Spill Prevention Program Template
advertisement

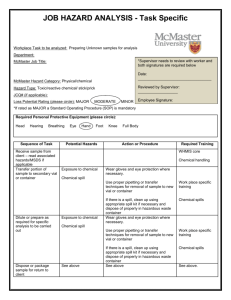
Company Name Chemical Spill Prevention & Clean-up Procedures Program Last Revised On 00/00/0000 This material was created using sources which we believe to be reliable. Hortica does not guarantee that this material will lead to improved results. Hortica does not assume liability arising from the use of any information provided in this document. The procedures that are discussed in this document are general in nature and depending on your particular operation may not apply to your company. There may be other safety procedures or information that have not been discussed in this material. PURPOSE The following program will discuss how to prevent chemical spills from occurring and set forth procedures to follow in the event that a spill occurs. SPILL PREVENTION Company Name has developed procedures for proper transportation, storage and handling of chemicals to reduce the chance of a chemical spill. These are in place to prevent chemical spills from occurring and to be followed at all times. If a chemical spill occurs, it may be very difficult and costly to contain and clean the spill. By following the procedures outlined in this program we can prevent chemical spills from occurring. Only authorized employees are allowed to enter the “Pesticide Storage Area” or handle pesticides. PREVENTING CHEMICAL SPILLS The following section will discuss the steps that all Company Name employees are expected to follow in order to prevent chemical spills from occurring and the procedures to follow if a spill occurs. READ THE LABEL!!!!! Obtain a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) on all new chemicals that are introduced into the workplace. Employees are responsible for reviewing the MSDS for each chemical that you work with before using it. Maintain good housekeeping practices. Ensure that all chemical containers are properly labeled, including secondary containers in accordance with OSHA regulations. Secondary containers must have at least the “Name of the Chemical”, “Manufacturer” and appropriate “Hazard Warning” information. Never use a container that could be mistaken for a food or beverage product as a secondary container. A couple of examples would be a soda can/bottle or milk/water jug. Only mix chemicals in designated areas. The mixing area location(s) are: o ____________________________ o ____________________________ o ____________________________ A complete pesticide inventory list will be given to the local fire department along with the location of all pesticide storage/accumulation areas. (Note: You may also want to invite your local fire department to tour your facility before an emergency occurs) A chemical spill kit will be kept in all mixing areas, storage areas and vehicles used to transport chemicals. CHEMICAL TRANSPORTATION Employees are responsible for transporting chemicals in a safe manner, so that they do not damage the integrity of the chemical container. The following procedures are to be followed when transporting chemicals: Never transport chemicals inside of the passenger cabin of a vehicle. Never transport chemicals with food or clothing. Always lock your vehicle when transporting chemicals if you have to leave it unattended. Never leave your vehicle unattended if you have chemicals in the bed of a truck. Do not transport damaged or leaking containers. If you have an emergency involving a spill, fire or exposure - call 911. Secure containers to ensure that they do not move during transport. All employees responsible for transporting chemicals will verify that the chemical spill kit is present prior to using the vehicle. CHEMICAL STORAGE AREA(S): General Chemicals are to be stored in our designated storage areas. All storage areas are to be kept clean and orderly at all times. All storage areas will be well lit. All above ground fuel storage tanks/drums shall be double walled or located within a dike containment unit. Flammables All flammable chemicals will be stored in our flammable materials cabinets. These areas will remain free of all sources of ignition. No smoking is to occur within 50’ of all flammable material storage areas. All flammable fuel storage areas are required to have a fire extinguisher located within 50’ of the storage area at all times. Extra Oxygen & Acetylene fuel cylinders that are not located in a fuel cart & connected to a regulator shall be stored at least 18’ apart. Pesticide Storage Areas All pesticides are to be stored in the “Pesticide Storage” cabinet/room. All pesticide storage areas will be labeled with the bilingual EPA Approved Pesticide Storage sign. All pesticide storage areas are to be kept locked when they are not in use. The shelving units inside of the pesticide storage area shall be constructed of metal, plastic or wood. If the shelves are made of wood then they are to be covered with a sheet of heavy-duty plastic or epoxy paint. This is to prevent wooden shelves from being contaminated if pesticides are spilled on them. Never store pesticides in direct sunlight. Because some pesticides will break down or deteriorate in extreme temperatures the storage area will be kept between 40 to 100 degrees Fahrenheit. CHEMICAL SPILL PROCEDURES Remember that the first priority of all spills is to ____________________ Small Spills (Less than 1 gallon) Untrained employees: Properly attending to a chemical spill requires special knowledge and training. If you have not been trained in “Spill Clean-up” you are not allowed to attempt to clean up the spill. If you are the first to discover a chemical spill you are to: Access the spill (Try to determine the approximate container size and content of the spill. Also, be able to give the location of the spill. This information is to assist our clean-up personnel.) Secure the spill area. You should not leave the area unattended unless you believe that you are in immediate danger. Use caution tape to rope off the area to make sure that employees and customers stay out of the area. If caution tape is unavailable, then station employees at the entrance(s) of the area where the spill has occurred, in order to inform people that they can not enter the area. Contact the appropriate personnel. If the spill poses a threat to life, evacuate the area. Trained employees A list of trained employees who are authorized to clean-up a chemical spill can be found in Appendix A (located at the end of this program). Their name(s), title, department and contact information is also listed. The following clean-up procedures are to be followed by trained employees only: 1. Don’t Panic. 2. Find the appropriate MSDS. If you are unsure of the spilled chemical, wear the maximum PPE required for our chemicals. This includes: a. Tyvek suit b. Heavy-duty chemical resistant gloves c. Rubber boots d. Chemical resistant goggles e. Face-shield f. Respirator g. Other:__________________ 3. If you know the contents of the spill, review the MSDS and put on all required Personal Protective Equipment. 4. Stop the source of the leak. If the container is small and tipped over, upright the container. If the container is leaking, then place it into a larger chemical-resistant container. Use either a plastic drum or heavy-duty plastic trash bag. If the container is overflowing from a hose, stop the inflow and try to cap the container. If the container is a spray tank or hopper that has ruptured or over-turned, you will not be able to stop the source. (This may require additional outside assistance for clean-up) 5. Contain the Spill. As soon as you have prevented any more material from leaking out from the source of the spill, you need to begin to control the leak and keep it from spreading. Take extra care to keep the spilled chemical from entering any water source. This may include but is not limited to: storm drains, wells, water systems, rivers/streams, etc. Use the absorbent socks or absorbent material located in the spill kit to surround the spill to assist you with the containment of the spill. Refer to the MSDS to be sure that you do not use a material that may increase the hazard of the spill. (Some chemicals may react with some of the absorbent materials) Liquids - Use the absorbent materials (Absorbent pads, kitty litter, sawdust, clay, etc.) located in the spill kit to soak up liquids. Cover the entire spill with the absorbent material. Solids – cover the spill with plastic and secure the edges to keep the plastic from moving. 6. Spill Clean-up - Refer to the MSDS of the spilled chemical for specific clean-up procedures. General Procedures Solids – Begin by slowly pulling up the edge of the plastic so that the wind (if outside) is blowing against the edge. Then using the plastic dust pan and broom/brush with plastic bristles located in the “Spill Kit”, begin to slowly sweep the material into the dust pan. Take extra care not to allow the material to become airborne. If the material has not been contaminated by other substances during the spill it may still be able to be used. If the material has been contaminated then it must be disposed of as hazardous waste. Liquids - Using the appropriate absorbent material, soak up as much of the spill liquid as possible. Refer to the MSDS when trying to decide on what type of absorbent to use. Place all materials in a leak proof container. Large Spills The proper clean-up of a large spill may be too difficult for our employees to handle or they may be unsure of what is necessary to do in order to properly clean up the spill. In either instance, our procedures are to evacuate the area and keep people away from the spill, make sure that anyone who may have been contaminated receives first aid, and try to confine the spill as best as possible if safe to do so. Call the local emergency services; the phone number is 911 (if there is a different emergency number in your area make sure to change the 911.), CHEMTREC and/or your State pesticide agency for assistance. CHEMTREC is a public service company that will provide you with immediate advice for those at the scene of an emergency. CHEMTREC’s toll free telephone number is 1-800-424-9300. This phone number is only to be used in the event of an emergency. Recommended Spill Kit Contents Facility Kit Contents Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. (4) – Pairs of chemical gloves (2) – Pairs of chemical splash goggles (2) – Tyvek suits (2) – Pairs of chemical boots or shoe covers (2) – Respirators** (with appropriate cartridge) Vehicle Kit Contents Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. (2) – Pairs of chemical gloves (1) – Pair of chemical goggles (1) – Tyvek suit (1) – Pair of chemical boots or shoe covers (1) – Respirator** (with appropriate cartridge) Absorbent Materials 1. (4) – Absorbent pillows 2. (2) – 3”x4’ absorbent socks 3. (1) – Bag of absorbent material 30 – 50 lbs. (Kitty litter, saw dust, commercial absorbent, etc.) Absorbent Materials 1. (4) – Absorbent pillows 2. (2) – 3”x4’ absorbent socks 3. (1) – Bag of absorbent material 10 – 30 lbs. (Kitty litter, saw dust, commercial absorbent, etc.) Decontamination Supplies 1. Liquid detergent soap (1 gallon) 2. Chlorine bleach (1 gallon) 3. Lime Decontamination Supplies 1. Liquid detergent soap (1 pint) 2. Chlorine bleach (1 pint) 3. Lime Clean-up Equipment Clean-up Equipment 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Plastic dust pan Brush or broom with plastic bristles (2) 5 – 20 gallon buckets (with covers) 55 gallon drum*** Small box of polyethylene trash bags w/ties Repair kit: Roll of duct tape & putty Roll of yellow “Caution” tape “Chemical Spill Keep Away” A-frame sign 5-10 blank adhesive labels Laminated emergency phone number list (Numbers to include: Poison Control, Fire/Police/Ambulance (911), Clinic/Hospital) 11. Sharpie marker 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Plastic dust pan Brush or broom with plastic bristles Small box of polyethylene trash bags w/ties Repair kit: Roll of duct tape & putty Roll of yellow “Caution” tape 5-10 blank adhesive labels Laminated emergency phone number list (Numbers to include: Poison Control, Fire/Police/Ambulance (911), Clinic/Hospital) 8. Sharpie marker 9. Portable eyewash (@ least 16 oz.) **Respirator requirements: Written Respiratory Protection Program, medical evaluation fit testing, annual training, etc. ***Depends on the quantity and size of containers carried.