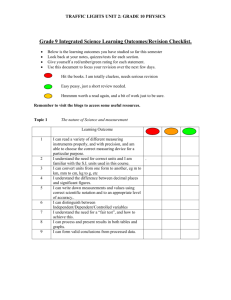
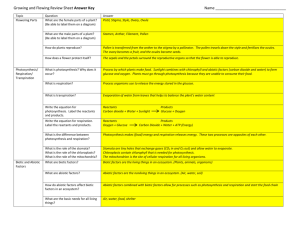
Water Unit Test Review

Water and the Environment
Test Review
Water is necessary to all living things. We cannot just look at water and know its quality. We need to test it chemically
(Learning Set 2)
Vocabulary: element, compound, mixture, symbol, solute, solvent, solution, concentration, eutrophication, acid, base, neutral, indicator, hypoxia, anoxia, turbulence, phosphate, nitrate, turbidity,
Chemistry Intro:
Know the 16 element symbols
Difference between an element, compound and mixture
Duckweed Experiment:
What does excess fertilizer in the water cause? Why is this bad? pH (pp. 63 – 69)
What is the pH scale?
Can you give an example of something that is in each category?
How do we test for it?
What environmental situations effect pH and how?
DO (pp. 70 – 74)
What is DO? Why is it important?
How do we test for it?
What environmental situations effect DO and how?
Turbidity ( p. 76)
What is turbidity? Why is it important?
How do we test for it?
What environmental situations effect turbidity and how?
Temperature ( pp. 75 - 76)
Why is temperature important to water quality?
Fecal Coliform (p. 77)
What is fecal coliform? Why is it important?
What environmental situations effect fecal coliform and how?
Turbulence (p. 73)
What is turbulence? Why is it important?
What environmental situations effect turbulence and how?
We then need to look at how it affects the living things around and in it (Learning Set 3)
Vocabulary: ecosystem, interactions, abiotic, biotic, habitat, community, biome, diversity, abundance, classify, macroinvertebrates, taxonomy, biotic indicator, food chain, food web, producer, consumer, herbivore, carnivore, omnivore, predator,
prey, photosynthesis, glucose, chlorophyll, chloroplasts, respiration, scavenger, decomposer, detritivore, biodiversity
Taxonomy ( pp. 86 – 91)
Who came up with our current system of classification?
Can you name the levels of taxonomy in order (KPCOFGS)?
What two levels constitute our scientific name? (capitalization rule)
Branching and dichotomous keys:
Can you use a dichotomous key to figure out the name of something?
Microscopes (journal)
Name the parts of a microscope
How do you focus on an organism or specimen?
How do you safely use a microscope?
Why do scientists study the macroinvertebrates found in a water system? (p. 97)
All living things are made of cells (we will focus more on animal cells 3 rd
quarter):
Compare a plant cell to an animal cell – what makes them different?
How do you think poor water quality could affect the cells of an organism?
Environment ( pp. 109 – 111, pp. 129 – 130)
Can you draw a four link food chain?
What is a food web?
What happens when we destroy one link in the food web?
What is the difference between abiotic and biotic factors in an environment?
Plants (pp. 101 – 103)
What is the equation for photosynthesis? Ingredients
What is the equation for respiration?
In what organelle does photosynthesis occur?
How are photosynthesis and respiration related? products
How does the land surrounding an area affect the water quality? (Learning Set 1)
Vocabulary: watershed, slope, runoff, groundwater, erosion, deposition, manufacturing, agriculture, point-source pollution, residential, commercial, industrial,
Watersheds (pp. 21-22)
What is a watershed?
What is the difference between surface runoff and groundwater?
Land Use (pp. 35-38, pp. 42- 45)
What is the difference between erosion and deposition?
What is the difference between residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural land use? What are the effects of each the types of use on a river?
Pollution (pp.46-49)
What is the difference between point and non-point source pollution?
Use my BlackBoard/wiki site to get onto the textbook online if needed