Reaction and Reform: New Economic Theories
advertisement

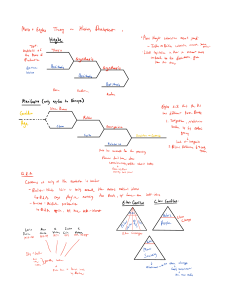
Reaction and Reform: New Economic Theories I. Industrialization’s Effects a. Gap between … b. Dominant European economic theory in 1700s = _____________________________ i. Worked for … ii. Actually hurt … c. Big question: What was the appropriate role of government, in society and the economy? i. Should government … ii. Should government … iii. Should government … II. Laissez Faire policy: Government, __________________________________!!!! a. Literally means “______________ ______________”, in French b. Based in French enlightenment criticism of Mercantilism i. Criticized … ii. Supported free trade => iii. Idea was that best products … c. Adam Smith (1723-1790) i. Scottish economics professor ii. Wrote Wealth of Nations in _______________ 1. Defended ______________ _________________________ 2. Economic freedom = _______________________ ________________________ 3. No … iii. Influenced development of _________________________________ III. Capitalism policy: Land, Labor & Capital, OH MY! a. Belief that factors of production … i. Factors of production => ii. Believed that privately held money should be … b. Believed in the “natural laws” of Adam Smith’s Wealth of Nations i. People work for … ii. Competition forces people … iii. The Law of Supply and Demand: enough goods will be ______________________, at the lowest possible ________________, to meet ____________________ in a market economy c. David Ricardo & Principles of Political Economy and Taxation (1817) i. Believed in ______________________ ________________________ => ii. Enunciated “The Iron Law of Wages” 1. Employers pay workers ____________________ when there are __________ workers around (why?) => 2. Workers who make more money can afford _________________ & ______________ 3. More ____________ eventually increases the number of _________________ looking for work 4. More workers = ____________ wages, ______________ living conditions, ___________ kids iii. Capitalists’ belief in a permanent underclass was basis for… 1. Government assistance upset … 2. Minimum wage, working conditions, etc would reduce _________________ of business and result in hiring fewer people => 3. Example => IV. Socialism: You’ve Got Your Government in My Economy! a. Belief that government was the only force strong enough to … b. Socialist reformers i. Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832) advocated Utilitarianism 1. People should judge ___________, ____________________ & _______________ based on their utility, or ________________________ 2. Government should promote … 3. Individuals should be free to pursue … ii. John Stuart Mill (1806-1873) 1. Challenged … 2. Argued that ordinary workers should … 3. Demanded that government should equalize people’s wealth => iii. Other reformers focused on … c. Socialist theory i. Belief in _______________________ __________________________________ 1. Government was a force for ________________, in society 2. Government should control key industries – why? => 3. Key industries in 1800s were … ii. ________________ ____________________________ would keep workers from being at mercy of employers V. Communism, or Radical Socialism: Workers of the World, Unite! a. Karl Marx (1818-1883) and Friedrich Engels (1820-1895) i. Believed that economic forces alone … ii. Wrote The Communist Manifesto in 1848 1. Human society divided into social classes, each … a. “Haves” = “Bourgeoisie” => b. “Have nots” = “Proletariat” => 2. Industrial revolution had made wealthy______________, and the workers (“proletariat”) ____________ 3. Predicted uprising of the proletariat => b. Marx’s “Dictatorship of the Proletariat” i. Believed that capitalism would destroy itself ii. Process 1. Big business would drive… 2. Eventually, only a few ____________________________ would control all wealth 3. The proletariat (workers) would revolt and … 4. The proletariat would run industry, producing … 5. Workers would share all the profits => 6. Government would be controlled by the proletariat => c. Classless society = ___________________________ i. Factors of production (______________, _______________, & ____________________) would be owned by the people ii. Private property would … iii. All _________________ & _____________________ would be shared equally by all people iv. Marxist slogan: “From each according to his _______________________, to each according to his ________________” => Concluded on next page Arrows indicate whether an economic theory evolved from, or in opposition to, the preceding theory Thus, Laissez Faire developed in opposition to Mercantilism, but led to Capitalism; Socialism developed in opposition to Capitalism, but led to Communism