CHAPTER I - MyNeonClass
advertisement

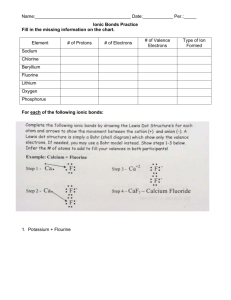
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study Public water or tap water in our community is now added with chlorine which kills pathogenic (disease causing) microorganisms that the water or its transport pipes might contain. This is one of the top reasons why people choose to buy mineral water as their drinking water. But people with less income or those who don’t have enough money to buy mineral water, prefer to have tap water or public water as their drinking water. Chlorine is used primarily as a disinfectant. Chlorine is often added to public water supplies to kill harmful bacteria, mold and algae, reduce odors or bad taste and remove minerals like iron. Chlorine was first added to water supplies in the 1800's to kill widespread diseases and epidemics such as typhoid and cholera. But despite its power to disinfect water, it can be harmful. Chlorine is ingested in tap water and may be inhaled and absorbed through the skin during showering. Chlorine can be harmful because it forms trihalomethanes (THMs). THM is produced when chlorine reacts with organic matter in water. The known toxin chloroform is a THM. Chloroform is a probable carcinogen and has been linked to liver and kidney cancer in laboratory animals. has been linked to miscarriages and birth defects in laboratory animals. Humans are not the only ones who use tap water every day, Animals and plants are also consumers of tap water or public water in our community. It is used to water plants. The mung bean, also known as mungbean, mung, green gram, golden gram; or in other languages, choroko (in Swahili), monggo, moong, moog (whole) or moog dal (split) (in Bengali , Marathi), munggo or monggo (in East Timor), is the seed of Vigna radiata. Munggos can germinate/sprout within 48-72 hrs. They are not expensive and rare. This plant is a suitable test subject because of its fast germination period and because it is less expensive. This study is of interest to the researchers because they would like to know the effects of chlorine to monggo plants. B. Statement of the Problem Due to the addition of chlorine to tap water or public water, the water that is being used to water the plants, is also added with chlorine. Due to the health effects of chlorine to humans, chlorine should be in small amounts, so people can use monggo plants to know the amount of chlorine present in water through testing. This study can also conclude that monggo can be a base indicator to chlorine. It can also be a replacement to artemia test and allum test. Main problem: Can Chlorine affect the growth of Monggo Plants? Sub-problems: 1. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with unchlorinated water from Hinaplanon River, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 2. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 2 mg Cl per Liter of water from Hinaplanon River, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 3. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 5 mg Cl per Liter of water from Hinaplanon River, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 4. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 7 mg Cl per Liter of water from Hinaplanon River, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 5. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 10 mg Cl per Liter of water from Hinaplanon River, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 6. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 20 mg Cl per Liter of water from Hinaplanon River, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 7. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Distilled water, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 8. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 2 mg Cl per Liter of Distilled water, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 9. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 5 mg Cl per Liter of Distilled water, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 10. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 7 mg Cl per Liter of Distilled water, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 11. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 10 mg Cl per Liter of Distilled water, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 12. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 20 mg Cl per Liter of Distilled water, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 13. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Rainwater, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 14. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 2 mg Cl per Liter of Rainwater, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 15. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 5 mg Cl per Liter of Rainwater, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 16. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 7 mg Cl per Liter of Rainwater, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 17. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 10 mg Cl per Liter of Rainwater, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves 18. What are physical characteristics of the monggo plants, watered with Chlorinated water with 20 mg Cl per Liter of Rainwater, in terms of: a. Leaf color b. Leaf texture c. Plant height e. No. of Leaves C. Objectives of the Study This study aims to: 1. Determine the effects of chlorine to the growth of Monggo plants. 2. Determine the hazardous concentration of chlorinated water to Monggo plants. 3. Determine if Monggo plants can be used as a base indicator to Chlorine. 4. Make an alternative way to Allum and Artemia Test. D. Hypotheses 1. Chlorine will not affect the growth of Monggo plants. 2. The concentration of chlorine does have an effect to the growth of Monggo plants. E. Significance of the Study This research paper aims to let the people know the effects of chlorine to monggo growth, the right concentration of chlorine needed to monggo plants. This study aims to develop a cheaper and easier alternative to Artemia and Allum test. It also concludes that monggo plants can be used as base indicators to chlorine. This study can help people measure the concentration of Chlorine in tap water and prevent them from drinking tap water with high amounts of chlorine. F. Scope and Limitations of the Study Although many plants can be used in the experiment, we will use monggo seeds because it is affordable and available on the market and it grows fast and will meet the deadline for the experiment. The researchers will use 180 mongo seeds all in all. 10 monggo seeds are to be used in each concentration of chlorine of each source of water. The source of water could already contain chlorine so we will use water from different sources to avoid a bias. The study will be conducted over a two-week observation period. The growing of monggo plants will be done in the residences of Marba. The measuring of chlorine and the mixing of chlorine to water will be done in the MSU-IIT IDS Chemistry laboratory due to the presence of a precise electronic weighing scale. G. Definition of Terms Chlorine It is used in purifying water, as a disinfectant and bleach. In this study it is combined with water in different amounts to make Chlorinated water Soil The upper layer of earth in which plants grow. We will use the loam type of soil. Monggo Mungbean commonly called monggo, is the cheapest source of vegetable protein with protein content of 20-25 percent. It is an excellent crop for green manuring, because it matures early, grows fast and produces abundant vegetative tops. This will be used in the experiment. Plant Height The measurement from base(soil) to top (top stem). Leaf A flattened structure of a higher plant, typically green and blade-like, that is attached to a stem directly or via a stalk. Leaves are the main organs of photosynthesis and transpiration. Unchlorinated water Water without chlorine added. Chlorinated water Water with chlorine added. CHAPTER II REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES The Mung bean, also known as mungbean, mung, green gram, golden gram; or in other languages, choroko (in Swahili), monggo, moong, moog (whole) or moog dal (split) (in Bengali , Marathi), munggo or monggo (in East Timor), is the seed of Vigna radiate. Mung beans are commonly used in Chinese cuisine, and are generally eaten either whole (with or without skins) or as bean sprouts, or used to make the dessert "green bean soup". The starch of mung beans is also extracted from them to make jellies and "transparent" or "cellophane" noodles. Mung Beans can germinate within 48-72 hrs. How fast they grow depends on the temperature, if they are growing in darkness or light, & if they have been soaked overnight before planting "Within the temperatures that mung beans can germinate & grow, the higher the temperature, the better the mung beans will germinate & grow." This plant is very common and very cheap. It grows fast and is a good source of food. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mung_bean) (http://www.usc.edu/CSSF/History/2004/Projects/J1631.pdf) Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is a halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. Chlorine is a powerful oxidant and is used in bleaching and disinfectants, as well as an essential reagent in the chemical industry. As a common disinfectant, chlorine compounds are used in swimming pools to keep them clean and sanitary. Chlorine is a powerful combatant against many parasites and disease-causing bacteria because of its harsh nature. Chlorine, though, is also a poison. Just as its harshness attacks pathogens and parasites, it attacks delicate body tissues when breathed or absorbed through the skin. When used in taking a bath Chlorinated water can leave skin feeling dry and itchy and leave hair dry, brittle, and prone to dandruff. It can cause or further aggravate rashes and other skin irritations and it leaves eyes feeling sore and itchy. Besides the damaging effects on skin and hair, chlorine can cause health problems when inhaled. Inhaling shower water also allows exposure to volatile organic chemicals (VOCs). Combined with chlorine, these chemicals can be incredibly dangerous to the delicate tissues in the lungs. The hot water and confined nature of a shower vaporizes chlorine and VOCs and this chemical vapor is then taken into the lungs. Inhalation of such chemical vapor causes great problems for asthmatics, and it can cause similar lung and sinus problems even for those with healthy respiratory systems. In fact, inhaling chemical-laced steam during a shower actually provides more exposure to dangerous chemicals than drinking that very same water. To plants Chlorine can be harmful because it combines with other naturally-occurring elements, like leaves and vegetation, to form trihalomethanes (THMs). The known toxin chloroform is a THM. Chloroform is a probable carcinogen and has been linked to liver and kidney cancer in laboratory animals. A human study published by the American Journal of Epidemiology shows bladder cancer risk to double with exposure to chlorine by-products. Another human study reported by the American Journal of Public Health shows a 21 percent increase bladder cancer risk and a 38 percent increase in rectal cancer risk. The long term effects of chlorinated drinking water have just recently being recognized. According to the U.S. Council of Environmental Quality, "Cancer risk among people drinking chlorinated water is 93% higher than among those whose water does not contain chlorine." Simply stated chlorine is a pesticide, as defined by the U.S. EPA, whose sole purpose is to kill living organisms. When we consume water containing chlorine, it kills some part of us, destroying cells and tissue inside our body. Aside from all the health risks related to chlorine in our water, it is the primary cause of bad taste and odor in drinking water. The objectionable taste causes many people to turn to other less healthful beverages like soft drinks, tea or other sweetened drinks. A decreased intake of water, for any reason, can only result in a lower degree of health. According to Iligan Waterworks the concentration that is right for humans and the concentration that they use is 2 mg Cl /L H20 to 4 mg Cl /L H20. Also if you leave the chlorinated water out in the open, the chlorine will evaporate within 24 hours. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chlorine) (http://www.ecomall.com) (http://www.ehow.com) (http://www.healthynewage.com) (http://www.squidoo.com) (U.S. Council of Environmental Quality) (Iligan Waterworks) Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. Its molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state (water vapor or steam). Water also exists in a liquid crystal state near hydrophilic surfaces. Water covers 70.9% of the Earth's surface, and is vital for all known forms of life. On Earth, it is found mostly in oceans and other large water bodies, with 1.6% of water below ground in aquifers and 0.001% in the air as vapor, clouds (formed of solid and liquid water particles suspended in air), and precipitation. Oceans hold 97% of surface water, glaciers and polar ice caps 2.4%, and other land surface water such as rivers, lakes and ponds 0.6%. A very small amount of the Earth's water is contained within biological bodies and manufactured products. Water on Earth moves continually through a cycle of evaporation or transpiration (evapotranspiration), precipitation, and runoff, usually reaching the sea. Over land, evaporation and transpiration contribute to the precipitation over land. Water is very important to humans, animals, and plants. Humans and animals drink water to keep the body hydrated and balance the body temperature. Plants need water too, especially in producing their own food through photosynthesis, water is needed in the reaction. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Water) (http://importanceofwater.org/29/the-importance-of-water) (Encarta) CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY A. Research Design Monggo seeds that will be used will be bought from 1 source only, the market. It needs to be healthy, completely green. The researchers will plant the monggo seeds and water it with Chlorinated water with different concentrations and observe, track changes and physical characteristics. B. Materials and Equipments Materials Equipment 180 Monggo seeds Precise electronic weighing scale 5 gallons of water from Hinaplanon River Measuring tape 5 gallons Rainwater Spray bottle 5 gallons Distilled water. Stirring rod 50 grams of powdered chlorine Cotton Soil 18 Plastic containers C. General Procedure Monggo seeds collection We will buy a bag of monggo seeds and separate the healthy ones. Then we will place it in a plastic container and store it at room temperature. Chlorine collection We will buy 50 grams of powdered Chlorine and place it in a plastic container and store it at room temperature. Acquiring of water We will get water from different sources. We will collect 5 gallons of rainwater and place it in a 5 gallon plastic container. We will get 5 gallons of distilled water from the MSU-IIT CSM distillation facility and place it in a 5 gallon plastic container. We will collect 5 gallons of water from the Hinaplanon River 5 days after it rains and place it in a 5 gallon plastic container. Label. Preparation of Chlorine Solution Measure (3) 2 mg, (3) 5 mg, (3) 7 mg, (3) 10 mg, (3) 20 mg of powdered Chlorine using a precise electronic weighing scale. Measure (6) 1 liter rainwater, (6) 1 liter distilled water, and (6) 1 liter water from Hinaplanon river and place it in 1 liter bottles. Mix the different of amounts of chlorine to each bottle. Label. Germination of the monggo seeds Place cotton beddings in 18 plastic containers. Equally place 10 monggo seeds to each plastic container. Spray trice with a spray bottle each plastic container with the different concentrations of Chlorine to water and the source of water. After 60 hours (2.5 days) transfer the seedlings to plastic containers with soil. Growing of Monggo seeds Spray three times, twice a day each plastic container with the different concentrations of Chlorine. D. Experimental Set-up 2 mg powdered chlorine to 1 liter… (Rain water) (Distilled water) (Water from Hinaplanon River) 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 5 mg powdered chlorine to 1 liter… (Rain water) (Distilled water) (Water from Hinaplanon River) 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 7 mg powdered chlorine to 1 liter… (Rain water) (Distilled water) (Water from Hinaplanon River) 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 10 mg powdered chlorine to 1 liter… (Rain water) (Distilled water) (Water from Hinaplanon River) 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 20 mg powdered chlorine to 1 liter… (Rain water) (Distilled water) (Water from Hinaplanon River) 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds 10 monggo seeds