Geography year 1 to Year 6 Medium Term Plan
advertisement

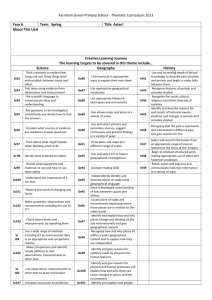
Geography Medium Term Planning Year Group Autumn Term 1 The city we live in and it surrounding areas. (H) Continents and Oceans of the World. (P) 2 Geography Spring Term Summer Term England, Ireland, Scotland, Wales (H) Weather in the UK. (P) Comparing two contrasting Localities (P/H) Hot and Cold areas of the World (P) Land and its change over time (mountains, hills coasts and rivers) (P) Rainforests – Biomes and vegetation belts (P) Africa – human and physical characteristics and topographical features (H) Economic activity and Trade (H) 3 County and Cities in the UK (H) Countries around the world – Europe, North and South America (H) 4 Volcanos (P) Coordinates, maps and time zones (P) 5 Earthquakes (P) The Water Cycle (P) 6 Macro and Micro Climates – climate zones (P) Distribution of natural resources – energy, food, minerals and water (P) Purpose of study A high-quality geography education should inspire in pupils a curiosity and fascination about the world and its people that will remain with them for the rest of their lives. Teaching should equip pupils with knowledge about diverse places, people, resources and natural and human environments, together with a deep understanding of the Earth’s key physical and human processes. As pupils progress, their growing knowledge about the world should help them to deepen their understanding of the interaction between physical and human processes, and of the formation and use of landscapes and environments. Geographical knowledge provides the tools and approaches that explain how the Earth’s features at different scales are shaped, interconnected and change over time. Aims The national curriculum for geography aims to ensure that all pupils: Develop contextual knowledge of the location of places, seas and oceans, including their defining physical and human characteristics Understand the processes that give rise to key physical and human geographical features of the world, how these are interdependent and how they bring about spatial variation and change over time Are competent in the geographical skills needed to: Collect, analyse and communicate with a range of data gathered through experiences of fieldwork that deepen their understanding of geographical processes Interpret a range of sources of geographical information, including maps, diagrams, globes, aerial photographs and Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Communicate geographical information in a variety of ways, including through maps and writing at length. Attainment targets By the end of each key stage, pupils are expected to know, apply and understand the matters, skills and processes specified in the relevant programme of study. Key Stage 1 Pupils should develop knowledge about the world, the United Kingdom and their locality. They should understand basic subjectspecific vocabulary relating to human and physical geography and begin to use geographical skills, including first-hand observation, to enhance their locational awareness. Pupils should be taught to: Location knowledge name and locate the world’s seven continents and five oceans name, locate and identify characteristics of the four countries and capital cities of the United Kingdom and its surrounding seas Place knowledge understand geographical similarities and differences through studying the human and physical geography of a small area of the United Kingdom, and of a small area in a contrasting non-European country Human and physical geography Identify seasonal and daily weather patterns in the United Kingdom and the location of hot and cold areas of the world in relation to the Equator and the North and South Poles Use basic geographical vocabulary to refer to: Key physical features, including: beach, cliff, coast, forest, hill, mountain, sea, ocean, river, soil, valley, vegetation, season and weather Key human features, including: city, town, village, factory, farm, house, office, port, harbour and shop Geographical skills and fieldwork Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify the United Kingdom and its countries, as well as the countries, continents and oceans studied at this key stage Use simple compass directions (North, South, East and West) and locational and directional language (e.g. near and far; left and right) to describe the location of features and routes on a map Use aerial photographs and plan perspectives to recognise landmarks and basic human and physical features; devise a simple map; and use and construct basic symbols in a key Use simple fieldwork and observational skills to study the geography of their school and its grounds and the key human and physical features of its surrounding environment. Year 1 – Autumn Term The city we live in and its surrounding areas: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at pictures of Hammersmith and London focusing on amenities within their local areas – Where can you go to buy Ask geographical questions about their surrounding area food? Where can you go to shop? Where can you go to Express their own views about people, places and play? environment Introduce the concept of North, South, East and West. Identify and describe what a place is like Basic maps with keys Identify and describe where places are Make observations about where things are located Year 1 – Spring Term England, Ireland, Scotland, Wales: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at picture of different places and compare –similarities and differences. Recognise how places compare with other places Talk about and share ideas about where they live and the Express their own views about people, places and places around them. environment Use maps and globes and find key countries and where they Identify and describe what a place is like are in relation to England. Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify key areas Use secondary sources of information Year 1 – Summer Term Weather in the UK: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at the different season in England-How do they compare? What impact does it have on our area? Recognise changes in the environment (transport/clothes/activities) Identify seasons and daily weather patterns Record a weather chart over time, creating discussion about Express their own views about the environment the changes. Communicate in different ways Record data and presents their findings about the weather Observe and record over time. Year 2 – Autumn Term Continents and oceans of the world: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Use maps and atlases to locate continents and oceans. Name and locate 7 continents and 5 oceans Look at the different oceans d the countries their surround. Use globes, maps and plans What countries are on each continent and how do different continents compare? Identify and describe where places are Make observations about where things are located Year 2 – Spring Term Comparing two countries: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Pick two locations and compare them –How have they changed? Recognise how places compare with other places Look at different countries with contrasting cultures – How do Express their own views about people, places and we live? How do people live on the reed islands on Lake environment Titicaca? How are they the same or different? Identify and describe what a place is like Use world maps, atlases and globes to identify key areas Use secondary sources of information Year 2 – Summer Term Hot and Cold areas of the world: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Compare two countries with contrasting weather-dessert/artic Recognise changes in the environment Talk about the features of the localities – Who lives there? What animal’s life there? What plants grow there? What Communicate in different ways amenities are there? Observe and record Research a hot or cold location, create and present Identify and describe key features of a location information found. Carry out fieldwork investigation outside the classroom Key Stage 2 Pupils should extend their knowledge and understanding beyond the local area to include the United Kingdom and Europe, North and South America. This will include the location and characteristics of a range of the world’s most significant human and physical features. They should develop their use of geographical tools and skills to enhance their locational and place knowledge. Pupils should be taught to: Location knowledge Locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities Name and locate counties and cities of the United Kingdom, geographical regions and their identifying human and physical characteristics, key topographical features (including hills, mountains, coasts and rivers), and land-use patterns; and understand how some of these aspects have changed over time Identify the position and significance of latitude, longitude, Equator, Northern Hemisphere, Southern Hemisphere, the Tropics of Cancer and Capricorn, Arctic and Antarctic Circle, the Prime/Greenwich Meridian and time zones (including day and night) Place knowledge Understand geographical similarities and differences through the study of human and physical geography of a region of the United Kingdom, a region in a European country, and a region within North or South America Human and Physical geography Describe and understand key aspects of: Physical geography, including: climate zones, biomes and vegetation belts, rivers, mountains, volcanoes and earthquakes, and the water cycle Human geography, including: types of settlement and land use, economic activity including trade links, and the distribution of natural resources including energy, food, minerals and water Geographical skills and fieldwork Use maps, atlases, globes and digital/computer mapping to locate countries and describe features studied Use the eight points of a compass, four and six figure grid references, symbols and key (including Ordnance Survey maps) to build their knowledge of the United Kingdom and the wider world Use fieldwork to observe, measure and record the human and physical features in the local area using a range of methods, including sketch maps, plans and graphs and digital technologies Year 3 – Autumn Term Countries and cities in the UK: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at how cities in the UK compare? Seaside towns/inner cities towns. Ask geographical questions Comparing amenities in towns and villages to cities. Identify and describe what places are like Look at how cities support the surrounding towns. Recognise how places fit within a wider geographical context. Compare cities now and then. How have they changed? Recognise how people can improve the environment Year 3 – Spring Term Countries around the world-Europe, North and South Suggested Activities America: Research a country looking at its physical and human Pupils should be taught to: features. Describe and explain how and why places are similar and How do these countries compare to others? different from other places in the same counter and What impact do these countries have on the wider world? elsewhere in the world Eg. Sri Lanka – tea, Argentina – meat, Spain – oranges. Recognise how places fit within a wider geographical Look at how these countries have changed and developed in context. the environment. Use secondary sources of information (stories, internet, photographs) Explain why places are like they are Year 3 – Summer Term Land and its change over time: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Comparing a location now and then. What are the changes? Use appropriate geographical vocabulary Look at the how the weather has an impact on our land, Eg. Water erosion, wind erosion, sun damage – how has it Explain patterns made by individual physical features in the changed the land? environment Look at maps of an area from now and then Analyse evidence and draw conclusions Research and present findings Use atlases, globes, maps and plans Identify how and why places change Year 4 – Autumn Term Volcanos: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at what happened in Pompeii in 79AD and the impact it Use secondary sources of information (stories, internet, had. photographs) Compare photographs from then and now – How has it changed? Recognise some physical processes and explain how these can cause changes to places and the environment Research and discuss what a volcano is and what features it has. Recognise and explain patterns made by individual physical features in the environment Use secondary sources to find information; reports, internet, stories to create a report/presentation on key events. Ask geographical questions Compare different types of volcanos. Use geographical language when describing a volcano. Look at volcanos in the world today. Use ICT to help in geographical investigations Year 4 – Spring Term Coordinates, maps and time zones: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at maps and locate features of the area using a key. Analyse evidence and draw conclusions Follow coordinates to locate an area. Use appropriate fieldwork techniques Use a map to find routes to different locations. Use decision making skills. Eg. when planning a route Create their own map using a range of scales Identify and describe what places are like Use the eight points of a compass, four and six-figure grid reference and ordinance survey maps. Draw plans and maps at a range of scales. Eg. sketch a map of a locality Year 4 – Summer Term Rainforests Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: What is a rainforest? Where re the different rainforest around the world? To understand the key features of an environment Identify and describe a rainforest and its physical features. Recognise how people can effect an environment and the overall impact they might have on a country. What is the importance of a rainforest? Identify and explain different views that people hold about What do people think of rainforest around the world and how topical geographical issues do their opinions differ? Look at the human impact on rainforests; deforestation. Year 5 – Autumn Term Earthquakes: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Research relevant (recent) earthquakes around the world Use secondary sources of information (stories, internet, and the impact they had on the community and its photographs) surrounding areas. Look at what causes earthquakes and how the earth moves. Use geographical language when describing an earthquake Use secondary sources such as maps, books and computers Recognise and explain patterns made by individual physical to obtain information about earthquakes and volcanoes. features in the environment Recognise some physical processes and explain how these can cause changes in places and environments Year 5 – Spring Term The water cycle: Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Why is water so important in our lives? Collect, record and analyse evidence and then draw How does it affect other people around the world? conclusions Look at climate change and how the UK’s weather has Describe and explain how and why places are similar and changed over the last fifty years – what impact has this had? different from other places in the world Look at the elements of the water cycle. Example Use appropriate fieldwork techniques and instruments evaporation, condensation, precipitation and collection Recognise the effect water has on landscapes and people To draw plans and maps at a range of scales Year 5 – Summer Term Africa – Human and physical characteristics and Suggested Activities topographical features: Select contrasting countries/cities to research Pupils should be taught to: Look at how cities/towns/landscapes have changed over time Describe and explain how and why places are similar and – How might they continue to change with climate change? different from other places in the world Identify why places are like they are and how they might change in the future. Identify how the human and physical features of a country can affect the quality of people’s lives. Macro and Micro Climates Pupils should be taught to: Understand the term macro climate Understand the term micro climate Identify macro and micro climates Understand their formations Year 6– Autumn Term Suggested Activities Look at pictures of macro and micro climates and understanding their definitions Year 6 – Spring Term Distribution of natural resources; energy, food, minerals Suggested Activities and water Look at a country and explore the features (physical and Pupils should be taught to: human) Know about the main physical and human features and Look at a country and discuss any environmental issues e.g. environmental issues in particular localities UK with landfill sites, Japan with tectonic plates, Brazil with Shanty Towns, Amazon Rainforest and deforestation/logging Understand how the geographical features of the host country affect the lives of the people who live there Year 6 – Summer Term Economic activity and trade Suggested Activities Pupils should be taught to: Look at fair Trade/Global swap shop Explain how physical and human processes lead to similarities and differences between places Research how places are linked through movement of goods and people