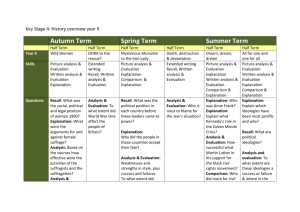
Common approaches to numeracy
advertisement

Mental Computation Automaticity Problem Solving Definitions Mental Computation is the understanding and use Automaticity is instant recall. of effective mathematical strategies and concepts in your head. Problem Solving: Recognise the problem Identify the strategy and or operation to use Apply the identified strategy/operation identified Check and Justify Learning Intentions For children to build an understanding of strategies to aid mental computation using the 4 processes. For children to develop speed and accuracy when recalling basic facts using the 4 processes. Instant recall of friends of 10 Instant recall of doubles/halves Instant recall of place value (ThHTOs) Instant recall of subitising cards Instant recall of strategies covered including explanations of eg. Bridging 10, Number Splitting For children to understand how to identify the relevant information, use a specific and effective strategy and choose the appropriate calculation, to solve problems. Note: The integration of ICT should be considered (where applicable) when working on mental computation, automaticity and problem solving. Common vocabulary should be used across the school, regardless of grade or teacher, so students are aware of concepts regardless of where they are at in their schooling. Automaticity vs Fluency: This is the AC definition of fluency- it includes aspects of automaticity but not just that- as you can see students who are fluent choose and use strategies, and the bit that is automaticity is recall factual knowledge and concepts readily. Fluency Students develop skills in choosing appropriate procedures, carrying out procedures flexibly, accurately, efficiently and appropriately, and recalling factual knowledge and concepts readily. Students are fluent when they calculate answers efficiently, when they recognise robust ways of answering questions, when they choose appropriate methods and approximations, when they recall definitions and regularly use facts, and when they can manipulate expressions and equations to find solutions. Know your students and know their strengths. Show how to use these strategies by: Modelling Making connections explicit Choosing appropriate concrete materials Asking children which items are suitable for solving the problem Using authentic learning tasks – use real life problems Self-reflect – through class discussion (promoting common vocabulary) Draw on prior knowledge from earlier in the year or previous years