remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms that can tell
advertisement

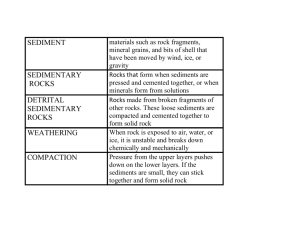
thin residue preserved as a fossil a type of body fossil that forms in rock when an organism with hard parts is buried, decays or dissolves, and leaves a cavity in the rock a type of body fossil that forms when crystals fill a mold or sediments wash into a mold and harden into rock age, in years, of a rock or other object; determined by using properties of the atoms that make up materials process in which some isotopes break down into other isotopes and particles time it takes for half the atoms of an isotope to decay principle stating that Earth processes occurring today are similar to those that occurred in the past mechanical or chemical surface processes that break rock into smaller and smaller pieces physical processes that break rock apart without changing its chemical makeup and can be caused by ice wedging, animals, and plant roots a type of erosion that occurs when wind-blown sediments strike rocks and sediments, polishing and pitting their surface process in which surface materials are worn away and transported from one place to another by agents such as gravity, water, wind, and glaciers a type of erosion that occurs when wind blows over loose sediments, removes small particles, and leaves coarser sediments behind chemical weathering process that occurs when some minerals are exposed to oxygen and water over time large, moving masses of ice and snow that change large areas of Earth’s surface through erosion and deposition process that adds gravel, sand, and boulders to a glacier’s bottom and sides as water freezes and thaws, breaking off pieces of surrounding rock occurs when chemical reactions dissolve the minerals in rocks or change them into different minerals the age of something compared with other things remains, imprints, or traces of prehistoric organisms that can tell when and where organisms once lived and how they lived fossils in which the spaces inside are filled with minerals from groundwater any type of erosion that occurs as gravity moves materials down-slope sedimentary rock-forming process in which sediment grains are held together by natural cements that are produced when water moves through rock and soil a type of mass movement that occurs when a mass of material moves down a curved slope dropping of sediments that occurs when an agent of erosion, such as gravity, a glacier, wind, or water loses its energy and can no longer carry its load mechanical weathering process that occurs when water freezes in the cracks of rocks and expands, causing the rock to break apart states that in undisturbed rock layers, the oldest rocks are on the bottom and the rocks become progressively younger toward the top large ridge of rocks and soil deposited by a glacier when it stops moving forward mixture of different-sized sediments that is dropped from the base of a retreating glacier and can cover huge areas of land process that forms sedimentary rocks when layers of sediments are compressed by the weight of the layers above them remains of species that existed on Earth for relatively short period of time, were abundant, and were widespread geographically and can be used by geologists to assign the ages of rock layers type of mass movement in which sediments move down-slope very slowly and can cause walls, trees, and fences to lean downhill