Lab 2: Circuit Simulation

Model, Measure, Repeat
Objective
In this lab we’ll be exploring one of the strategies engineers use to explore the physical world.
As a tool to help us explore we’ll be working with a new category of electronic device, the semiconductor diode. It’s behavior is a little different from the other circuit devices you’ve become used to working with. Engineers and scientists often use mathematical models to predict the behavior of physical systems. We’ll be using Matlab to describe the behavior of our diodes.
Other engineers will embed those mathematical models into more useful forms to simulate more complex systems. In order to be sure the model correctly predicts the system’s behavior, careful measurements are taken. Differences between the theoretical predictions and actual performance have to be accounted for, explained, and hopefully built into the model for the next iteration.
We’re going to follow this path on this experiment and see what develops.
A simple description of a diode is that it is a device that lets current flow in only one direction.
The prelab requires the use of Matlab to obtain a diode I (current) vs. V (voltage) curve. In lab, you’ll use a function generator and oscilloscope to observe the behavior of a diode circuit. Then, you’ll experimentally determine its I vs. V curve. You’ll also use PSpice to simulate the same circuits, and again obtain a plot of the current through the diode versus the voltage across the diode. These plots will then be compared to each other and manufacturer’s data, and you’ll include the comparisons in a lab report. As you work through this lab, keep the METHOD in mind.
Concepts
A diode allows current to flow one way and not the other. If we consider the circuit shown in Figure
1, we can see a visual explanation of this.
Figure 1: Series Diode Circuit
Let’s assume the input of the circuit is the sinusoid shown in Figure 2. We’ll also assume the diode is an ideal diode, which turns on (allows current to pass through it) at 0 V, and exhibits no voltage drop when current passes through it. The diode only allows positive current to flow, so negative current will be zero. Thus, if we plot the circuit output across R2, we get the result in Figure 3. The positive voltages are shown, but the negative voltage gets cut to zero, since current can’t flow in a negative direction. The output shown in Figure 3 is the result of a circuit called a half-wave rectifier.
1
Figure 2: V1 input for Figure 1 Figure 3: Output across R2 in Figure 1
In reality, diodes are not ideal, and do have a voltage across them. This voltage corresponds to the
‘turn-on’ or ‘knee’ voltage that you will observe in the I-V characteristics in the prelab and lab. For the first part of the lab, you’ll observe the half-wave rectifying characteristics of a non-ideal diode.
The second part of the lab is where you’ll experimentally determine the I-V characteristic.
Equipment and Components
1N4004 Diode
470 and 1000 Ω resistors
Wavetek function generator
Fluke Multimeter
Agilent 41622D Oscilloscope
P-Spice
Matlab
Prelab (25 points) – Due at the beginning of lab
The Shockley Equation is given in Equation (1).
(1)
1. Why is this equation useful? Write the answer on the data sheet.
2.
Using the Shockley Equation, write a Matlab program to calculate and plot I d for V d from 0 to 1 V. Assume ambient temperature is 300 K, n = 1 and Is ~ 10
-14 A
. Boltzman’s constant and the magnitude of the charge on an electron are available in many standard references.
Make sure you use proper units.
3.
Obtain manufacturer’s data of the I vs. V curve for the 1N4001, 1N4002, 1N4004.
4.
Bring a couple of floppy disks to the lab.
Part 1: Half-wave Rectifier
2
As promised, we’ll first look at a half-wave rectifier. Only the positive half of the input voltage is coupled to the load resistor. The ability of this device to conduct current only on one direction offers a lot of interesting possibilities. For instance, most electronic systems require DC voltage to operate, and diode rectifiers can be used to convert AC voltage to DC voltage.
1.
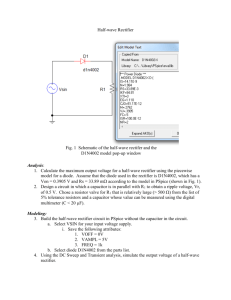
Connect the circuit shown in Figure 4 on your breadboard. The 1N4XXX series of diodes are very similar in performance.
D1N4002/1N4004
R1
D1
470
V1
0V DC
2 Vp
60 Hz
R2
1k
0 0
Figure 4: Half-wave rectifier
2.
Use the oscilloscope to display the output voltage across R2. Save the waveform to disk for use in your report.
3.
Have your TA initial your data sheet for Part 1.
4.
Use PSpice to simulate the same circuit. The diode you’ll use in the simulation will be the D1N4002. Since the frequency is 60 Hz, you can use either a VAC source
(automatically 60 Hz), or a VSIN source (in which you set the frequency). In the timedomain simulation show two or three simulations (pick an appropriate run time according to the AC frequency). On the output plot, show the voltage across R1, the voltage across
R2, and the input voltage. Save the plot and schematic to disk for use in your report. In your report, you can address some of the differences between the 4002 and the 4004 diodes.
Part 2: Nonlinear Diode Operation – Determining the I v.s V Characteristic
Now we’ll look at diode I-V characteristics. We’re going to use input voltages from 0 V to 1.5 V, then measure the diode voltage and resistor voltage. By dividing the resistor voltage by the measured resistance, we’ll get the resistor current, which is equal to the diode current because the two are in series. Then, you’ll plot your diode current data vs. the diode voltage data for use in your report comparisons.
1.
Reconfigure the function generator to output DC voltage only and set it to initially be 0 V.
2.
Measure the resistance of the resistor and enter it on your data sheet.
3.
Build the circuit shown in Figure 5. Remember the source is now DC.
3
+
VR1
R1
-
470
0V DC
V1
+
VD1
-
D1N4002/1N4004
D1
0 0
Figure 5: Series diode circuit
4.
Since we’re measuring DC voltage, use the Fluke multimeter. For each input voltage given in the table on your data sheet, record the diode voltage and the resistor voltage, then calculate the current.
5.
Have your TA verify your results on the data sheet.
6.
Use PSpice to simulate the same circuit by doing a DC sweep from -2 V to 2 V. Remember that you want to plot I
D
vs. V
D
(not V in
, which the plot will give you by default), since
Shockley’s equation only applies to voltage and current through a diode. This means you’ll have to figure out how to do an axis change to V
D
instead of V in
. Save the schematic and plot to disk for use in your report.
7.
Use the experimental data in your data sheet table to plot I
D
vs. V
D
.
8.
Obtain the manufacturer’s plot of the characteristic curve.
Post-lab: Report
Using the data obtained in the lab, prepare a short report using the following guidelines. Be sure to use proper format, as dictated by the lab website.
What you should have before you start the report:
Prelab:
Manufacturer’s I
D
vs. V
D
characteristic for the diode.
-Matlab plot of I
D
vs. V
D
.
Part I:
-Output plot from lab circuit.
-P-Spice of V
RL
vs. time.
Part II:
-Completed table with V
R
, V
D
, and I
D
and resulting I vs. V plot.
-P-Spice plot of V
R
and V
D
vs. V in
(-2 V to +2 V)
-P-Spice plot of I
D
vs. V
D
.
Outline:
COVER SHEET
Look on the website for what to put on it.
4
OBJECTIVE
You looked at diode operation characteristics and a half-wave rectifier. Briefly describe what a diode is, and what characteristics you wanted to observe from the diode and half-wave rectifier circuit. Use past tense paragraph format, and don’t put any results in here.
PROCEDURE
This part tells what you did in past-tense paragraph form . No need to make it overly detailed.
Tell what circuits you built (include circuit diagrams) and why – i.e. “The circuit in Figure 2 was constructed using a N39d08g402s23478 diode, and a 5 k
resistor. The A838edj8wh3 function generator was used to supply DC voltage. The voltage across the resistor and the diode were measured for input voltages of 0 to 1.5 V in steps of 0.1 V. Blah blah blah diode current, I
D
was calculated by blah blah blah, then compared to manufacturer’s specification, P-Spice, and
Matlab, blah blah blah.” Don’t put results in this part.
DISCUSSION
Describe the diode in more detail. Explain how the operation of a diode works in the half-wave rectifier. Give the results of the half-wave rectifier lab circuit and compare them to what you expected based on what you know about the diode operation. Explain diode operation using a simple description of a p-n junction. For the diode characteristics, give the results of the lab circuit for V
R
vs. V
D
and I
D
vs. V
D
. Compare V
R
vs. V
D
to PSpice results and tell if they matched and why or why not. Compare I
D
vs. V
D
against your other three sources of data, and tell if they matched and why or why not. Compared the results to what you know about the I-V characteristic of the diode. Use plots and also give numerical comparisons. Use paragraph form with subheadings.
CONCLUSION
Briefly summarize the results of each part of the lab. Tell whether or not each matched theory, and if not, why. Describe what conclusions you can make from each result (what was learned).
APPENDIX
It’s best to put immediately relevant figures, tables, and other data in the body of the report.
Supplemental material (such as original data sheets) should go in the Appendix. In this case, PSpice plots are best put in the body of the report, but if you couldn’t save the plots to disk, put them in the index.
Some notes:
Cite any sources you use for your report.
Generally use past tense when describing what was done or what was observed. You can use present tense when talking about theory. Use passive verbs rather than active (i.e. "The circuit was constructed" rather than "I constructed the circuit"_). Avoid using "I," "me," etc., as this is an academic and industry standard.
Put figures on the first page on which you reference them. Only put results in the discussion and conclusion, not in the objective and procedure.
Refer to the guidelines and the grading matrix for the reports, which can be found on the 2303 policies page: http://www.ece.mtu.edu/labs/EElabs/EE2303/EE2303LabSpecificInformationandGuidelines.pdf
5
Lab 9: Semiconductors
Name_____________________________
Prelab (due at the beginning of lab)
1.
Why is the Shockley Equation useful?
2.
Bring in your Matlab results.
Part 1: Half-wave Rectifier
1.
TA signature for Part 1: ________
2.
Save scope and PSpice plots to disk for your report.
Part 2: Nonlinear Diode Operation – Determining the I v.s V Characteristic
1.
Measured value of R1: ___________
Vin Vr Vd
0.0
Section________
Id = Vr/R1
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
1.0
1.1
1.2
1.3
1.4
1.5
2.
TA signature for Part 2: ________
3.
Save PSpice plots to disk for your report.
4.
Save your plot of the experimental data
5.
Obtain manufacturer’s data of the I vs. V curve for the 1N4001, 1N4002, 1N4004.
6