What Is a Database?
advertisement

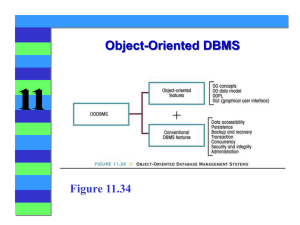
Chapter 14 Databases and Database Management Systems What Is a Database? Database—a collection of related data stored and organized in a manner so it can be retrieved as needed. Database management system (DBMS)—the software used to create, maintain, and access computer databases. Databases typically consist of tables containing fields (columns) and records (rows). Individuals Involved With a Data Management System Users Database designers Database developers and programmers Database administrators Evolution of Databases Advantages and Disadvantages of the Database Approach Advantages: Better information. Faster response time. Lower operating costs and storage requirements. Improved data integrity and better data management. Disadvantages: Higher software cost. Increased vulnerability . Data Concepts and Characteristics Data hierarchy (characters, fields/columns, records/rows, tables, database). Entity relationships: One-to-one relationships One-to-many relationships Many-to-many relationships Data Concepts and Characteristics, Cont’d. Data definition—the process of describing the characteristics of data that is to be included in a database table. For each field, need to define: Name (must be unique within the table). Data type (such as number, text, date, and so forth). Any needed properties (such as any allowable range or required format). Data dictionary—contains all data definitions for a database (metadata). Data integrity—the accuracy of data. Data validation—the process of ensuring that data entered into the database matches the specifications. Data security—protecting data against destruction and misuse. Data organization: most methods use a primary key. Indexed organization—uses an index to keep track of where each record is stored. Direct organization—uses hashing procedures with a record’s primary key field to determine the storage location. Database Classifications Single-user vs. multiuser systems Client-server systems Database Classifications N-tier database systems (middle tiers contain one or more programs stored on one or more computers). Centralized vs. distributed database systems. In-memory databases. Database Models Five main models: Hierarchical Network Relational Object-oriented Multidimensional Relational Database Model Relational database management system (RDBMS) Designing a relational database: Identify the purpose of the database and needed output. Determine the tables and fields. Assign the fields to the appropriate tables and restructure as needed (normalization process). Finalize the structure (data definition process). Creating a relational database: Create the structure of the table. Enter data using a created form or the regular Datasheet view. Tables can be related. Tables can be modified using the Design view, if needed. Retrieving information from a relational database Queries (SQL or built-in query features) Reports (more formal output) Maintaining a relational database Modifying the table structure. Adding new indexes to speed up queries. Deleting obsolete data. Upgrading database software and installing patches. Repairing or restoring data that has become corrupt. Object-Oriented Database Model Can contain a wide variety of objects (text, graphics, music, DNA, photographs, etc.). Objects are manipulated with methods, similar to object-oriented programs. Creating using an object-oriented database management system (OODBMS). Multidimensional Databases Typically contains data collected from enterprise-wide activities. Can be viewed from multiple perspectives (dimensions). Commonly used with data warehousing. Database and the Web Database are commonly used in conjunction with Web pages, such as for: Information retrieval E-commerce Dynamic Web pages How Web Databases Work Database use often initiated with a request from the Web page visitor. Middleware—used to connect the Web page to the database. Common types of middleware: CGI (common gateway interface) API (application interface) PHP (PHP Hypertext Preprocessor) Key Terms Column Data definition Data dictionary Data integrity Data security Data validation Database Database management system (DBMS) Direct organization Entity Field Index Indexed organization Middleware Multidimensional database (MDDB) Object-oriented database management system (OODBMS) Primary key Query Record Relational database management system (RDBMS) Report Row Structured query language (SQL) Table