(DISTRICT/ISD)
advertisement

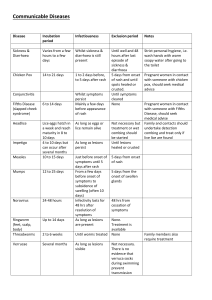
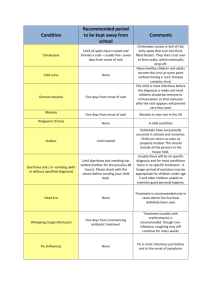
CONTROL OF CASUAL-CONTACT COMMUNICABLE DISEASES The Board of Education recognizes that control of the spread of communicable disease through casual contact is essential to the well-being of the school community and to the efficient District operation. For purposes of this policy, “casual-contact communicable disease” shall include diphtheria, scarlet fever and other strep infections, whooping cough, mumps, measles, rubella, and other designated by the Michigan Department of Public Health. In order to protect the health and safety of the students, District personnel, and the community at large, the Board shall follow all State statutes and Health Department regulations which pertain to immunization and other means for controlling communicable disease spread through normal interaction in the school setting. The teacher may remove from the classroom and the Director may exclude from the building or isolate in the District any student who appears to be ill or has been exposed to a communicable disease. The Superintendent shall develop administrative guidelines for the control of communicable disease which shall include: A. instruction of professional staff members in the detection of these common disease and measures for their prevention and control; B. removal of students from District property to the care of a responsible adult; C. preparation of standards for the readmission of students who have recovered from casual-contact communicable diseases; D. filing of reports as required by statute and the State Department of Health. Management of Selected Casual-Contact Diseases Diseases spread by airborne and/or direct contact with germs from sneezing, coughing, and speaking. DISEASE SYMPTOMS INCUBATION PERIOD CONTAGIOUS RETURN TO SCHOOL PERIOD CHICKENPOX are dry and (Varicella) and no new General discomfort, slight to high 10-21 days fever, headache, and loss of av: 14-16 5 days before When lesions rash to 6 days crusted appetite. Lesions appear in after rash first eruptions. At bunches with most on upper starts least 7 days appears. body. Face and extremities are less affected. Typical lesions 1 after rash first have teardrop shape surrounded by reddened area. Blistered (new) and broken and crusted (old) eruptions are on the skin at the same time. FIFTH DISEASE diagnosis. (Erythema 4-5 days Infectiosum) no treatment Rash begins as a solid red area 6-14 days Probably 2 days Exclude for on cheeks (“slapped cheek” Before rash and appearance), spreading to upper later. Usually arms and legs, trunk, hands needed. Cause unknown. and feet INFLUENZA Starts suddenly with chills, fever, at discretion (Viral Influenza) headache, muscle pains, and school nurse or principal coughing. Followed by other cold symptoms. 24-72 hours SCARLET FEVER until 48 hours (Scarletina) completed. 1-7 days Begins with fever and sore throat. About 3 days About 3 days, from first of symptoms Variable. If not Exclude Rash appears as a pink-red flush av: 2-4 days treated, can be after treatment which looks like a sunburn with goose pimples that spread to all parts of the body. Afterward, the skin peels off like a sunburn. Often the tongue has a “strawberry” appearance. contagious for months SPINAL MENINGITIS Sudden onset of high fever, Requires doctor’s note for (Meningococcal) and headache, and stiff neck. In admittance. (Haemophilus) severe cases, delirium stupor or coma can also occur. In meningococcal meningitis small purplish spots are occasionally seen in skin and mucous membranes. 1-10 days STREP THROAT as above. (Streptococcal sore 1-7 days av: 2-4 days Unknown. Probably re- throughout the duration of symptoms. Similar to scarlet fever but without a rash. A sore throat and 2 av: 2-4 days Same as above. Same throat) fever are the most pronounced symptoms. ROSEOLA symptoms. (Exanthem Subitum) Sudden high fever (104-105 degrees) RUBELLA rash onset. (German Measles) Rash begins on the face and MEASLES after disappearance (Rubeola) rash. Begins 3-4 days of gradually which falls with the appearance of a rash on about the third or fourth day. Rash consists of small rose-pink spots which first appear on the chest and abdomen but may spread to the face, legs, and arms. Rash is usually limited to only one or two days. Unknown. The Until no disease does not appear very contagious. 14-21 days 7 days before 7 days after spreads to the rest of the body av: 16-19 days to 7 days within 24 hours and is usually after rash onset, gone by the end of the third day. Often present is a pronounced swelling of the lymph nodes behind the ear and at the base of the skull. Mild coughing, sneezing, and reddened eyes are common early in the course of the illness. 8-13 days increasing fever, runny nose, (red) inflamed eyes, and especially coughing. Rash usually begins around ears and hairline, spreading down to cover face, trunk and arms by second day. Rash is initially bright pink with distinct raised spots. Tiny blue-white pinpoint-sized swelling inside the cheeks may be observed a day before the rash first appears. The rash usually lasts about five days. Sensitivity to light is also common. MUMPS onset and no 5-15 days av: 10 days 4 days rash and for of the up to 4 days after disappearance of the rash. Onset is gradual. There may be 2 to 3 weeks 3 4 days before Usually 5, but 5-9 days after (Infectious Parotitis) symptoms. TUBERCULOSIS note (TB) admittance. chills, discomfort, headache, av: 18 days may be as long pain below ears accompanied by a moderate fever of 101-102 degrees or higher followed by swelling of one or both salivary glands. Swelling is below and in front of ear. Usually swelling in one gland subsides as the other begins to swell. The ear lobe is often pushed forward by the swelling of the gland. Swelling usually lasts 5 to 7 days. as 7 to 9 days prior to the onset of salivary gland swelling. Starts with fever, night sweats, 2-10 weeks Variable. After Requires a doctor’s and weight loss early. Later starting treat- for re- symptoms include a persistent non-productive cough, chest pain, hoarseness, and coughing of blood. ment with anti TB drugs, a patient may become noninfectious in as little as two weeks. WHOOPING COUGH Coughing and sneezing followed 7-10 days Early, when the Requires doctor’s note (Pertussis) 1 to 2 weeks later by breathing av: 7 days patient has for re-admittance. characterized by a series of common coldshort convulsive-like coughs, like symptoms. and a high pitched gasp of The patient air called a whoop becomes less infectious as the convulsive-like coughs begin. Infectious stage ends in about four weeks Diseases spread by contact with tiny parasites on contaminated belongings of others. DISEASE SCHOOL SYMPTOMS INCUBATION PERIOD RINGWORM after treatment has Ringworm of the scalp begins PERIOD 4-14 days 4 CONTAGIOUS RETURN TO As long as any Return (Tinea Capitis; with bandaid Tinea Corporis) when possible as a small pimple which grows untreated lesions and spreads, leaving scaly are present and or clothing, patches of temporary baldness. Ringworm of the body appears as flat, spreading, ring-shaped lesions. The outside is usually reddish and filled with pus while the skin on the inside tends to return to normal. PINWORM treatment. begun – cover spores persist on contaminated materials. Itching in anal areas, disturbed 3 weeks sleep, irritability and local irritation due to scratching. As long as the Return after to 3 months female worm survives in the intestine. Diseases spread by the fecal-oral route – contamination of food, drink or objects placed in the mouth. DISEASE SCHOOL SYMPTOMS INCUBATION PERIOD PERIOD CAMPYLOBACTER Sudden onset of fever and Requires doctor’s note for (Vibriosis Vibrionic abdominal pain and diarrhea admittance. Enteritis) which may be severe. May also be vomiting and sometimes blood in the stools GIARDIASIS (Protozoan Diarrhea) SALMONELLOSIS as above. (Acute Gastro Enteritis) (Food Poisoning) SHIGELLOSIS (Bacillary Dysentery) Chronic, intermittent diarrhea, bloating, foul-smelling stools and fatigue and weight loss. Sometimes observable symptoms are not present. Sudden onset of fever, 1-20 days av: 3-4 days Throughout the illness (1-4 re- days). If not treated, up to 7 weeks. 1 to 4 weeks Entire period after exposure of infection 6-72 hours abdominal cramps, diarrhea and possibly vomiting. CONTAGIOUS RETURN TO Variable.. Same as above. Same av: 12-36 hours throughout course of illness. Sudden onset of fever, diarrhea 1-7 days abdominal pain. Loss of av: 2-3 days appetite and vomiting may also occur. There may be blood, 5 From onset of illness until 4 weeks later. Same as above. mucous, or pus in the stools. VIRAL GASTROENTERITIS (Viral Diarrhea; Winter Vomiting Rotoviral Diarrhea) Abrupt onset of nausea, vomiting diarrhea, abdominal pain, and discomfort. Fever, if present, is usually low grade. Very contagious. 24-48 hours From onset of Same as above. illness until symptoms subside. Hepatitis A (Infectious Hepatitis) (Epidemic Jaundice) Sudden loss of appetite, nausea, 15-40 days 10-15 days and abdominal pain or av: 28 days before discomfort. Within a few days, symptoms jaundice occurs with yellowing appear until of eyes and skin and darkening the first few of urine. days of jaundice. Same as above. Diseases spread by direct skin contact with wounds or discharges from an infected person. DISEASE SCHOOL SYMPTOMS INCUBATION PERIOD IMPETIGO Isolated pus filled spots which when lesions are (Impetigo Contagiosa) become crusted and break there is no seeping releasing a straw-colored treatment. fluid. Occurs principally around the mouth and nostrils. PINKEYE under treatment. (Epidemic Form of Acute Conjunctivitis) CONTAGIOUS RETURN TO PERIOD 4-10 days As long as pus filled lesions con- Return dry, and under tinue to drain. Cover, if possible, while at school. Irritation of the eye accompanied by tears, swelling of the lids, extreme sensitivity to light, and a buildup of a sticky fluid that dries to a straw-colored, crusty material accumulating at the corners of the eye. 6 27-72 hours During the period of active infection. Some children recover in only a few days but many cases take 2-3 weeks. Until