is actually expanding very slowly. The Sun produces its energy through A) B) C) D) 6. 380,000 km 93,000,000 km. 150,000,000 km. One light year. The surface of the Sun is about ______ and the core is about _______. A) B) C) D) 5. 71% helium / 27% hydrogen 50% hydrogen / 50% helium 71% hydrogen / 27% helium 77% nitrogen / 22% oxygen What holds the Sun together? A) B) C) D) 4. name:_______________________ The Sun is about how far from Earth? A) B) C) D) 3 Sun Lab The Sun is composed of about ______ and _______ plus 2% other elements. A) B) C) D) 2 PES 109 Fall 2009 Hydrostatic equilibrium Thermography. The proton-proton chain. Radiative transfer. The sun's energy comes from A) B) C) D) The release of magnetic energy. The conversion of mass into energy. Its rotation slowing down. Meteors and asteroids striking its surface. 8. What is the visible surface of the Sun called? A) B) C) D) 9. What is the Sun’s outermost atmosphere called? A) B) C) D) 10. B) C) D) Can reveal the Sun's inner magnetic field. Give information about the nuclear reactions in the Sun's core. Prove the Sun will explode in a few thousand years Prove the Sun is only about 2 million years old. What is solar seismology? A) B) C) D) 14. A prominence is a huge plume of glowing gas trapped in the Sun's magnetic field; a flare is a brief, bright eruption in the chromosphere. A prominence is brief, bright eruption in the chromosphere; a flare is a tenuous flow of hydrogen and helium that sweeps across the Solar System. A prominence is a jet of hot gas thousands of kilometers long; a flare is an immense bubble of hot gas rising from deep within the Sun. There is no difference. Why are astronomers interested in detecting neutrinos from the Sun? Neutrinos A) B) C) D) 13. They are made of different material than the surrounding gas. They are hotter than the surrounding gas. They are cooler than the surrounding gas. Their magnetic fields block light. How do a prominence and a flare differ? A) 12. The corona The chromosphere The photosphere The radiative zone Why do sunspots appear dark? A) B) C) D) 11. The corona The chromosphere The photosphere The radiative zone The study of the Sun's atmosphere by analyzing waves in the Sun's interior. The study of the Sun's interior by analyzing waves in the Sun's atmosphere. The study of gravitational waves from the Sun. The study of the Sun's changing size. About how long is the solar cycle (evidenced by sunspots)? A) B) C) D) 3 years 5 days 11 years 33 years 15. Which of the following is evidence that solar activity affects Earth's climate? A) B) C) D) 16. How many stars are there in the Solar System? A) B) C) D) 17. Solar Wind Supergranulation Sunspots Solar Spicules What do we call the swarm of comet nuclei in a huge shell surrounding the Sun and planets? A) B) C) D) 20. Solar Oscillations Helioseismology Standard solar mode Hydrostatic equilibrium __________ typically measure about 10,000 km across – about the size of the Earth. At any given instant, the Sun may have hundreds of these, or it may have none at all. A) B) C) D) 19. 0 1 9 100 billion In the interior of a star such as the Sun, the outward pressure of hot gas balances the inward pull of gravity. Such state is known as: A) B) C) D) 18. The Maunder minimum - a period of abnormally low sunspot numbers - coincided with abnormally cold northern winters The Schwab Cycle - a period of abnormally numerous and large sunspots preceded a 250 year drought in Africa. The dust bowl of the 1930's in the United States coincided with the complete disappearance of sunspots during that time. All of the above. The Solar System The asteroid belt The ecliptic. The Oort Cloud. Approximately how old is the Solar System? A) B) C) D) 4.5 thousand years. 4.5 million years. 4.5 billion years. 4.5 trillion years. 21. A huge interstellar cloud collapsed into a rotating disk with a central bulge. What was this? A) B) C) D) 22. Which of the following features of the Solar System does the solar nebula hypothesis explain? A) B) C) D) 23. Polarity Filaments Prominence Flares Sometimes (but not always) a flare or a prominence is associated with a ____________. This giant magnetic “bubble” of ionized gas separates from the rest of the solar atmosphere and escapes into interplanetary space A) B) C) D) 25. All the planets orbit the Sun in the same direction. All the planets' orbits lie in nearly the same plane. The planets nearest the Sun contain only small amounts of substances that condense at low temperatures. All of the above. The __________ of a sunspot simply indicates which way its magnetic field is directed. A) B) C) D) 24. The disk was the solar nebula and the bulge became Jupiter. A large belt containing asteroids in a gap between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The disk was the solar nebula and the bulge became the Sun. The formed the outer planets which eventually met up with the Sun. Coronal hole Coronal mass ejection Magnetosphere Maunder Minimum The lightest and most common element in the universe is __________, and it is the fusion of H nuclei (protons) to form nuclei of __________, the next lightest element, that powers the Sun. A) B) C) D) Carbon; Oxygen; Hydrogen Hydrogen; Hydrogen Helium Oxygen Helium